Why does a spinal hernia occur?
The causes of a herniated disc are well known, but despite this, more and more people are faced with this disease, ignoring the simple rules of prevention. Destruction and prolapse of the disc occurs gradually, which in 90% of cases is preceded by degenerative-dystrophic changes in individual structures of the spine.
Osteochondrosis and trauma are the main causes of hernia, which at the same time act as aggravating factors of the disease.
Disc pathology can be the result of the lack of movement of the vertebrae, when they are malnourished, they shrink and form an ideal condition for the destruction of the intervertebral disc, which will begin to compress the surrounding tissues, especially the nerve roots and spinal cord.
Pathological processes in the spine begin with minor changes that occur chronically. Often the prerequisites for a hernia are formed even in adolescence and childhood, when the child leads a sedentary lifestyle or, on the contrary, overloads the spine with hard physical work or sports.
Why does a disc herniation occur?
The causes of intervertebral hernia lie in the spine itself, which, with age, ceases to receive the necessary amount of nutrients and suffers from a high load. This exacerbates the fact that after the age of 25, the aging of the body begins, and if you do not take care of your health, the risk of various chronic pathologies increases significantly.
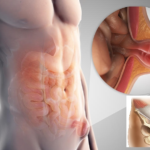
With a herniated disc, a portion of the disc protrudes into the spinal canal. The loss of individual fragments leads to compression of nerve endings and central nerve roots. The intervertebral disc in the spine performs a shock-absorbing function, giving strength and flexibility. It is located between the vertebrae, and consists of an annulus fibrosus and an elastic nucleus in the center.
A hernia begins with a protrusion, when a number of pathological processes occur in the disc, leading to a loss of its strength and elasticity.
Without maintaining the health of the spine, this ends with the appearance of cracks, and even then, at any moment, the disc can rupture, and the pulp comes out. This is how an intervertebral hernia is formed.
What causes an intervertebral hernia:
- age-related changes in the disk;
- spinal injury.
Main reasons
Age-related changes affect the nutrition of the intervertebral disc. It does not have blood vessels and feeds in a diffuse way, getting everything it needs from the surrounding tissues, mainly from the muscles. Diffusion occurs only during movement, when there are pressure drops. Physical work that involves the muscles is the main mechanism that triggers the nutrition of the intervertebral disc.
When there is no movement or muscle atrophy occurs, the natural shock absorber of the spine ceases to receive nutrients, and even then there are prerequisites for the development of a hernia in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar region.
Due to insufficient nutrition, the disk loses moisture, microcracks begin to appear on it. But this is not enough to rupture the fibrous ring. In order for a hernia to form, other factors are also needed.
A hernia of the spine may appear due to the influence of such factors:
changes .
The intervertebral discs themselves are strong, but subject to various damages. Their integrity is violated when inflammation occurs and atrophic processes begin. The destruction of the fibrous ring of the disc can occur as a result of a high load that exceeds the allowable rate. If you constantly engage in hard physical work, but do not strengthen your back muscles, this will gradually lead to thinning and loss of strength discs . Weak areas are formed on the annulus fibrosus, and they will later become the site of protrusion of the nucleus pulposus.
Spinal injury.
The intervertebral disc can suffer from a strong blow and compression of the spine, which changes its shape, deformation occurs, and concave areas may form. The resulting flaws will be a vulnerable spot, and if the protrusion does not occur immediately, then any other indirect causes of a spinal hernia will become a decisive factor in the appearance of the disease.
Risk factors
To the main causes of a hernia of the spine:
- metabolic disorders, endocrine pathologies;
- hormonal imbalance;
- forced bed rest;
- rachiocampsis;
- work associated with monotonous movements;
- chronic viral diseases;
- congenital and acquired pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- osteochondrosis, protrusion of the intervertebral disc.
There are a number of inevitable risk factors leading to spinal pathology:
- involutional processes, physiological aging of the organism;
- wear of discs and vertebrae, atrophy of muscle tissue;
- fragility of the structures of the spine;
- sports injuries, fractures and dislocations;
- surgical operations on the spine with complications.
