Causes and treatments for inguinal hernia in boys
Inguinal hernia in boys is a common disease in young children under three years of age. This pathology often has a congenital nature of the acquisition, but there are also hernias in the groin and acquired ones. Newborns may be born with an existing hernia, but this is more common in premature babies.
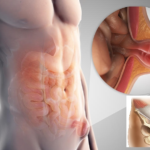
The hernia itself is the exit of the internal organs of the abdomen wrapped in the abdominal sheet through the inguinal ring into the region of the groin itself. Mostly this pathology occurs in boys, but girls also suffer, albeit much less frequently. The high incidence of inguinal hernia in boys is explained by the anatomical features of the male body.
How and why the formation of a protrusion occurs
During the first few months of fetal development, the testicles are located in the peritoneal cavity. During the maturation of the fetus, the testicles descend into the lower abdomen and pass through the ring located between the peritoneum and groin. Closer to birth, the normal testicles of the fetus descend completely into the scrotum and remain there until the end of life.
However, there is one significant nuance: the testicles, descending to their final destination, pull part of the peritoneum along the inguinal canal. Thus, a small anatomical pocket is formed, which is called the vaginal process.
In the course of normal development, the latter should completely overgrow, but due to a number of reasons this may not happen, and the internal organs of the peritoneum may descend after the testicles.
However, it should be remembered that this canal sometimes does not completely overgrow, and during life, against the background of provoking factors, the abdominal organs can easily enter the scrotal cavity. Pathology with this development option is called an oblique hernia. It got its name due to its oblique position. There is another version of the children's inguinal hernia, in which the protrusion passes through the walls of the abdomen itself, without affecting the inguinal canal.
In girls, bulging in this area occurs 20 times less than in boys. This is also due to the anatomical features of the female body. Girls do not have testicles, and the ovaries from the beginning of the formation of the fetus according to the female type remain lying in the pelvic area. That is, in the course of development, girls do not have something that could pull a sheet of peritoneum along with it. Another protective factor is that in girls, the uterine ligament is located in the inguinal canal, which strengthens the passage itself.
Not always inguinal hernia is congenital. Older boys also suffer from this disease.
Causes that provoke the development of an acquired hernia in the groin:
- operations;
- injuries such as blows, falls on the stomach or groin;
- diseases of internal organs, namely the organs of the digestive tract;
- respiratory diseases, accompanied by a constant strong cough;
- excess body weight;
- lifting large weights, leading to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
The risk group includes those boys who, according to their constitution, are weak and "frail" from birth. Their restraining intra-abdominal pressure factors are not able to compensate for the exerted load. It often happens that parents send their child to sports sections where strength and endurance are required, without being aware of the consequences.
Varieties of hernias
Pathological protrusions are different in origin, structure and course.
Kinds:
- Congenital - these are those hernias that formed during the period of intrauterine development.
- Acquired - hernias that have formed throughout life due to a number of reasons that contribute to the weakening of the abdominal muscles.
- Combined - these are bulges that have in their structure several hernial sacs with different organs.
- Complicated and uncomplicated.
- Reducible - those hernias that can disappear on their own for a short period.
- Irreducible . They are not eliminated without the intervention of medical personnel and treatment. Such hernias are usually fused, that is, the contents of the hernia are connected to the inner side of the wall of the hernial sac.
- Depending on the side of the location : right-handed, left-handed or double-sided.
Congenital inguinal hernia and its symptoms
A hernia, like any disease, is manifested by general and specific symptoms. The first group of signs is determined by the body's response to the onset of the disease.
These include:
- malaise;
- increase in body temperature;
- headache;
- irritability;
- the child often cries and is disturbed for no apparent reason.
What does a hernia in the groin look like? A small tumor-like formation of an elastic consistency appears in the groin area. Outwardly, it may resemble a small bump protruding from the skin. Education in shape can be round and oval.
The second group of signs is determined by the local effect of the hernia on neighboring organs and surrounding tissues.
Specific symptoms include:
- protrusion on average up to 10 cm;
- disorders of the digestive tract: constipation, bloating, impaired gas emission, belching and bad breath;
- severe pain in the groin or scrotum; pains in this case are aching in nature;
- outwardly, there is swelling in the scrotum, and this part of the body can greatly increase in size;
- if the child is older, he may complain of a burning sensation in the lower abdomen;
- difficult urination;
It is important to remember that the protrusion can disappear on its own. In addition, a hernia at the first time of its development often does not have a pronounced clinical picture.
Features of diagnostics
The study of the disease involves an assessment of the general condition of the boy, the specifics of the hernia, its size, position. To do this, the doctor may prescribe a number of instrumental research methods.
Among them are the main ways:
- Ultrasound diagnostics , which can give accurate information about the contents of the hernial sac, its location and the state of the entrance gate;
- Gastroduodenoscopy is a method that allows you to assess the condition of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. In this case, this allows us to study the involvement of these organs in the pathological process.
Also, the diagnosis of the disease implies differentiation with pathologies that have a similar clinical picture.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with such ailments:
- dropsy of the ovaries;
- cryptorchidism.
Treatment
This type of hernia is subject to surgical treatment. Conservative therapy in this case does not prevent a number of complications that may occur after treatment in a hospital. The main method of surgical intervention is called hernia repair.
The surgical process consists of several stages:
- The introduction of general anesthesia and the introduction of the child into a state of sleep.
- A small incision of 3 cm is made, thus opening up access to the hernial sac.
- The latter is amenable to study and evaluation. Its content is being explored.
- The organs in the bag are subject to reduction towards their normal location.
- A section of excess tissue is made and the bag itself is removed.
- Suturing and fixing the peritoneum.
In the usual case, this operation does not cause difficulties for surgeons and it is performed within no more than half an hour.
However, there is always a risk of surgical complications:
- wound infection;
- trauma to the testicle or surrounding structures (arteries, veins);
- recurrence, in which case a second operation is required.
Recurrence is a common occurrence in hernia surgery. The recurrence of pathology is due to several reasons.
Relapse factors:
- errors in the process of intervention;
- background bowel diseases, accompanied by excessive gas formation;
- strong physical activity in the first time after surgery.
The postoperative period involves active management of the patient. The boy is being carefully cared for.
Also at this stage, lifestyle correction is carried out:
- Exclusion of certain foods that can lead to disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Avoiding all physical activity.
Despite the fact that the next day the child will feel significant relief, these restrictions should not be overlooked.
The prognosis for the boy's life is favorable.
It is important to remember that insufficient attention given to a hernia in a child can lead to a complication of the disease. The consequences include infringement - a sudden rapid compression of the organs in the hernial sac.