Treatment of inguinal hernia in boys
An inguinal hernia in children is a congenital disease in which the abdominal organs penetrate the inguinal canal, freely moving to their place at rest. This disease in a child does not threaten health and life, provided timely surgical treatment and prevention of postoperative complications.
Inguinal hernia in boys is diagnosed more often, a defect in the groin area is visible from birth. Outwardly, a hernia manifests itself in the form of a round or oval formation in the perineum, and such a type of pathology as an inguinal-scrotal hernia is characterized by an increase in one or two testicles. Signs of illness in infants are visible not only externally, the pathology affects the well-being of boys, because they behave restlessly, often cry, and sleep poorly.
In this case, the baby can be cured only surgically, otherwise there is a risk of infringement of the organs in the hernial sac, and this threatens with many complications, including infertility.
Why does a hernia occur in newborns
During fetal development in boys, the testicles descend into the groin from the abdominal cavity, during which the vaginal process is formed, through which the intestines, omentum or bladder will penetrate in the future. The very presence of the appendix cannot yet create the conditions for the appearance of a hernia, provoking factors associated with congenital anomalies and acquired conditions are needed.
Acquired inguinal hernia in newborn boys and its treatment is the task of several specialists and parents at the same time.
The child is monitored by a pediatrician, a pediatric surgeon and a urologist. And only the attending physician knows when it is necessary to perform the operation, and what methods of conservative therapy will help before and after hernia repair. It is not only the clinical picture and the results of studies that help to understand this, but also the cause of the disease, which can affect the condition of the baby for a long time.
What can cause an inguinal hernia in a newborn boy:
- anomalies in the formation of the inguinal fissure, which prevents the normal descent of the testicles;
- delay in the movement of the testicles in the thickness of the abdominal wall;
- birth trauma, damage to the abdominal cavity of the newborn;
- dysfunction of the connective tissue;
- genetic predisposition, inheritance of developmental anomalies.
Already after birth, an inguinal hernia in a child occurs due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which occurs during a hysterical cry, frequent crying and due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. These factors provoke the occurrence of a defect in both boys and girls.
How does an inguinal hernia manifest in boys
Symptoms of inguinal hernia in children are typical, external and general manifestations of an uncomplicated form of the disease are similar in all newborns. Outwardly visible swelling in the groin, it periodically decreases, increases and completely disappears. The protrusion is well manifested during tension, when the boy screams, actively moves his legs, cries.
The hernial sac has an elastic structure; when pressed, a gurgling sound can be heard. In the supine position, the swelling disappears altogether, while standing - it increases sharply.
With light pressure on the hernia, you can feel the expansion of the opening of the inguinal ring, while the protrusion is easily reduced into the peritoneum. In boys, the formation is more often oval in shape, in girls it is rounded.
A rumbling and gurgling sound when pressed is heard when there is a loop of intestine in the hernial sac. For a child, education is painless, it can cause only slight discomfort. If complications join, the symptoms increase, the child begins to be disturbed by severe pain.
Examination of the child
Before treating an inguinal hernia, the child undergoes a comprehensive examination. Diagnosis begins with an external examination. The surgeon sees a characteristic protrusion in the groin and the absence of signs of similar diseases. To confirm the diagnosis and choose the tactics of therapy, an ultrasound examination is performed. On the image, the doctor sees the contents of the hernia sac and the condition of the surrounding structures.
In the process of diagnosis, the doctor determines the form of the hernia, it can be:
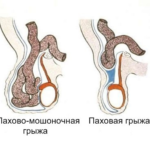
- inguinal - located in the region of the external opening of the inguinal canal;
- inguinal-scrotal - located near the testicle, affects the scrotum;
- cord - located in the scrotum above the testicles, near the spermatic cord;
- oblique - passes through the groin canal near the spermatic cord;
- direct - passes through the peritoneum without affecting the inguinal canal;
- combined - oblique and direct view, which arose independently of each other.
