Signs, forms and treatment of strangulated abdominal hernias
Infringement of hernias of the abdominal cavity occurs as a complication in case of non-compliance with the prescribed regimen. This is a dangerous condition in which the internal organs are compressed in the hernial orifice, and this is followed by life-threatening disorders.
All hernias of the abdominal cavity require surgical treatment due to the risk of strangulation.
Patients with such a diagnosis are prescribed a sparing regimen, diet, bandage, medications and other measures. All this helps to exclude pinching of the hernia of the abdomen until the operation. Abdominal hernias are of different types, depending on the location. They have some distinctive symptoms and pinching factors.
How does infringement of a hernia occur?
Through the gaps in the abdominal cavity, for certain reasons, internal organs can exit. Normally, the natural openings are narrow and elastic, but when the pressure inside the abdominal cavity is disturbed or the ligaments are injured, the tissues weaken and the gaps expand.
More often, the intestines, part of the stomach, bladder, omentum, kidneys, and uterine appendages leave their anatomical place. This happens in the area of the white line of the abdomen, umbilical ring, groin and thigh.
The hernia gets its name from the place where it occurs. More often in adults and children, inguinal and umbilical hernias are diagnosed, less often the defect occurs in the lumen of the white line and thigh.
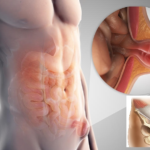
All hernias of the abdomen, unlike diaphragmatic and vertebral, have one common symptom - a swelling in the form of a bump directly at the site of protrusion of the organs. The defect can be of various sizes, sometimes surgeons have to remove giant hernias in the groin and near the navel, when part of the intestine or the entire organ is located at the gate.
The hernia consists of the following elements:
- contents - part of one or more organs;
- gate - the area of \u200b\u200bthe exit of organs between the muscles and ligaments;
- sac - a formation from the skin or part of an organ that surrounds the contents.
Infringement of a hernia can occur in the area of the hernial sac and gate. At this point, the contents begin to compress, blood circulation is disturbed, and tissue necrosis occurs.
Internal organs can be infringed at the time of a sudden increase in load and intra-abdominal pressure. The first signs concern sensations. There is severe pain in the area of the defect, it radiates to the back and legs. When the pressure rises sharply, the hernial ring stretches, more organs enter the sac, then the hole returns to its previous size. This is how abuse happens.
There are primary and secondary infringements. In the first case, the complication occurs immediately from the moment the hernia appears. This is preceded by a high load, as a result of which the organs go under the skin or into the adjacent cavity and are immediately infringed in the area of the hernial orifice or sac. Secondary infringement does not occur immediately, but may appear at any time with an already existing hernia.
Symptoms
Pinched abdominal hernia gives early and late symptoms. The first alarm signal will be pain and irreducibility of the defect. Late ones begin in the process of ischemia and tissue death in the hernial sac.
Early signs of infringement of hernias of the abdominal cavity with clamping of part of the intestine:
- intense paroxysmal pain;
- repeated vomiting without relief;
- hiccups, heartburn, belching;
- a noticeable but slight increase in the volume of the abdominal cavity;
- bloating without passing gas.
When the omentum is pinched, the symptoms are less pronounced. There is pain, there is nausea, but no vomiting. Outwardly, the complication increases, becomes dense. A specific sign of infringement will be the absence of a cough shock.
Infringement can be determined independently, especially when the hernia has already been diagnosed and the patient is aware of the existing risk of complications. Surgeons are often approached with a complaint of pain and the inability to correct the defect, which will not make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
Late symptoms of a pinched hernia, regardless of the compressed organ:
- redness of the skin over the protrusion;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- general malaise, lethargy;
- chronic fatigue;
- fever, fever up to 40 degrees.
Less often you can observe such a complication as phlegmon. The purulent process carries a particular threat, quickly moving to neighboring tissues.
inguinal
With inguinal infringement, swelling occurs in the perineum, swelling increases and hurts. This is complemented by the inability to correct the hernia, an increase in its size. The state of health worsens, the temperature rises, urinary retention, constipation, bloating are observed.
Clamping of the bladder leads to painful discharge of urine. When the intestines suffer, there is no stool, gases accumulate, which further aggravates the condition.
umbilical
Infringement of organs in the umbilical ring has pronounced symptoms:
- paroxysmal pain;
- lack of stool, constipation;
- rumbling in the stomach, flatulence;
- vomiting with blood, excretion of blood with feces;
- irreducibility of the defect;
- persistent nausea and repeated vomiting without relief;
- associated disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Umbilical hernias often manifest with intoxication, weakness, dizziness, incoordination, confusion.
femoral
Femoral protrusion is relatively rare. It appears on the front of the thigh. The most severe complications are peritonitis and tissue necrosis.
Clamping of organs in a femoral hernia is manifested by such a clinic:
- pain aggravated during movement and straining;
- showing the skin of the leg;
- dyspeptic symptoms;
- inflammation of the skin in the area of the hernia;
- frequent constipation, which can result in intestinal obstruction.
White line of the abdomen
With a hernia of the white line, intestinal obstruction almost never occurs, which distinguishes this type of disease from others. But there is a risk of shock due to circulatory disorders.
Symptoms of organ compression during protrusion in the area of the white line of the abdomen:
- bloating;
- anemic syndrome, pallor of the skin;
- tachycardia, hypotension;
- dyspepsia;
- general malaise.
Types of infringement of hernias of the abdominal cavity
There are retrograde, fecal, parietal, elastic, mixed infringement. The clinical picture will depend on this. Pinching can also be internal or external, depending on the location.
