Strangulated hernia symptoms and treatment methods
A strangulated hernia is a complication that any person suffering from hernial protrusions, regardless of their location, may encounter. Since pathology is quite widespread, it is necessary to imagine what its features, varieties and causes of development are.
In order to start treatment of a strangulated hernia in a timely manner, the patient must be aware of the symptoms that manifest the complication, as well as the methods of diagnosis.
What is this pathology
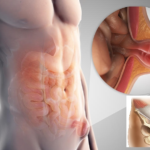
Strangulated hernia - what is this pathology? This is a complication of a classic hernia, mainly in the external abdominal region. It occurs in 15-20% of patients suffering from this disease. In the practice of aesthetic surgery, the treatment of this complication plays a rather large role due to its wide prevalence.
The elderly are mostly at risk. Often, any treatment is complicated by a rather high mortality (up to 10%) in this category of patients.
According to the mechanism of occurrence, two types of protrusions are distinguished: mechanical or fecal. Elastic infringement is a consequence of a sharp hit of large volumes of viscera in the hernial sac. It develops most often due to a rapid increase in intra-abdominal pressure due to active physical exertion. The strangulated hernial sac does not resolve itself and requires the intervention of specialists.
Fecal infringement of a hernia has a completely different pathogenesis. It develops due to the fact that the intestine, located in the hernial sac, is overflowing with feces. As a result, the intestine flattens at the site of overflow and puts pressure on the hernial ring, provoking the same symptoms as with elastic infringement.
It is important to keep in mind that the first pathology develops quickly, the development of necrosis is often formed within a few hours. With fecal pathology, necrosis of intestinal loops is not so fast and takes several days.
In principle, almost any organs can be in the hernial sac, but in practice their list is very limited. Most often, the development of a strangulated hernia clinic is a consequence of the loops of the small intestine getting into the sac. A little less often there is a large intestine. Very rarely - the uterus and its appendages, bladder, stomach.
Varieties
In medical practice, there are different types of infringement of hernias. This is explained by a different mechanism for the development of pathologies and, accordingly, different approaches to therapy. To establish the type of defect and select the most optimal method of treatment, a doctor should conduct a differential diagnosis.
Retrograde pathology
Retrograde infringement is an infrequent type of pathology. It is characterized by the fact that the hernial sac is filled with two intestinal loops, which are in a relatively good condition. Because of what, then, a specific clinic develops?
The fact is that in the abdominal cavity there is a third intestinal loop, which is a connecting element between the two that were in the hernial sac. It is she who receives the minimum blood supply and, one might say, is infringed, because of which her necrosis develops. The mesentery of the damaged loop is kinked several times, which makes it difficult for normal metabolism in its tissues.
Retrograde infringement is characterized by a rather severe course. This is due to the fact that necrosis does not develop in an isolated hernial sac, but in the abdominal cavity, which is not limited by anything. The likelihood of developing peritonitis is high.
In order not to face the severe consequences of the disease, it is necessary that the surgeon carefully examine the intestinal loop located in the abdominal cavity during the surgical intervention.
hernia littre
Litre's hernia is a separate type of strangulated hernia. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that in the hernial sac there is not an intestinal loop, but the so-called Meckel's diverticulum (protrusion of the intestinal wall, resembling a bag in shape). Since diverticula of this type are not characteristic of the intestine and are often poorly supplied with blood, their necrosis develops rather quickly.
Wall type
Often in medical practice, the presence of parietal or, as it is also called the Richter infringement of a hernia, is diagnosed. In the case of the development of this type of pathology, the intestine is in the hernial sac not with all its lumen, but only with a small part. Often this part is adjacent to the mesentery, which is why the pathology got its name.
With the development of parietal pinching of the hernia, intestinal obstruction, characteristic of the retrograde type of pathology, does not develop. The disease itself is difficult to diagnose, since there is no clear clinical picture (since the mesentery is not involved in the process, pain practically does not develop, and if it does, then their severity is minimal). At the same time, the danger of developing necrotic changes in the intestinal wall does not disappear.
This type of complication is not typical for large defects. Most often, parietal pathology is a consequence of the presence of a small hernial ring with a small sac.
false pathology
False strangulation of a hernia is a type of pathology that any clinician in medical practice may encounter. The disease is characterized by a set of symptoms characteristic of infringement, but at the same time, the complete absence of the defect itself. The consequence of the presence of symptoms without a strangulated hernial sac in its absence leads to the fact that the doctor incorrectly diagnoses and chooses the tactics of the operation incorrectly.
An erroneous diagnosis can be prevented if sufficient attention is paid to the collection of anamnesis and examination of the patient. Without a thorough analysis of complaints and symptoms, an accurate diagnosis will always be difficult, and errors are inevitable.
Alternative classification
Strangulated hernia is a phenomenon that occurs quite often in surgical practice. Doctors distinguish primary pathology and secondary.
The primary disease is extremely rare, but represents the greatest danger to the patient's body. Basically, people try to engage in self-treatment, which leads to necrotic changes in organs, peritonitis, and a pronounced intoxication syndrome.
A secondary disease is a consequence of a complication of a hernia that the patient already has. At the same time, patients often correctly assess their own condition and turn to the surgeon before any irreparable consequences develop.
Causes leading to pathology
A hernia is most often infringed for the following reasons:
- an attempt to quickly, with a single jerk, lift a heavy object;
- athletes involved in swimming have a strong primary shock during immersion in water;
- a prolonged and severe attack of coughing or sneezing;
- the habit of pushing hard with stagnation of feces in the intestines or urine in the bladder due to the development of prostate adenoma.
