How to identify and treat a hernia in a child
An umbilical hernia in a child is the most common surgical disease in children under one year old, which requires surgery. This pathology does not threaten the life of the baby, but only if the parents follow all the recommendations of the surgeon regarding the prevention of complications and agree to the planned surgical treatment.
Congenital hernia in young children is visible from the moment of birth. If this is an acquired disease, the first signs may occur after several months and years. The period of onset of the disease largely depends on the activity of the child and associated pathologies.
When there are congenital diseases of the muscular and connective tissue, an umbilical hernia in children will be the result of a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which can occur at any time.
It is important for parents to know that a hernia in a one-year-old child is treated much easier and with a favorable prognosis, but if the disease is started, this can result in serious consequences for a teenager and an adult.
An umbilical hernia is a congenital or acquired disease characterized by the exit of the abdominal organs through the umbilical ring or muscles near the navel due to tissue weakness and increased intra-abdominal pressure.
Hernia in children under one year old
A hernia in a month-old baby and children under one year old usually does not bother the baby, and is manifested only by an external defect in the form of a protrusion of the navel. Rarely, colic, bloating, nausea and weakness can disturb. The child may be inactive, eat poorly and cry often, but these will already be signs of complications or the appearance of other gastrointestinal pathologies.
Surgeons prescribe an operation from 6 to 12 months of age, and this is due to the fact that a hernia of the abdomen in children under one year old can disappear on its own.
Parents, having learned about such a problem, often resort to alternative methods of treatment. This makes sense only in the first months of a baby's life, and if only proven and safe means are used. Some techniques do help the hernia disappear, but they do not give any guarantee. It is possible to understand what to do for the recovery of the child only after consulting a surgeon, who, based on the results of the examination and research, will prescribe adequate treatment.
Why does a child have a hernia
The main cause of a hernia is the weakness of the anterior abdominal wall. But by itself, this factor does not always lead to a hernia, and the disease occurs much more often when other provocative phenomena are present.
What can lead to a hernia in a child:
- genetic predisposition and prematurity;
- low weight of the newborn;
- difficult childbirth;
- severe crying, screaming, bloating, coughing;
- pathology of the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract;
- anomalies of intrauterine development;
- rickets and malnutrition.
How to identify an umbilical hernia
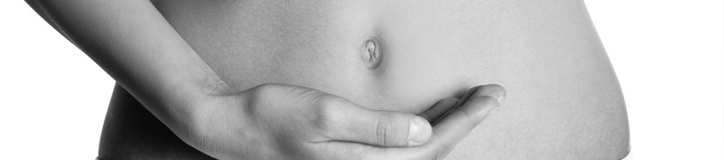
The hernia manifests itself externally, and this greatly facilitates timely diagnosis. Parents may see a protrusion of the navel, but such a phenomenon may simply be an anatomical feature, so you need to pay attention to other signs.
How to understand that a child has a hernia:
- oval or rounded bulge in the navel, it can be from a few millimeters, and reach 10 centimeters;
- the navel is set into the abdominal cavity with pressure, and when the child lies on his back in a relaxed state;
- the baby behaves restlessly, refuses to eat, often cries, is naughty and does not sleep well;
- pain is absent, discomfort occurs only when there is bloating.
A large protrusion can be infringed at any time, and the disease in this case is often accompanied by a violation of digestion. Smaller hernias practically do not threaten anything, but only if the parents understand the importance of treatment.
Treatment Methods
Children under one year old are prescribed conservative methods of treatment, but as soon as signs of complications appear, an operation is necessarily performed.
Which methods of treatment are acceptable without removal of a hernia:
- Massage and gymnastics . These are the main measures that will save the baby from discomfort and affect the cause of the disease, namely muscle weakness. You can work out with your child at home, performing standard exercises on a fitball or a hard surface. The key is to be systematic. You need to do gymnastics every day several times. You can also massage the abdomen every day when the child is calm.
- P plaster . Special fixing plasters are an alternative to a bandage. They are attached for 7-10 days, then removed. With a small defect, three courses may be enough for the hernia to disappear. You only need to choose a hypoallergenic high-quality patch, and if an allergy or irritation occurs, it should be removed immediately.
