What exercises are allowed with a hernia of the esophagus
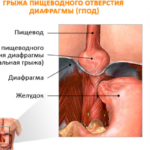
Hiatus hernia is an acquired disease resulting from increased intra-abdominal pressure and weakness of the diaphragmatic ligament. Such a violation is more often found in adults with excess weight and concomitant pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. In children, there is a congenital variant of the disease, which is fatal. In adults, this type of hernia is considered the least dangerous, because surgical treatment is prescribed as a last resort, and the main therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptomatic complex.
Therapeutic exercises for hernia of the esophagus is an important part of the fight against the consequences of the pathological movement of organs from the abdominal cavity to the chest.
Charging and various physical exercises help strengthen muscles, which is necessary for any form of pathology. In addition, exercise therapy for hiatal hernia helps to normalize the functioning of the stomach and intestines, which will prevent the negative impact of constipation and bloating on the patient's condition. During training and breathing exercises, relaxation occurs, which reduces the pressure on the internal organs, respectively, the symptomatic complex in the form of esophagitis, dysphagia, and angina pectoris disappears.
Causes of a hernia
The main goal of the treatment of any pathological process will be the impact on the cause of the disease. In order for the therapy to be as successful as possible, it is important to accurately determine all the risk factors that affect the aggravation of the pathology and provoke complications.
What affects the formation and development of diaphragmatic hernia:
- overeating - frequent overflow of the stomach leads to compression of the chest organs, while the patient feels discomfort in the sternum, this is accompanied by dyspeptic disorders in the form of heartburn, hiccups, belching;
- lifting weights - high loads provoke an increase in pressure inside the peritoneum, and the organs under the influence of this exit through the enlarged opening of the diaphragm;
- constipation and bloating - these phenomena also lead to increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- overweight and the period of gestation is an extra load on the body and muscles of the anterior wall of the abdomen, which does not contribute to the normal position of the organs in the abdominal cavity;
- bending forward - this causes squeezing of the organs in the diaphragm, which gives symptoms of soreness and dyspepsia.
Exercises for a hernia of the esophagus are selected taking into account the physiological characteristics of the patient and the constitution of his body.
If you are overweight, gymnastics will be aimed at burning fat and strengthening muscles. During pregnancy, a woman will benefit from breathing exercises and yoga. Those who are engaged in hard physical work are shown exercises aimed at strengthening individual muscle groups that are practically not involved in everyday life, which is important for evenly distributing the load and reducing it on the abdominal muscles.
Gymnastics with HH
Therapeutic measures for HH are aimed at eliminating the symptom complex: reflux, inflammation of the walls of the esophagus, dyspepsia, pain, false angina, general malaise. Every day you can do simple exercises that do not require special skills, but proper breathing and mindset when performing them will already be the key to combating various disorders.
Recommended set of exercises for hiatal hernia:
- Lying on its side, head raised, held by hand. Take a deep breath, sticking out your stomach, relax as you exhale. Repeat 5 times.
- On my knees While inhaling, do a slow bend forward, straighten your back as you exit .
- Lying on your back. Make turns to the right and left side, keeping even breathing.
- Lying on the back, the upper body is elevated, the index and middle fingers lie under the ribs along the midline of the abdomen. As you exhale, press your fingers into the abdominal cavity.
- Sitting, the body is slightly tilted forward. Place your fingers under the ribs, while inhaling, place the fingers deeper under the ribs, on the way out, apply pressure in the opposite direction.
- Standing, arms extended along the body, back straight. The torso is rotated so that the pelvis does not move.
- Lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, arms crossed behind the head. with the right elbow to the left knee, then the left to the right.
- Lying on your back, the body is relaxed. Make a deep entry, hold your breath for 10 seconds, exhale slowly.
- Kneeling , palms rest on the floor. Slowly lower your body down, sliding your palms along the floor.
- Lying on its side, the hand holds the head. Extend your free arm as far back as possible. Repeat several times on the right and left side.
Rules for performing exercises during the treatment of HH:
- you can not make sharp inclinations;
- to practice in loose clothing;
- begins before eating on an empty stomach;
- the lesson is postponed with severe heartburn and discomfort behind the sternum;
- All exercises are performed with proper breathing.
Means for the treatment of hernia of the esophagus
Physical education alone will not be able to fully ensure good health, therefore it can be combined with traditional medicine recipes. Some natural remedies are ideal for combating reflux and its effects by reducing inflammation, lining the esophagus, and relieving frequent heartburn.
Folk remedies for diaphragmatic hernia:
- gooseberry infusion three times a day half an hour before meals;
- milk with a few drops of alcohol tincture of propolis can be drunk 2 times;
- a glass of yogurt with a spoonful of olive oil should be taken for constipation;
- potato and carrot juice will help calm the inflammatory process;
- a decoction of coltsfoot, propolis, mint, marshmallow root will be useful for heartburn.
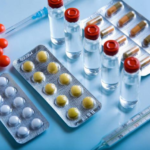
Medications are no less important in complex therapy:
- antacids to prevent irritation of the esophageal mucosa by the acidic contents of the stomach, these are Maalox, Gastal preparations;
- blockers of histamine receptors to inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid, these are drugs Ranitidine, Cimetidine;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to all patients in order to eliminate the consequences of reflux esophagitis;
- ursodeoxycholic acid preparations are prescribed when the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus, these drugs break down bile, thereby eliminating irritation of the walls of the esophageal tube;
- prokinetics help to normalize the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract to prevent reflux;
- proton pump inhibitors inhibit the synthesis of hydrochloric acid, for this purpose, drugs Omeprazole, Pantoprazole can be prescribed.
Diet
Nutrition with a hernia of the esophagus is of great importance, because the disease is almost always accompanied by reflux, the severity of which depends on the frequency of food intake, its quantity and quality.
Principles of nutrition for HH:
- products that increase the acidity are excluded ;
- dishes that contribute to gas formation and constipation are removed
- overeating and heavy dinner are contraindicated
- adheres to fractional nutrition;
- is minimized ;
- daily diet includes a variety of foods;
- gradual rejection of coffee, carbonated drinks, acidic foods, sweets.
Dietary nutrition in HH is aimed at normalizing the processes of digestion.
If you reasonably approach the choice of diet, the effectiveness of complex treatment will increase significantly. Sparing nutrition, physiotherapy exercises, medications are key measures for the treatment of diaphragmatic hernia and the elimination of a complex of symptoms.
Complications
If you do not follow preventive measures, you may encounter the following complications:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach due to irritation with hydrochloric acid, which aggravates the intake of certain drugs ;
- aspiration pneumonia - inflammation of the lungs due food particles entering the respiratory tract is aggravated by dysphagia, when the patient has problems with swallowing;
- pinched hernia - the stomach and abdominal segment of the esophagus are fixed in the area of the diaphragm and compressed, which causes a violation of blood circulation, which threatens with a loss of the functional ability of the organs;
- heart pathology - in severe cases, a heart attack can occur, which occurs due to squeezing of organs and circulatory disorders;
- persistent dyspeptic symptoms.