Additionally, doctors identify a number of predisposing causes, which include:
- difficult childbirth, passing quite often;
- sudden weight loss;
- traumatization of the abdominal wall with involvement in the process of the peritoneum;
- pronounced power loads.
Any pathological protrusion can be infringed, regardless of its location and size. The pathological process is always based on a strong infringing effect of the abdominal muscles.
Symptoms
What are the main signs of a strangulated hernia? In the first place, most doctors bring pain syndrome. In this case, pain can vary significantly in localization and intensity, depending on the area in which the pathological defect is located. Also, pain can capture either only the affected area, or spread over the entire surface of the abdomen. Irradiation is not ruled out.
Interestingly, the pain syndrome is initially acute. As necrotic changes develop in the organ, the pain gradually subsides. This is due to the death of nerve endings, which are no longer able to transmit an alarm signal to the brain. A pinched hernia, accompanied by necrosis, is characterized by a gradual change from pain to a feeling of anxiety. In this case, it is possible to develop a sense of imaginary well-being.
Symptoms of a strangulated hernia may include:
- severe pallor of the skin, accompanied by severe tachycardia (increased heart rate over 120 beats per 1 minute) and a decrease in pressure (all this indicates the development of pain shock);
- pain shock may not develop if the pathology is of a fecal nature, since in this case the rate of necrosis is very low, the patient may not show much anxiety for a long time, enduring his poor condition;
- if intestinal obstruction has developed, in addition to pain, the patient will complain of paroxysmal vomiting, which does not bring relief (possible fecal odor in vomit);
- with parietal infringement of a hernia, there are no symptoms of fecal obstruction and pain shock, but an admixture of blood can be detected in the urine, and the pain syndrome is characterized by patients as moderate, which leads to a delay in contacting a doctor;
- the irreducibility of the defect can be determined by the large size of the protrusion and its strong tension.
As the pathology progresses without specialized help, a gangrenous lesion of the intestine develops. As a result, a phlegmon of the hernial sac or peritonitis may form.
Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosis of a strangulated hernia in most cases is not difficult if the pathology is not primary. By comparing the patient's history with his complaints, the doctor can easily make the correct diagnosis.
A visual examination of the complaining person is mandatory. The detection of a characteristic protrusion that does not disappear with a change in body position and hurts on palpation is one of the reliable signs of pathology. One of the most characteristic features is the absence of a transmission cough shock. This means that if you ask a person to cough, vibrations in the hernial sac will not be felt, since it is delimited from the abdominal cavity by a narrowed hernial ring.
There may be symptoms of intestinal obstruction, which should also undergo a full medical assessment.
The following methods can be used to make a diagnosis:
- survey radiography of the abdominal cavity (allows you to detect Kloiber's cups with intestinal obstruction);
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- CT;
- MRI.
The last two methods are used very rarely and only if there are difficulties in making the correct diagnosis. It is necessary to differentiate the pathology from spermatocele, hydrocele, inguinal-type lymphadenitis and some other diseases.
First Aid Basics: Do's and Don'ts
What are the rules for providing emergency care for a strangulated hernia? First aid, first of all, consists in calling an ambulance. In any case, the patient will need surgical intervention, and it will be carried out according to vital indications (in this case, the only significant contraindication is the dying state).
First aid before the ambulance arrives is to keep the patient calm. It is necessary to provide him with the opportunity to lie on his back, and put a small pillow or a folded blanket under the pelvis. Thanks to this, it will be possible to slightly compensate for the lack of blood flow in the organs that are in the zone of infringement.
Absolutely forbidden:
- put the victim in a warm or hot bath;
- apply heating pads and warm compresses to the affected area;
- take drugs from the group of analgesics, antispasmodics or laxatives.
The only thing that can be done if the pain is very strong is to install an ice pack at the site of the defect. Attempts to reduce irreducible hernias that have been pinched are strictly prohibited until the ambulance arrives, regardless of the patient's condition.
Unprofessional actions in this case can lead to:
- damage to the vascular walls with the formation of bleeding;
- damage to the hernial membrane;
- the entry of necrotic tissues into the abdominal cavity and the development of peritonitis;
- deformation of the hernia neck.
Approaches to the therapy of infringement
Pathology can be treated only in an operating room. Often people try to practice the imaginary reduction of a strangulated hernia, but such an approach will not only not help the patient, but, on the contrary, will greatly worsen his condition.
The patient is urgently taken to the operating room, where a method for solving the problem is selected.
Can be used:
- Classic operational access.
A full cut of the defect area is performed. During the intervention, the doctor assesses the condition of the hernial protrusion and its contents. If the internal organs are not affected by necrotic changes, they are put back into the abdominal cavity, and the defect is sutured using the patient's own tissues or a special mesh. If the internal organs are damaged, then they are excised within the healthy tissue, and only then the hernial protrusion is sutured
- Laparoscopy.
To treat a hernia of a restrained type by this method began relatively recently. Special instruments and a camera are inserted into small incisions, which allows you to control the course of the intervention. After eliminating problems with internal organs, plastic surgery is performed using a special medical stapler or a mesh graft.
Laparoscopy is used much more often today, as it is a minimal intervention in the patient's body. At the same time, the operation reduces the risk of complications, the appearance of postoperative scars and traumatization of nearby tissues. True, according to some experts, laparoscopy does not allow to fully assess the degree of damage to the tissues involved in the pathological process, which is why many surgeons still prefer classical access to it.
A strangulated hernia is a serious pathology that is a complication of a conventional hernia, the treatment of which has not received sufficient attention.
Many patients do not consider this pathology a problem, completely forgetting that the disease in advanced cases can lead not only to disability, but also to death. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should contact a specialist.