Types of infringement and their distinctive characteristics:
- elastic.
Appears under the influence of a high load on the abdominal cavity. A sharp increase in pressure "pushes" the organs into the hernial sac, where they are compressed, which is facilitated by the stretching of the hernial orifice at the time of strong muscle tension.
- Fecal.
It has a different development mechanism. There is a gradual accumulation of feces in the part of the intestine located in the hernial sac. The cause will not be an increase in load, but a significant increase in the intestinal loop, which leads to compression. This is accompanied by impaired motility of the gastrointestinal tract, more often this variant of infringement is observed in the elderly.
- mixed.
Infringement occurs due to the accumulation of feces or high load, these factors are combined, while only one of them could not lead to a complication due to minor severity. The condition is accompanied by all the typical signs of infringement.
- retrograde.
There is compression of several segments of the intestine at the same time, but one suffers the most, and it needs to be saved from inflammation and necrosis. It is rarely diagnosed, mainly with giant hernias.
- parietal.
Infringement of a part of the intestinal loop, which happens when it is not completely passed through the hernial ring. It ends with necrosis, but intestinal obstruction is rare.
What is dangerous infringement
A patient with a strangulated hernia of the abdomen should immediately be hospitalized. As soon as the organs are compressed, irreversible processes begin, it is dangerous to delay the operation.
Attempts to correct a complicated hernia will never give the desired result, on the contrary, they will only aggravate an already serious condition. The hernial sac may rupture, then there are signs of peritonitis or "acute abdomen": the abdominal cavity is solid, increases in volume. The patient is in severe pain.
A strangulated hernia of the abdomen leads to the following consequences:
- Necrosis - the death of organs in the hernial sac. This is due to a violation of blood flow and lymph outflow. First, the mucous membrane dies, then the process passes to the muscle layer, which will no longer allow the organ to be preserved.
- Phlegmon - develops due to necrosis, but not only. The patient's condition worsens greatly, the process of digestion is disturbed, signs of intoxication appear. The inflammatory process spreads to the surrounding tissues.
- Peritonitis is an acute disorder in which the peritoneum becomes inflamed. The condition is extremely serious, the purpose of emergency care will be to save the patient's life, which is not always possible, even with timely treatment.
How is it diagnosed
Pinching is determined by the doctor already during an external examination of the patient and palpation of the abdominal cavity. The main diagnostic signs will be the hardness of the protrusion, the impossibility of reduction, the absence of a cough shock.
Additionally, the method of radiography and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is used. After the examination, the surgeon decides on an emergency operation. After the main treatment, conservative therapy is carried out to normalize the patient's condition, prevent relapse and postoperative (ventral) hernia.
Treatment Methods
After examination and confirmation of infringement, the patient is hospitalized in the surgical department. The type of operation and the likelihood of complications depend on how quickly the patient gets to the doctor.
Preparation for the operation is going quickly. An anesthesia option is selected, then a catheter is placed and the stomach is washed. Emergency surgery is performed using epidural anesthesia.
Operation
Surgical treatment for a strangulated hernia consists of the following steps:
- Skin incision.
- Layer-by-layer dissection of tissues to create access to the hernial sac.
- Opening of a hernia, removal of fluid.
- Dissection of the hernial ring.
- Determination of organ viability.
- Resection of the damaged part of the intestine.
- Hernioplasty with implant placement or tissue tension.
Rehabilitation
After the operation, the pain syndrome worries for some time, therefore, painkillers and injections are prescribed. When the treatment went without complications, the patient is discharged from the hospital for 3-5 days. The doctor prescribes drug therapy, wearing a bandage, rest and diet.
The early recovery period includes the following activities:
- taking painkillers and antibiotics in case of complications;
- bed rest, any movements are allowed only in a bandage;
- exclusion of stress on the abdominal muscles;
- prevention of constipation and bloating;
- dieting;
- taking fortifying agents, immunomodulators, vitamins.
Postoperative bandage will be an important measure after surgical treatment. Carrying out an emergency operation increases the risk of a recurrence of the disease, and this can be prevented by creating conditions for a uniform load on the muscles of different groups.
The bandage is a temporary measure, and after the wound has healed and the body's strength has been restored, it is necessary to get away from it and work on strengthening the abdominal muscles, which will serve as a supporting corset throughout life.
Recurrence of abdominal hernia
The reasons for the re-development of the disease will be medical errors and non-compliance with the regimen after surgery. Regardless of the factor, the treatment of recurrent disease will be performed surgically. It also happens that one patient in a lifetime can undergo several operations, which is associated with a frequently recurring hernia. And after any surgical technique there is a risk of infringement.
What affects the development of a hernia after surgery:
- non-compliance with the rest mode;
- diet violation;
- quick return to physical work;
- refusal to wear a bandage;
- selection of an inappropriate surgical technique;
- congenital muscle weakness that cannot be corrected surgically.
In order to prevent relapse, it will be good to do therapeutic exercises, and in the future, sign up for a gym and perform exercises on the muscles of the press, legs and back regularly. Excess weight also contributes to the protrusion of organs and weakness of the ligaments, this must be taken care of by reviewing the diet and lifestyle.
After surgery, many need to get rid of bad habits that contribute to muscle wear and tear and premature aging. This applies to smoking, alcohol, physical inactivity. Systemic diseases are also important, which are accompanied by cough, indigestion. These factors contribute to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which as a result leads to a recurrence of the disease.