Manifestations and methods of treatment of umbilical hernia in adults
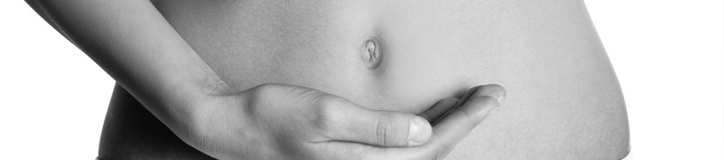
An umbilical hernia in adults is one of the most common pathologies, which is characterized by the formation of a tumor-like formation in the area of the umbilical ring. It is known that this disease ranks third among all hernias in terms of occurrence. An umbilical hernia is more common in women than in men.
The high incidence of the disease is associated primarily with the anatomical features of the umbilical region: in the umbilical region, adipose tissue is poorly developed, the muscle wall is thin, and the ligament system is poorly developed. All these are predisposing factors for the development of hernial pathology. Age also plays a role in the formation of pathology: people over 40 are more prone to herniation.
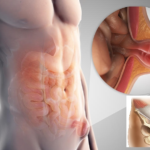
The disease as such consists in the prolapse of several internal organs through the umbilical ring, which later end up in the hernial sac. From the moment of formation, the protrusion does not catch the eye of a person, and the latter often believes that this is associated with temporary discomfort.
However, as the formation grows, it causes more and more trouble to its carrier in the form of pain and other disorders of the digestive system. Clinical signs are determined by the organs that are trapped. Most often these are: parts of the small intestine, elements of the large intestine, a large or small omentum.
Causes of an umbilical hernia
In the pathogenesis of the disease, two fundamental factors play a role: an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and a divergence of the muscle layers of the white line of the abdomen. So, the greater the pressure inside the abdomen, the more the muscles diverge. Therefore, there are a number of reasons that can affect the increase in pressure in the peritoneal cavity.
Causes of an umbilical hernia:
- Congenital features of human anatomy and physiology. These include diseases that are associated with weakness of the muscular corset, weakness of the connective fibers.
- Background diseases, manifested by such symptoms : persistent cough, constipation, excessive gas formation, sneezing, constipation. All this contributes to an increase in pressure.
- An umbilical hernia in women is often associated with pregnancy . As the fetus increases in size, the load on the internal organs of the abdomen increases, which leads to a weakening of the protective systems of the anterior abdominal wall. Often, the bulge goes away on its own after childbirth.
- Obesity, overweight body . This condition provokes the development of the fatty layer of the greater and lesser omentum, "shifting" the organs to the side. Low body weight is also harmful, the same applies to sudden weight loss.
- The complete absence of power loads. The consequence of a sedentary lifestyle is the process of weakening the muscle walls.
- Constant and inadequate physical activity.
- Pathological conditions of the abdominal cavity : ascites - accumulation of fluid in the cavities.
- Past trauma or surgery on the abdomen.
- Recurrences of previous hernias. This is especially true of surgical interventions where the sutures were applied poorly.
Types of umbilical hernia in adults
In medicine, the protrusion in the navel is divided into two types:
- Free or adjustable . This pathology is characterized by more functional disorders than organic ones. The contents of a free hernia can be reduced independently, without the help of the patient himself or even a doctor. Reduction most often occurs when a person assumes a horizontal position. However, this phenomenon is typical only for the first stages of the disease. In the future, the reducible hernia passes into another variety.
- Irreducible. This variant of the pathology is not reduced on its own. An irreducible hernia is one of the main signs of the start of adhesive processes, when the contents fuse to the inner wall of the hernial sac. This is a "launched" type of flow. With this development option, the likelihood of complications increases. It is treated exclusively by surgery.
Also, umbilical hernia in adults is:
- Congenital . This variant is formed due to congenital causes, such as weakness of the muscular belt, vulnerability of the elements of the umbilical ring;
- Acquired . This type of hernia speaks of lifetime acquisition.
