Signs and methods of treatment of hernia of the thoracic region
The thoracic spine is prone to diseases such as osteochondrosis, scoliosis, displacement of the vertebrae, but a hernia is diagnosed in it extremely rarely. Such a disease poses a threat to the health and life of the patient, unless the pathology is detected at the initial stage. The danger lies in the fact that the pulp that has gone beyond the disc begins to migrate along the spinal canal, damaging the nerve endings.
A hernia in the thoracic region, its symptoms and treatment is the task of several doctors. A vertebrologist, a surgeon, a chiropractor, a massage therapist, and a rehabilitation specialist deal with the patient.
Reasons for development
Until recently, a hernia of the spine occurred mainly in people of the older age group, but in recent years this disease has become “younger” and is detected in men and women from 20 years old. The reasons for this are very diverse, ranging from a sedentary lifestyle to sports injuries.
The immediate causes are the following:
- high load on the spine;
- blows and falls on the back;
- metabolic failure;
- rachiocampsis;
- untreated osteochondrosis.
Factors of the appearance of an intervertebral hernia in the thoracic region:
- genetic predisposition;
- spinal injuries (falls, bumps, sharp turns);
- transferred operations on the spinal column;
- congenital anomalies of connective tissue;
- hypodynamia, low physical activity;
- alcohol abuse and other bad habits;
- pathological posture;
- increased load on the chest;
- period of pregnancy;
- high growth;
- infectious pathologies;
- overweight, metabolic disorders, severe obesity.
How does it manifest
Typical symptoms of an intervertebral hernia of the thoracic region:
- pain in the upper back;
- pain in the ribs;
- feeling of squeezing the chest;
- false heart and stomach pains;
- shortness of breath after physical activity;
- numbness of the skin of the hands, problems with motor skills;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin of the extremities.
Any of these manifestations is a reason to consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. Typical symptoms of a hernia of the thoracic spine can be confused with signs of other pathologies. Only a specialist, having carried out a complete diagnosis, will make a correct diagnosis, eliminating the possibility of other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
It is important for the doctor to take into account all the symptoms and choose the treatment of a hernia in the thoracic spine depending on their severity.
Types and stages
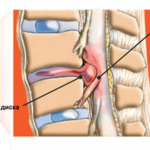
Intervertebral hernia of the thoracic region is of the following types:
- Anterolateral . Directed forward, proceeds for a long time without symptoms, the prognosis is favorable.
- Back . Directed into the spinal canal, which leads to its squeezing.
- Lateral . Directed away from the vertebral bodies. The exit of the pulp occurs through the holes of the roots.
- Schmorl's hernia . Directed vertically down or up.
Symptoms of a hernia of the thoracic region at different stages:
- Protrusion . Protrusion of the disc by 1-5 mm. There are no signs of the disease.
- Prolapse . Protrusion up to 5 mm with the appearance of pain and neurological signs.
- Formed hernia . protrusion more than 5 mm. Severe symptoms.
Diagnostic methods
Accurate methods for diagnosing a hernia of the spine are magnetic resonance and computed tomography. MRI allows the radiologist to look at the spine itself and the intervertebral discs, as well as the soft tissues adjacent to them. Computed tomography shows only the bony structures of the spinal column.
If additional studies are required to detect pathology, myelography is usually prescribed.
In this method, a radiopaque substance is injected under the membrane of the spinal cord. Thanks to him, the hernia itself and the spinal cord are visible in the picture, which allows you to assess the degree of its compression, as well as obtain information about the size and direction of the protrusion.
Choice of treatment
Treatment of spinal hernia without surgery combines several methods, including:
Anesthesia.
The pain causes maximum inconvenience to the patient, hinders his movements, makes it difficult to breathe, affecting the ability to do daily activities, not to mention physical work. To eliminate this symptom, pain medications are used - analgesics, steroid and non-steroid drugs. If the listed drugs are ineffective, the doctor prescribes a blockade of the spine.
exercise therapy.
With pathologies of the spine, it is important to combine sets of therapeutic exercises to improve the mobility of the patient's spine. Treatment can consist of classes both at home and on special simulators. This is complemented by traction of the spine, which can be performed in water for a more gentle effect on the body.
Considering that it is impossible to completely cure an intervertebral hernia, exercise therapy will become an important measure for the prevention of complications. Only physical methods can fully ensure tissue repair.
Useful sport.
