Factors of occurrence, symptoms and treatment of scrotal hernia
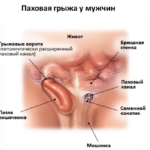
A scrotal hernia is said to be when some of the internal organs go out of their normal anatomical position and protrude into the scrotal cavity. This disease occurs only in men. The most common patient age is 50-55 years. However, scrotal hernia can also be found in children. Among the organs that go beyond their limits, the sections of the intestinal tract, omentums or the bladder are most often encountered.
The process of hernia development and causes
During normal development in male fetuses, the testicles mature in the abdomen. When the fetus reaches five months of age, the testicles increase in size and gradually descend towards the entrance to the inguinal canal. Having reached seven months of life in fetal development, the boy's testicles begin to move along the canal, and the vaginal process forms along its course. Before birth, the testicles enter the scrotum cavity completely. Thus, a certain communication with the abdominal cavity is preserved.
At birth, this canal normally closes and overgrows. But with defective maturation, the entrance to the abdominal cavity may remain open. Such a phenomenon in the future may serve as the development of a hernia in the scrotum. This is the boy's genetic predisposition to the development of pathology . There is another class of causes - acquired scrotal hernia.
The following factors influence the occurrence:
- weakness of the abdominal muscles;
- overweight , which increases the load on the abdominal organs;
- acquired injuries in the groin or abdomen;
- drastic weight loss . The fat layer is one of the factors that acts as a corset of internal organs. With the disappearance of fatty support in the abdominal cavity, an excess space is formed where organs can fall;
- long-term sedentary lifestyle , in which the muscles without a long load lose their tone and weaken. As a result, the failure of the abdominal muscles to resist pressure;
- strong physical activityleading to an increase in pressure inside the abdomen;
- chronic cough , loading weakened places on the abdominal wall.
- digestive disorders (constipation), leading to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
The inguinal canal normally contains some vessels and the spermatic cord. However, with a weakening of a number of muscles and damage to the connective tissue, as a result of influencing causes, the internal organs can go beyond their borders and descend through the inguinal canal into the scrotum.
Varieties of scrotal hernias
There are the following subspecies of hernias on the scrotum:
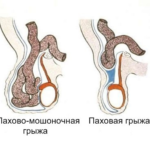
- Cord is a variety that is characterized by the lowering of the hernial sac to the spermatic cord.
- Inguinal-scrotal - a hernia descends to the line of the testicles.
Clinical stages of scrotal hernia formation
It should be emphasized that a hernia does not immediately appear in the scrotum, but goes through a series of transformations and stages before reaching its final destination.
Clinical stages of scrotal hernia formation:
- Minor changes in the position of the scrotum. Outwardly, there is a slight protrusion in the groin area.
- The appearance of pain in the scrotum . At this stage, pain does not extend beyond the groin.
- Stage of clinical development . This stage is characterized by severe symptoms.
- Enlargement in the groin of the lymph nodes.
hernia symptoms
Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the stage of formation and duration of the disease.
However, a herniated scrotum has a number of "recognizable" symptoms:
- Pain sensations appear both when the scrotum is loaded , and when it is calm.
- The pain is aggravated by touching the injured area.
- The pain syndrome can suddenly go away on its own.
- external deformation . There is asymmetry and elongation of the scrotum. The sizes can be different: from the volume of an acorn, to the size of a melon. Medicine knows cases when patients came with a scrotum the size of several soccer balls.
- General symptoms : fever, fatigue, irritability, decreased performance.
A complication of a hernia can be its pinching.
In this case, a few more symptoms are added:
- Deterioration of the patency of feces along the intestinal tract against the background of pinching of several sections of the colon. To this is also added difficulty in the emission of gases or their complete absence, resulting in flatulence - a pathological accumulation of gases and bloating.
- The chair can accumulate in the hernial sac , which is located in the scrotum. Then it becomes even larger in size.
- Nausea and vomiting of intestinal contents.
How the disease is diagnosed
A hernia on the scrotum has a number of similarities with other diseases. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must assess the patient's condition in general, examine the scrotum and prescribe additional studies.
Objective examination, which will be carried out by a specialist:
- examination and study of the scrotum , namely: its size, the presence of asymmetry, skin color changes and the height of the omission;
- by palpation, the doctor evaluates the content of the hernial sac , its condition, the likelihood of reduction;
- with the help of auscultation, the doctor receives additional information , such as: the presence of sounds of peristalsis (wave-like movements of the intestine), grumbling and movement of gases.
- may indicate a pinched or not pinched hernia . If it is positive, the hernia does not have pinching, and vice versa: if pinched, the symptom will be negative.
It is appropriate to conduct additional instrumental research methods:
- Ultrasound of the scrotum.
- contrast radiography of the abdominal organs. The method provides information about the presence of intestinal loops of the large or small intestine in the hernial sac.
- For differential diagnosis, physicians can sometimes use the sac puncture . This is done in order to remove or confirm suspicions of a cyst of the spermatic cord.
Scrotal hernia in children
Such a pathology in most cases occurs in premature babies (up to 30% of all cases) together with other congenital ailments of the musculoskeletal system, including congenital dislocation of the hip or hernia of the spinal cord. The reason for this high percentage is the fact that intrauterine development ends before the boy's testicles have time to sink into their natural position.
The clinical picture of scrotal hernia in children does not differ from that in adults. Most of the symptoms also accompany young patients.
In the future, the diagnosis of such an ailment as a hernia in newborns does not cause difficulties for the doctor, since the pathological protrusion becomes noticeable immediately after the birth of the baby. In addition, the child constantly screams and coughs, which further contributes to the protrusion of the internal organs into the scrotal cavity.
Treatment
Despite the stage of hernia formation, the presence of complications or the infringement factor, the patient will be recommended surgical intervention. Treatment without surgery has a high risk of recurrence in the future. Before surgeons begin surgery, the patient must undergo preparations.
It consists of the following activities:
- Use of a cleansing enema before surgery in the morning.
- Do not eat the day before.
- Introduction of antibiotics. This measure involves the prevention of further bacterial complications.
- Tight bandaging of the legs, if the patient has pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- Emptying the bladder by inserting a catheter.
The course of the operation is classic and the most common for a hernia of this localization:
- Incision and dissection of the tissues surrounding the hernial sac.
- External assessment of the contents in the bag. The doctor conducts an audit.
- Removal of bag tissue. The internal organs that were previously there are set back.
- Carrying out plastics of dissected tissues and the inguinal canal itself, preventing re-protrusion.
Postoperative period
In the first 10 days, the patient should be under the attention of doctors. The patient is advised to wear a bandage belt and avoid any load. Also, experts recommend wearing elastic underwear that supports the scrotum in the correct position. Medical treatment is indicated if there is pain or wound infection after surgery. Then doctors prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics and painkillers.
Consequences
A neglected scrotal hernia in men can give a number of complications.
Among the main ones are:
- Acute intestinal obstruction . This condition develops due to pinching of the intestinal sections in the hernial sac. Pathology is manifested by pain and swelling in the abdomen, vomiting.
- Peritonitis.
- Erectile dysfunction, possibly infertility, decreased libido.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable both for life and for productive professional activity. However, in the future, a man needs to observe the restriction of strong physical exertion on the abdominal muscles.
If left untreated, there is a high risk of complications. In this case, the prognosis for life is conditionally favorable, for professional activity - unfavorable.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of a scrotal hernia, a man should follow a number of measures, including:
- weight control : sudden jumps in body weight adversely affect the condition of internal organs and muscles;
- dosed physical activity;
- regular scheduled check-ups with doctors.