There are also factors that can be influenced by therapeutic and preventive measures:
- hypodynamia, lack of movement of the spine - this causes an imbalance of nutrients in the disk and vertebrae, this can be avoided if every day you devote at least half an hour to exercises and physical work;
- high loads on the spine - this is the other extreme, when a person is constantly busy with hard work and does not give his back regular rest, a long sitting position also has a detrimental effect, which increases the load on the lumbosacral region;
- bad habits - smoking and alcohol interfere with the normal nutrition of the spine, circulatory disorders occur, which leads to pathologies associated with ischemia and stagnant processes;
- obesity - excess weight increases the load on the spine, and a hernia can form precisely for this reason, in addition, excess fat in the body leads to muscle weakness, the spinal column loses its natural corset, and any damage can trigger the pathological process.
Manifestations
Hernia in the cervical region.
When a disc prolapses in the cervical region, the patient is disturbed by numbness of the neck, arms and shoulder girdle. In the same areas, pain periodically appears, and acute pain will already indicate an infringement of the nerve root.
A hernia in the neck also gives neurological symptoms in the form of frequent dizziness, impaired coordination of movements, and headaches.
Constant discomfort and impaired cerebral circulation affect the psychological state. The patient becomes irritable, but at the same time there is apathy, chronic fatigue, constant drowsiness.
Hernia in the chest.
Such a localization of the pathology is a rare phenomenon, because the thoracic segment of the spinal column receives the least load. A hernia can occur due to trauma, after surgery and difficult childbirth. If you wonder where the hernia comes from in this department, then other general factors can trigger the destruction of the disk, although this happens extremely rarely.
Manifestations of a herniated disc in the thoracic spine:
- chronic pain in the shoulder blades;
- numbness of the skin of the hands;
- rachiocampsis.
Hernia in the lumbar.
Lower back pain radiating to one leg is the main manifestation of a hernia in the lumbar and lumbosacral region. Also worried about numbness of the skin, discomfort while walking and sitting. The pain subsides in the supine position on a hard surface.
A hernia in the lumbar region can occur in response to a sharp increase in load when a person lifts a large weight. It can also form as a result of a long course of osteochondrosis, which could be diagnosed as early as adolescence, but treatment and prevention were ignored for a long time.
As soon as a hernia appears, this will be signaled by severe pain in the lower back, numbness in the groin and legs, and stiffness of movements.
This condition can be caused by other pathologies, so when symptoms appear, you need to be examined. It also happens that a hernia does not give symptoms for a long time, as long as there is no pressure on the nerves.
Treatment Methods
Conservative therapy for a hernia is aimed at eliminating the cause, namely, improving the nutrition of the disc, strengthening the muscle corset and improving the mobility of the vertebrae.
Comprehensive treatment includes the following activities:
- spinal traction - reduces compression of the vertebrae, increases the distance between the diseased disc and surrounding tissues, which prevents compression, the procedure helps to remove tissue swelling and reduces muscle tension;
- manual therapy - is indicated to return the vertebrae to their place, this treatment option is suitable for muscle spasms, when there is a curvature of the spine;
- drug treatment - NSAIDs, antispasmodics, tonics, chondroprotectors and local drugs for pain relief are prescribed;
- physiotherapy and non-traditional methods - acupuncture, drug electrophoresis, vacuum therapy, hirudotherapy.
Causes of hernia recurrence
When sequestration occurs, and parts of the disc begin to move freely along the spinal canal, an operation is prescribed. To eliminate the problem, the surgeon performs a partial or complete removal of the disc with the installation of the implant.
After the operation, for the first two months, any load on the spine is categorically contraindicated, with the exception of some exercises that are prescribed by the rehabilitation specialist or the attending physician. If you ignore this rule, there is a risk of re-disease in the same part of the spine, and the operation will be required again.