Signs and treatment of a sliding hernia of the esophagus
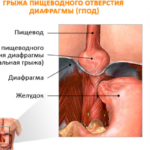
A sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm is characterized by the free movement of the abdominal organs into the chest and back. This phenomenon occurs due to the weakness of the diaphragmatic ligament, which is aggravated by the presence of an inflammatory process of the esophagus or its congenital anomalies.
In another way, pathology is defined as a hiatal hernia, cardiac or axial, and its clinic largely depends on the severity of the pathological process.
The main symptom of a sliding hernia is dyspepsia. The patient has frequent heartburn, belching of sour contents, hiccups. These conditions indicate damage to the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube due to the reflux of acidic contents from the stomach.
So what is a sliding hernia? This is the pathological movement of the abdominal organs through the esophagus into the chest. This condition is not dangerous, and practically does not affect the quality of life, unless the patient adequately assesses the potential risk and takes measures to prevent complications.
General characteristics of a sliding HH
Sliding hernia of the esophagus is mostly asymptomatic, which complicates the diagnosis. 75% of patients have no symptoms and treatment is therefore not carried out for a long time. Ignoring the problem leads to the fact that the hernia progresses, and more and more of the stomach penetrates through the diaphragm.
The main cause of the disease is muscle weakness.
But one factor alone is not enough for the appearance of the disease. The combination of the pathology of the musculoskeletal apparatus with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure is more likely to lead to a hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
Violation of the function of the slipped organ does not occur immediately. The consequences of pathology occur as the disease progresses. Uncomplicated sliding hernia of the esophagus of the first and second degree requires only dietary nutrition and medication. At the third stage, a specific treatment is already selected. An axial hiatal hernia of the fourth degree will require surgical treatment to restore the anatomy of the abdominal organs.
Etiology of the disease
Causes of hiatal hernia:
- Congenital anomalies of development . This applies to the period of lowering the stomach into the abdominal cavity. The process may be disturbed, which will cause the appearance of a congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Such a disease requires a surgical operation as soon as possible, otherwise there is a risk of death within a few days after birth. Hiatal hernia in newborns can be removed on the first day, but the operation during pregnancy will be even more effective, then the prognosis is more favorable if only the child undergoes normal rehabilitation in a specialized center.
- Underdevelopment of the muscles of the diaphragm . This phenomenon is associated with the physiological aging of the body, therefore it is almost impossible to avoid such a factor. This phenomenon can be prevented only by following the general prevention of pathologies of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus, which includes physiotherapy exercises, dietary nutrition, and the exclusion of bad habits.
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure . This factor is associated with frequent constipation, bloating, overeating, overweight, pregnancy. You can avoid this if you treat gastrointestinal pathologies in a timely manner, cope with excess weight, and use a special support belt during pregnancy.
Clinical manifestations of pathology will depend on the stage of formation of diaphragmatic hernia. At grade 1, there is a slight displacement of the abdominal part of the esophagus through the enlarged opening of the diaphragm, while the stomach remains in its place. At stage 2 of the pathological process, the cardia of the stomach is mixed, which is located at the level of the diaphragm. In the third stage, the body of the stomach is located above the diaphragm.
At the last stage of the formation of a hernia in the chest area, there is a large part of the stomach or the entire organ. In this case, it is necessary to treat the disease not only with conservative methods, but also with surgical intervention.
Without surgery, a severe course of pathology threatens with compression of the stomach with its subsequent death.
How HH manifests itself
The main clinical manifestations of a sliding hernia of the diaphragm:
- dyspepsia. This is heartburn, hiccups, belching. Symptoms increase especially after eating, and when the patient assumes a horizontal position after filling the stomach. Such manifestations can also occur for no apparent reason, for example, at night and in the morning.
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing. Such a phenomenon with a hernia of the esophagus will be more psychological, because while swallowing food, the patient may feel discomfort and pain associated with inflammation of the esophagus, which causes a fear of a repetition of unpleasant sensations. From this, eating begins to be accompanied by a lack of a swallowing reflex. The patient switches to the use of exclusively liquid and semi-liquid food. This, in turn, leads to weight loss. In this regard, the patient is shown a therapeutic diet.
- Frequent pathologies of the respiratory system . Bronchitis, aspiration pneumonia appear as a result of particles of poorly chewed food entering the respiratory tract. This threatens with purulent pneumonia and chronic respiratory diseases, which only aggravate the already serious condition of the patient.
- Regulation . This phenomenon is associated with the reverse reflux of the contents of the stomach into the oral cavity. Prolonged exposure to gastric acid leads to dental diseases. A patient with a hernia of the esophagus is faced with increased sensitivity of the enamel, papillitis, various stomatitis and gingivitis. Treatment of a local problem in the oral cavity does not lead to positive results, and until the main problem is eliminated, dental pathologies will only progress, and constant irritation of the mucous membrane can result in precancerous conditions and even oncology.
Diagnosis of a hernia of the esophageal opening is carried out by endoscopic examination.
Additionally, the patient is assigned laboratory tests to detect or exclude the inflammatory process. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is also shown, that is, a study of the state of the gastric mucosa. The introduction of the probe will not be the most pleasant procedure for the patient, but only in this way can many associated problems be detected that need to be dealt with in parallel.
Principles of treatment
With a hernia of the esophagus, it will be extremely important to comply with dietary nutrition, which should become part of not only treatment in the acute period, but also the prevention of complications and relapse throughout life. Additional measures will be therapeutic exercises, swimming, taking medicines.
The patient must undergo a course of treatment with a gastroenterologist to prevent such a frequent hernia companion as reflux esophagitis.
The latter is manifested by the release of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus, which leads to inflammatory processes and the addition of a complex of disorders. An additional symptomatic complex in esophagitis requires separate treatment.
In order to eliminate reflux without surgery, the following means are used:
- Antacids . Shown to reduce the negative impact of acidic contents on the walls of the esophagus.
- enveloping . They are used to eliminate irritation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus.
- Antispasmodic drugs. They are prescribed by a doctor when a sliding diaphragmatic hernia is accompanied by a peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
- De-Nol. It is indicated for inflammatory and ulcerative diseases of the gastric mucosa and esophageal tube.
- Motilium . It is prescribed to improve the processes of digestion.
- proton pump inhibitors . They inhibit the synthesis of hydrochloric acid, thereby reducing its irritating effect on the walls of the esophagus and stomach.
Surgical treatment of a sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm is prescribed by the attending physician in the case when the organs in the diaphragm area are infringed.
Other complications of the pathological process are internal bleeding and stenosis, that is, narrowing of the esophageal tube. During the operation, the diaphragmatic ligament is strengthened, and a special tube can be additionally installed, which artificially expands the esophagus, eliminating stenosis. After the operation, a long period of rehabilitation begins. It includes adherence to a diet, the exclusion of physical activity, the implementation of a set of therapeutic exercises.