Features of an inguinal hernia in a child
When the contents of the peritoneum exit through the inguinal opening, an inguinal hernia is formed in children, the walls of this formation consist of a parietal sheet of the peritoneum. According to statistics, in boys, a protrusion in the groin area occurs several times more often than in girls. The appearance of a hernia is due to the peculiarities of the development of the male embryo in the womb. Often this ailment is accompanied by other pathological conditions (dropsy of the testicle, anomalies in the development of the hip joint and spine, Marfan's syndrome).
The main mechanism and causes of hernia
The mechanism of formation in the inguinal region of weakness of the ring, followed by the formation of a protrusion in boys, mainly consists in a violation of the obliterating processes of the process of the peritoneum. Normally, after the descent of the testicles into the scrotum, which occurs in utero, the vaginal process overgrows. If this does not happen, then it begins to act as a hernial sac, into which, with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the intestine falls out and other organs suffer.
At the moment, all causes of inguinal hernia in children . At an early age, the etiology of the disease is often based on congenital abnormalities, and studies confirm that the tendency to develop a protrusion in a quarter of cases is hereditary.
In this case, the sick baby is found:
- insufficient infection of the vaginal process of the peritoneum;
- anatomical and physiological insufficiency of the hole;
- other defects in the structures that form the inguinal canal.
There are also predisposing factors that lead to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity , and this phenomenon, against the background of other abnormalities, increases the likelihood that an inguinal hernia occurs in a child:
- constant crying and screaming;
- colds and respiratory diseases with frequent coughing;
- vomiting of any genesis (disturbance in the work of the digestive organs, poisoning, high cranial pressure);
- frequent constipation or diarrhea;
- prematurity (the frequency of hernia in such babies increases by 15%);
- urination disorders, leading to the need to constantly strain to empty the bladder.
In older children, an acquired hernia may form in the groin as a result of a lack of physical activity, as well as metabolic disorders leading to a sharp decrease or increase in weight. Often, a traumatic injury to the anterior wall of the abdomen can become a provoking factor, as a result of which the integrity of the tissues of the muscles and ligamentous apparatus is violated. Often there is a problem as a result of lifting heavy objects or being too active in the weightlifting section.
Types and manifestations
Manifestations of children's inguinal hernia are not specific, but they require the close attention of parents. Congenital deviation becomes noticeable immediately.
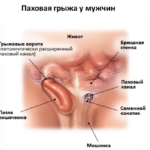
If we talk about what an inguinal hernia looks like, then it is a protruding round or oval subcutaneous formation , which increases with coughing, sneezing, straining.
At first, in a horizontal position and at rest, it passes, and increases during a stay in an upright position.
Signs of a hernia are that the baby becomes restless, often crying, especially if you press on it. Older children note soreness in the area of the protrusion, extending to the inner part of the thigh.
By their variety, the vast majority of congenital hernias are oblique, and come to the surface through the internal inguinal ring. Quite rarely, a direct hernia appears in childhood, the formation of which results from a weakening of the muscles of the abdominal wall, while the sac with contents comes out of the outer ring.
Inguinal hernia in children is unilateral (left- or right-sided), or bilateral. In boys, the vast majority of hernias are formed on the right side. And in girls, this pathology occurs with approximately the same frequency.
In boys, such varieties of the disease as inguinal-scrotal hernia can occur, and it is divided into funicular and testicular. On examination, the patient noted an asymmetric enlargement of the scrotum. In girls, the hernia can descend into the labia, while it increases in size and becomes painful.
Features of manifestation in case of infringement
The most dangerous complication of an inguinal hernia is its infringement. This phenomenon is considered an acute condition and requires immediate hospitalization. Compression leads to a violation of blood circulation, while the following symptoms are noted:
- Soreness, which was previously temporary, sharply increases, becomes unbearable;
- Indigestion develops in the intestines due to a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure. There is constipation and bloating. In severe cases, there are all signs of intestinal obstruction with vomiting, intoxication and severe flatulence;
- The hernia becomes irreducible, and in the absence of immediate help, necrosis and peritonitis develop .
Since in girls in the hernial sac during infringement, ovarian atrophy occurs, and in boys, the activity of the testicle from the side of the hernia is disrupted, it can be said that infringement can lead to impaired reproductive function. Such an outcome is possible in approximately 5% of all cases of such complications.
How is the diagnosis carried out
In order to detect a hernia in the groin of a child, it should be shown to a specialist. It could be a pediatrician or pediatric surgeon. Often it is discovered during a routine routine examination. To clarify the diagnosis, an older child is asked to strain, cough or walk. In the absence of complications, this formation is soft to the touch and elastic. In the supine position, it can be easily reduced, after which it is possible to clearly determine the expansion of the inguinal ring.
An ultrasound of the inguinal hernia plays a significant role. Using this research technique, it is possible to determine the presence of an intestinal loop and other organs inside the hernial sac. It allows you to assess the blood supply and find out the degree of probability of developing necrosis, as well as to conduct a differential diagnosis with similar pathological conditions (for example, with dropsy of the testicle).
But of particular importance is the study using ultrasound, when the disease occurs in a latent form, and the hernia has no content. In this case, it is difficult to detect a hernia in a child in other ways.
On ultrasound, a strip with an echo-negative characteristic is visualized in the inguinal canal, and it increases when the baby cries or strains.
In this case, one can see that one end of the formation passes freely into the abdominal cavity, and on the other hand ends blindly in the canal region or in the scrotum.
Modern methods of treatment
Before determining what treatment is needed when a protrusion is found in the inguinal region, it is necessary to understand whether the hernia can go away on its own. For small children with a slight protrusion, it is recommended to carry out preventive measures. According to doctors, before the age of five, in 4% of children, the disease resolves on its own.
Conservative treatment should be carried out immediately, from the very birth of the baby, as soon as the slightest swelling appears. With a neglected, strangulated congenital hernia, the only way to solve the problem is to perform surgery. No other methods, including wearing a special bandage for a child, can guarantee that there will be no recurrence of the disease or infringement.
How to determine at what age a child needs to have surgery? At the moment, experts recommend doing this as early as possible - starting from the age of six months. Such treatment is not indicated for premature and debilitated children. Such a swelling cannot pass by itself, and children are usually given massive antispasmodic therapy and then the hernia is reduced. Then they are constantly monitored by a specialist.
conclusions
The appearance of a protrusion in the groin of a child or its detection immediately after birth should alert parents. This disease necessarily requires consultation of specialists, a full examination, and the adoption of adequate measures. An urgent operation is necessary if, against the background of a hernia, a deterioration in the condition, severe pain, and other signs of infringement appear.
Prevention of recurrence of the disease consists in protecting the child from physical overload, normalizing digestion (preventing constipation) and regular examination by the surgeon.