A special approach to the child is needed when identifying a strangulated hernia. This condition is life threatening and requires immediate surgery. Infringement is the clamping of organs in the region of the hernial ring or directly in the sac, which is accompanied by ischemia and death of the compressed tissues.
Characteristic signs of infringement of an inguinal hernia in girls and boys:
- strong pain;
- restlessness and crying of the boy;
- protrusion tension, the impossibility of its reduction;
- lack of stool;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pallor of the child, decreased activity.
Methods of treatment
Treatment of inguinal hernia in children is performed surgically. A planned operation is prescribed, and the baby is being prepared for hernia repair. Removing a hernia always has risks, but without treatment, the disease is even more dangerous.
The goals of treating a hernia in a newborn will be:
- elimination of unpleasant sensations - wearing a bandage, prevention of colic and bloating;
- prevention of infringement - exclusion of sudden movements, relaxing massage;
- normalization of blood circulation of the pelvic organs - exercise therapy, swimming;
- removal of a hernia - hernioplasty.
The optimal period for the operation is 6-12 months of the baby's life. Until this age, non-surgical techniques are used to prevent complications.
conservative methods
An integrated approach for a hernia in a boy includes the following activities:
- Wearing an inguinal bandage. Such a useful device is necessary before and after the operation in order to fix the hernia, which will prevent the progress of the disease. Properly selected bandage, taking into account age characteristics, will allow the child to safely perform various movements without the risk of infringement. But such a belt can do harm. If a groin bandage is used for a long time, this will lead to muscle weakness, aggravate the child's condition, and become a factor in relapse after surgery.
- Therapeutic exercise . A boy needs gymnastics with an inguinal hernia to strengthen the muscles of the inguinal canal. It is useful to work with a child in the pool, on a fitball and a regular changing table. Exercises are selected by the doctor, but usually these are simple rotations of the legs, turning the baby from back to side, “scissors” and others. You need to deal with the child when he is in good health.
- Massage . It is possible to perform massage with a hernia, but first you need to check with your doctor which movements are undesirable for the child. Massaging the tummy is also useful in case of digestive problems that often accompany a hernia.
Operation
Elective hernioplasty is the main treatment for inguinal hernia in boys. The operation lasts no more than 40 minutes, the duration and type of anesthesia will depend on the technique. Hernioplasty is performed by a closed or open method. In the first case, access to the hernia is created through small punctures of the abdominal wall, after which there are no wide scars.
An open operation involves a wide incision up to 10 cm, which allows you to quickly suture the defect, remove pathological tissues in a “manual” way. In the case of laparoscopy (closed method), the recovery of the child is faster, the operation has better cosmetic results, but this is a complex technique that requires high professionalism and does not forgive the mistakes of the surgeon.
When there are complications and conditions dangerous for the baby, only open hernioplasty is performed under general anesthesia.
Laparoscopic surgery is performed under video control and belongs to minimally invasive techniques. The risk of complications after such an operation is lower, because there is minimal tissue injury.
Postoperative recovery
Rehabilitation after hernia repair in children is stable, due to the rapid development and active formation of new tissues. In the early period, wearing an inguinal bandage, a special diet are prescribed, overloads are excluded. A few weeks after the operation with the child, you can start doing therapeutic exercises, visit a masseur, swim in the pool.
The main goal of rehabilitation is to eliminate risk factors that can lead to relapse and complications.
Complications after hernioplasty can manifest themselves in the form of such conditions:
- high testicular fixation;
- suppuration of the postoperative wound;
- bleeding and extensive hematoma;
- pain syndrome;
- inflammation of the epididymis;
- lymphocele, testicular atrophy.
Relapse and its prevention
Repeated inguinal hernia often occurs after tension plasty against the background of congenital muscle weakness. High physical exertion, non-compliance with the postoperative regimen, suppuration of the suture, constipation, and accidental injuries can provoke a relapse. To avoid this, proper preparation for the operation is important.
A planned operation with preliminary sanitation of the body is the key to the boy's recovery. The hernial formation must be removed, and the organs returned to their place, and then it is already possible to provide the correct regimen for the baby to feel normal and live without the risk of serious complications.