You should choose sports that are aimed at stretching the spine - Pilates, yoga, swimming. Gentle stretching allows you to remove the muscle spasm that accompanies the intervertebral hernia of the thoracic region.
Physiotherapy procedures.
Physiotherapeutic procedures such as laser therapy, ultrasound, magnetotherapy, mud therapy, electrophoresis are more often prescribed. These methods help reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation and eliminate muscle spasms. The frequency and duration of procedures is determined by the attending physician.
Change of diet and normalization of weight.
In the treatment of intervertebral hernias, diet is of great importance. Weight loss helps to reduce the load on the spine, and therefore alleviate the condition. The diet should be dominated by dairy products, vegetables, fruits, nuts, that is, natural food.
It is important to exclude flour products, sweets, fried foods from the diet, as well as minimize salt and sugar intake.
Massage and manual therapy.
These procedures normalize muscle tone and improve blood circulation. Massage can be not only manual, but also vacuum. The latter is performed using cans. During the procedure, blood flow increases, thereby reducing inflammation and normalizing metabolism. Treating a hernia with manual therapy is necessary to increase the space between the vertebrae, which reduces pressure on the disc and soft tissues.
Gentle mode.
With exacerbation of pain syndrome, bed rest is observed. During the remission period, physical activity and traumatic and heavy sports are excluded.
Bandage.
With a hernia in the thoracic region, the doctor prescribes wearing a rigid or semi-rigid corset that fixes the spine, removing a significant part of the load from it.
Folk recipes.
Home treatment includes the following procedures:
- compresses;
- taking tinctures and decoctions of herbs;
- rubbing the diseased spine with oils.
Indications for surgery
Surgical treatment of an intervertebral hernia of the thoracic spine is indicated only in a life-threatening condition, and when no methods help to get rid of the pain syndrome.
At any stage of the disease, the treatment of a hernia of the thoracic spine should be under the strict supervision of the attending physician. In the case when the pathology threatens the patient with paralysis, it remains to resort to surgical methods. The main task of removing the protrusion is to eliminate the compression of the hernia of the spinal cord and nerve endings.
The decision on the need for surgical intervention in spinal hernia is made by a neurosurgeon. The main indication will be the large size of the hernia, when compression of the spinal cord begins, and all non-surgical methods do not give the desired results.
Other indications for radical treatment are:
- persistent pain syndrome;
- neurological symptoms in the form of paralysis and paresis;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Applied methods of surgical removal:
- laminectomy and discectomy.
- Microdiscectomy.
- laser destruction.
- Chemonucleolysis.
- Endoscopic nucleotomy.
Before radical removal, minimally invasive methods can be used, in which the intervertebral hernia is reduced. However, even after such procedures, it is required to follow preventive measures, strictly following all the instructions of the attending physician.
Rehabilitation
How is rehabilitation after removal of the thoracic disc:
- The first 2 weeks - drugs are prescribed for pain relief, the efforts of specialists are aimed at normalizing the patient's condition, and a sparing diet is also shown to prevent early postoperative complications.
- From 2 to 8 weeks - physiotherapy procedures, physiotherapy exercises are prescribed, the diet changes, therapy is aimed at restoring the function of the spine and increasing its movement.
- From 8 to 48 weeks - prevention of late complications is carried out, the patient is prescribed a set of exercises to strengthen the muscular frame of the back, treatment will include measures to fully restore the function of the damaged area of the spine.
Complications and prevention
A hernia located between the thoracic vertebrae occurs less frequently than others and can be asymptomatic for a long time. This disease has typical manifestations for other diseases, therefore it is possible that treatment may be absent for a long time until the protrusion reaches an impressive size.
A neglected hernia of the thoracic spine often results in paresis, limited mobility of the arms, and posture disorders. In severe cases, a thoracic disc herniation threatens with paralysis, and then the only treatment option is surgery.
What else is dangerous pathology of the disc in the thoracic region:
- infringement of a hernia - there is a compression of the convex part of the disc, which is accompanied by acute pain, paralysis of the limbs, impaired sensitivity of the limbs;
- pinching of the nerve root;
- spinal cord compression.
Preventive measures for hernia of the spine :
- body weight control;
- sports;
- complete rejection of hard physical work;
- the gradual elimination of bad habits;
- use of an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- regular examination by a vertebrologist.
A hernia of the thoracic region is treated without surgery, but if the pathology is started, complications cannot be avoided. The best prevention is a healthy lifestyle. In modern conditions, this is not so easy to achieve, but any change will already be a factor in improving the health of the spine.