Symptoms of an umbilical hernia
At first, bulging does not appear, the patient does not suspect that he has a hernia. Any indefinite discomfort is associated with time periods. After some time, a person during random probing may notice a small protrusion in the navel area. However, when taking a horizontal position, the primary signs are again smeared, and the clinical picture tends to absolute zero.
There is another development option. A hernia appears suddenly after lifting heavy weights. Then the process is accompanied by pain, attention to the protrusion is drawn immediately.
As the tumor grows, the following symptoms appear:
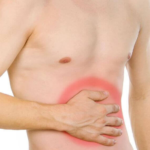
- Signs of indigestion : constipation, frequent, sharp or sharp pains in or below the abdomen; the patient may feel heaviness in the navel or in the entire abdomen; nausea, sometimes vomiting; increased gas formation; diarrhea, pain during defecation.
- Pain syndrome . It arises from the fact that the hernia, increasing, begins to compress the local nerve endings. There are false nerve impulses that occur in excessive amounts. Usually the intensity of pain is small, but the pain can increase when performing heavy exercises, bending over.
- An umbilical hernia in men can be manifested by such signs : sexual dysfunction (reduced libido, erectile dysfunction), pain during urination. In this case, we can say that the urogenital organs were drawn into the pathological process.
Common symptoms of a hernia in adults include:
- constant weakness of the body;
- increased fatigue, even insignificant work requires significant resource costs;
- increased body temperature;
- lack of appetite for more than two or three days.
Diagnostics
Usually hernial pathology is easy to diagnose.
Its symptoms are specific, visually noticeable, and therefore it is not difficult for a doctor to make a diagnosis. The study of the disease begins with a general examination of the patient. The specialist examines the general condition of a person, his well-being. Then the doctor proceeds to an objective examination, where he evaluates such indicators: the localization of the formation, its size, pain. Also, heredity plays a role in the diagnosis.
For final confirmation, it is necessary to undergo a series of instrumental studies.
These include the following methods:
- Ultrasonic diagnostics . Ultrasound allows you to study the anatomy of hernial pathology. This study determines the state of the internal organs, their size. The ultrasound method allows you to identify a hernia of any size: from small to large volume.
- Herniography . This method is carried out through the painless injection of a contrast agent. There is a visual staining of the organs that are located in the hernial sac.
- Radiography . This method provides information about inflammatory processes.
- CT scan. The method allows obtaining information about the structure in the form of layer-by-layer sections.
- Gastroduodenoscopy . The method is aimed at clarifying the state of the stomach and duodenum.
Treatment
Therapeutic activities are carried out by a surgeon. Consultation with other specialists is also necessary: a gastroenterologist and a nutritionist. Doctors in these areas are responsible for disorders of the intestinal tract and overweight.
Currently, the most effective treatment is surgery. It will allow not only to eliminate a number of symptoms, but also to remove the cause of the disease.
There are several ways to remove a hernia, the goal of each is to remove the hernial sac, set the organs in their place, and prevent relapses and complications.
Operation types:
- Tension hernioplasty . Doctors, choosing this method, use the patient's own tissues. The purpose of these tissues is to close the defect of the umbilical ring. To begin with, a small incision is made, then the bag is removed and the organs are immersed back. After that, measures are taken to strengthen the tissues, which are then sutured.
- Tension-free hernioplasty . In this case, a special medical mesh made of synthetic material is used. The advantage of this method is the low recurrence rate.
- laparoscopic method . This method of treating the disease is considered one of the safest. Its advantages: the absence of scars after the intervention, the minimum likelihood of re-protrusion, low traumatism. Laparoscopy is performed through several small punctures. And to strengthen the muscle walls, synthetic meshes are used.
rehabilitation period
The more successfully the operation was performed, the fewer days the actual recovery takes place. After the operation, doctors recommend wearing a bandage, which must be worn for up to two months. In the first few days, the patient must be in the ward. He can't do heavy exercise.
If after several days of being in the hospital there are no complications, the patient is discharged.
Also, the patient is obliged to appear every two weeks to the attending physician for a consultation in order to bandage and monitor the general condition. After treatment, a person is recommended to follow a special diet, which consists in a light diet.