Features of the course and methods of treatment of paraumbilical hernia
Paraumbilical hernia (from Latin para - around something, umbilicus - navel) is a disease characterized by pathological protrusion of a part of the intestine, part of the peritoneum or omentum through the weakened muscles of the white line of the peritoneum into the paraumbilical space. Belongs to the class of hernias of the abdominal cavity.
This pathology occurs in 5% of adults among all abdominal hernias. Most often people of mature age - 40 and more years suffer. In children, the incidence of the disease is much higher than in adults. Often this disease is confused with an umbilical hernia, but these are different in origin and mechanism of the disease.
The upper abdomen is the most common area for the occurrence of the disease due to the fact that it is here that the tendon adhesions are less thick than in any other department.
How and why does it occur
The mechanism of formation lies in the imbalance between internal pressure and restraining forces. Every healthy person has “gaps” in the anterior abdominal wall that contribute to muscle weakness, but normally the muscle corset compensates for adequate loads and withstands intra-abdominal pressure. A common reason why a pathological protrusion occurs is the pathology of the internal organs of the abdomen or an inappropriate lifestyle.
Factors and causes that provoke the development of the disease:
- constant sports , in which the load is not controlled and is not dosed;
- obesity or excessive wasting;
- abdominal wall injuries : surgeries, bumps, falls;
- in women - the period of gestation;
- congenital structural features of the body , which include thinning of the white line of the abdomen, weakness of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, impaired development of the aponeurosis during intrauterine development;
- background pathological conditions : ascites (fluid accumulation in the peritoneal cavity), flatulence (gas accumulation) - all this contributes to an increase in pressure inside the peritoneum;
- genetic diseases : Marfan's syndrome, in which there is a violation of the development of connective tissue;
- diseases of the respiratory systemaccompanied by chronic cough;
In children, an umbilical hernia is formed even during fetal development due to an incorrectly formed muscle aponeurosis.
Varieties of the disease
The first classification is based on the period of education, namely:
- congenital hernia;
- acquired during life.
The second classification is determined by the specifics of the structure of the bulge itself:
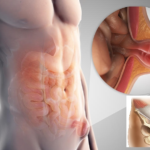
- direct - the contents of the hernia sac passes through the umbilical ring and is formed by the transverse fascia;
- oblique - a paired formation under and above the umbilical ring, the contents of the bag are located between the white line and the fascia, then pass through the ring and are limited to the subcutaneous tissue.
The last classification is based on the development of the protrusion itself:
- Formation stage . The formation of a hernia begins from the moment of a slight bulge, while the signs of pathology are poorly noticeable and the hernia itself almost does not bother the patient. Outwardly, it resembles a temporary defect in the skin.
- The second stage of education is characterized by the involvement of more and more organs and tissues in the process . There is a dimensional tumor-like formation and the height of symptoms. A hernia causes discomfort to its wearer.
Clinical picture of the disease
Paraumbilical hernia in adults is accompanied by such signs:
- Above the navel or around it there is a rounded swelling, elastic in its consistency. May be pressed on palpation.
- In a state of calm when lying down, the swelling may disappear on its own.
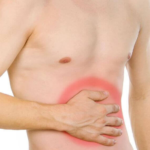
- Pain syndrome of varying intensity. The sensation of pain in this case depends on the individual threshold of sensitivity: some suffer from severe pain, and some do not feel it at all. However, with a load on the abdomen, the pain always intensifies.
- After eating, patients, as a rule, feel severe discomfort in the navel and abdomen as a whole. Also, after eating, pain may appear, which can spread to the area of the shoulder blades or the lumbar region.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: flatulence, constipation, nausea with periodic vomiting, bad breath.
- Outwardly, the patient can observe the progression of the protrusion: the hernia becomes larger in size over time.
Common signs: chronic fatigue, malaise, sleep disturbance, headaches, irritability, fever.
Symptoms of an umbilical hernia in children:
- from the first months, the child emits a strong cry, in which the parent can observe a strong spasm of the abdominal muscles;
- an elastic formation appears under the skin, the dimensions of which do not exceed two centimeters;
- often a hernia above the navel is disguised as colic: the child is constantly crying, bending his legs under him, thus trying to reduce the stretching of the muscles of the peritoneum and relieve pain;
- violation of the gastrointestinal tract: excessive gas formation and stool disorders (most often constipation is observed);
The main difference between a child's hernia and an adult's is that in infants in the supine position, the protrusion does not disappear on its own. This is due to the fact that the child's body has a narrow hernial orifice, while the hernial sac exceeds its input dimensions, and cannot "reset". So, an ectomy (section) of the bulge is done after six years, when the diameter of the hernial ring will correspond to the size of the bag.
Diagnosis of supra-umbilical hernia
The diagnostic process consists of several stages:
- General examination by a specialist . An objective examination by a doctor involves palpation of a painful place, an assessment of the general condition. The doctor also collects complaints, anamnesis of life and illness.
- The second stage is laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods . At this stage, as a rule, a general blood test and its biochemistry are prescribed.
The second stage involves the passage of such studies:
- gastroduodenoscopy - a method that allows you to assess the condition of the abdominal organs (stomach and duodenum), identify their pathology and assess the risk of complications;
- radiography of the abdominal cavity - a method by which the doctor will be able to assess and study the exact location of the hernia and its size;
- ultrasound diagnostics - it studies what is in the hernia and the condition of the tissues in contact with the hernial sac.
Treatment of supra-umbilical hernia
Paraumbilical hernia, like any similar pathology of the white line of the abdomen, almost does not respond to conservative treatment. So, in the clinic for umbilical hernias, the leading method of treatment is surgical intervention.
The operation that eliminates such a protrusion is called hernioplasty (from the Latin hernia - hernia). It is carried out in a hospital.
Hernia repair, surgery, consists of several stages:
- Dissection of tissues and gaining access to the hernial sac.
- Excision, removal or reduction of content. This variability depends on the indications, but the most common is the usual reduction of organs.
- Stitching of the gate of the hernia.
The second type of hernioplasty is the Liechtenstein section . Unlike the first option, the Lichtenstein method is not as traumatic. Preparation for intervention is minimal. During the operation, the mesh graft is sutured under the muscle tendons, while neighboring structures are not susceptible to damage. This method is performed laparoscopically.
An umbilical hernia is treated with conservative therapy when patients have contraindications to surgical manipulations.
Main restrictions:
- pregnancy;
- period of relapse or exacerbation of existing diseases;
- the patient's age is more than 70 years;
In this case, one of the most common methods of non-invasive treatment of an umbilical hernia is used - the use and wearing of a bandage.
Recovery and rehabilitation
The stitches are removed after seven days. At this time, the person is actively monitored: he is prescribed a sparing diet, periodically inspect the site of the operation and his condition as a whole. In the future, the patient is recommended to wear a bandage continuously for the next few months. Parallel to this, the cured person must perform simple gymnastic exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles, restore their endurance and strength.