- Bandage . _ The umbilical belt with a hernia is important in order to reduce the protrusion and hold the organs in the abdominal cavity. The bandage prevents infringement, which can occur due to sudden movement, crying or muscle strain during exercise.
- National means . Coin, cabbage and oatmeal compresses are commonly used methods for a hernia in a child, and they are safe, but not always effective. It is important to understand that each item must be securely fixed on the navel, and this can only be done with an adhesive plaster, which will irritate the skin and interfere with the child. Each folk remedy can be replaced with a bandage and a special plaster, which will be easier, but more effective.
Hernia removal
An operation will be prescribed for a child when the diameter of the umbilical ring exceeds 2 cm, this is the borderline when conservative methods cannot affect tissue repair in any way, and they must be sutured and additionally strengthened.
A child can be prescribed a standard plastic of the umbilical ring with suturing the defect with his own tissues and hernioplasty, which can be of two types.
In the ides of hernioplasty for hernia of the umbilical ring in children:
- Laparoscopic . The intervention is performed through 3 punctures in the abdominal wall. This is an atraumatic version of the operation with a short rehabilitation period. The child is discharged home on the second or third day. After such a hernia repair, there are no wide scars, the risk of postoperative hernia is minimal.
- With the installation of a mesh implant . During the operation, the defect is closed not by the patient's tissues, but by a special mesh, which further prevents the exit of organs through the umbilical ring. Over time, the implant fuses with the tissues. It does not interfere with the life of the child, does not affect the work of internal organs.
Urgent open surgery will be scheduled for the baby when his condition worsened due to complications. The most common consequence of a hernia without treatment will be infringement - clamping of organs in the area of the hernial orifice or sac with tissue necrosis.
Complications
In addition to infringement of the contents of the hernia, inflammation may occur. This is a serious condition, because the infection gradually spreads to neighboring tissues, leading to the death of vital structures. Symptoms of this complication will be general malaise, high fever, intoxication of the body, severe abdominal pain, lack of stool.
There is also a risk of coprostasis with intestinal obstruction, when feces accumulate in the part of the intestine located in the hernial sac and do not pass further. It is also a life-threatening condition that requires immediate surgery.
Peritonitis is another dangerous phenomenon that occurs more often due to organ rupture. Inflammation of the abdominal cavity is manifested by an increase in the tummy and muscle tension. The risk of this condition increases with the infringement of the hernia. Compression of organs can occur at any time, even with slight physical exertion. In this regard, doctors strongly recommend the use of a bandage, which reduces the risk of infringement.
All complications are dangerous and cannot be treated at home. But not every child experiences them. Some children can live with a hernia for years (when surgery is contraindicated) without any problems, but the risk always remains.
The following symptoms will indicate a complication of a hernia :
- the navel does not retract into the abdominal cavity;
- the hernia gradually increases in size;
- the child begins to cry a lot, which is associated with acute pain;
- the stomach increases in size, becomes hard;
- nausea with vomiting occurs, bleeding is possible;
- there is no stool, bloating is disturbing.
Relapse prevention
After removal of the umbilical hernia, it may occur again. This is due to congenital muscle weakness or a violation of the operating technique and non-compliance with the postoperative regimen.
During the recovery period after hernia repair, surgeons give the following recommendations:
- wear a postoperative bandage to reduce pressure on the stitches;
- provide the child with peace so that he cries less and does not make sudden movements;
- follow the diet prescribed by the doctor;
- start doing gymnastics 2-3 weeks after the operation.
To prevent recurrence or postoperative hernia, it is important to exclude constipation and bloating.
These conditions lead to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, and this is a key factor in the divergence of the muscles (and sutures, if we are talking about the postoperative period), which will lead to a protrusion of the navel.
The primary prevention of the disease is to strengthen the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, which can be achieved by doing gymnastics, swimming, ensuring the physical activity of the child as soon as he begins to walk. When there is a predisposition to a hernia, it is recommended to consult a doctor who will prescribe a special set of exercises and diet.