How is an inguinal hernia removed in women
Inguinal hernia in women is extremely rare, and it is a more male disease that occurs due to muscle weakness and congenital anomalies of the inguinal canal. In young girls and women, this disease is associated with acquired conditions, namely increased intra-abdominal pressure, overweight, gestation, and hard physical work.
Removal of an inguinal hernia in women is always carried out, because the protrusion of such localization in adult patients is never reduced on its own. The operation involves the restoration of the anatomy of the inguinal canal and abdominal cavity and the removal of the hernial sac, followed by plasty with own tissues or mesh implants.
Rehabilitation after surgery includes a number of conservative measures that are aimed at eliminating constipation, bloating and weight gain.
Given that the main cause of the disease in women will be muscle divergence and weakness, a set of exercises will be prescribed during the rehabilitation period, aimed at strengthening the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
The course of an inguinal hernia
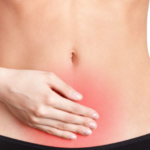
Inguinal hernia is easy to recognize, it has specific manifestations in women, depending on the form and stage of the course. Protrusions lasting more than six months have pronounced clinical manifestations, which is due to a violation of the function of the internal organs located in the hernial sac. In the latter, the omentum and intestinal loops are more often found.
Less commonly, the uterine appendages, the uterus itself and the bladder enter the hernial sac, and with giant hernias, all abdominal organs can also penetrate through the groin canal.
A typical symptomatic complex with a hernia in the groin in women :
- slight soreness during tension of the abdominal muscles;
- discomfort while walking;
- increased symptoms when straining and lifting weights;
- outwardly visible round or oval formation;
- the protrusion recovers into place with a slight pressure;
- periodically there is pain in the lower abdomen;
- the menstrual cycle is disturbed, it becomes more painful;
- less often nausea, vomiting;
- there are problems with bowel movements.
With a complicated course of a hernia, the symptomatic complex is supplemented by an increase in body temperature, general malaise, and pallor of the skin.
If the hernia is incarcerated, this will be indicated by the absence of a cough shock. During coughing and muscle tension, the hernia does not enlarge and does not move, as it always did before. When such a condition is observed, an operation is urgently prescribed and the inguinal hernia in women is immediately removed with an examination and sanitation of the internal organs.
What is dangerous hernia for women
An operation to remove an inguinal hernia in women is needed to prevent complications of this disease. Surgery considers several major conditions that will be mandatory indications for urgent hernia repair.
remove a hernia due to the risk of such conditions :
- stagnation of feces in the large intestine, coprostasis and intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis, inflammation of the abdominal cavity due to violation of the integrity of the organ;
- infringement of a hernia is a frequent consequence of protrusion of organs, threatens with a fatal outcome, proceeds with inflammation of the organs located in the hernial sac.
Therapeutic measures aimed at preventing pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory organs can reduce the risks before surgery. For this purpose, medicines, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, it is permissible to use traditional medicine methods as an auxiliary measure to reduce the severity of symptoms.
Treatment methods
The main way to treat a hernia in the groin in women is removal by open or laparoscopic hernioplasty. This operation can be performed with the tension of the patient's tissues and the installation of a mesh implant. The first method consists in the layer-by-layer imposition of muscles on top of each other to close the defect in the inguinal canal. Tension-free hernioplasty involves the installation of a mesh implant as a reliable protection against prolapse of organs in the early and late period after surgery.
Tension hernioplasty is performed as follows:
- Two incisions are made near the navel.
- Instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity.
- The hernial sac is cut off, the organs are returned to their place.
- A mesh is installed, which is held by internal pressure.
Tension plastic has more disadvantages, because after the operation there is always a possibility of a recurrence of the disease, and then the hernia repair will have to be repeated. During an open operation, internal organs can be injured, which will affect the duration of the patient's recovery period. On average, hernioplasty lasts 35-60 minutes.
Laparoscopic surgery is considered the least traumatic option for hernia repair. It is also recommended for women due to the good cosmetic effect.
Only small marks from three punctures remain on the stomach, which are easy to hide with cosmetics or completely removed with a laser. The advantage of laparoscopic surgery will be how long the recovery period after it lasts. The patient can go home already on the 2nd day after hernia repair, and after 3 days go outside, start doing their usual things.
Stitches after laparoscopy are removed on the 7th day, and for this period you need to exclude physical work and follow a diet. Such measures are necessary in order not to cause problems with digestion, because they lead to an increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity, and this already has a negative effect on the postoperative wound and the defect itself.
Surgery for a hernia in pregnant women is performed as a last resort according to strict indications, when there is a threat to the life of a woman. If the pathology occurs already during the gestation of the fetus, the expectant mother is prescribed an inguinal bandage, a special diet and a set of exercises.
The operation during pregnancy will be carried out with infringement and inflammation in the abdominal cavity. With a slight protrusion, a woman can give birth naturally, and a caesarean section will be indicated for a complicated pathology.
An inguinal hernia will disturb with soreness and discomfort while walking, so the woman will be prescribed weak painkillers and muscle relaxation exercises.
Contraindications
In the belt restrictions for hernia repair in women:
- acute inflammatory processes;
- recurrent infectious pathologies;
- decompensated diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- dermatological incurable diseases;
- malignant or benign neoplasm.
Rehabilitation
The early period of rehabilitation after removal of an inguinal hernia in women includes preventive and therapeutic measures aimed at the speedy healing of the surgical wound and improving the patient's well-being.
In the late period of recovery after hernioplasty, the restrictions are gentle. For the first 2-3 weeks, the patient follows a therapeutic diet No. 5. Nutrition after surgery should exclude conditions that lead to increased intra-abdominal pressure (constipation, bloating).
Delayed rehabilitation is a lifelong measure to prevent recurrence or development of ventral (postoperative) hernia.
Therapeutic exercise is prescribed from 3-4 weeks after the operation, and it includes a set of exercises to strengthen the muscles of the press, legs, buttocks and back. Gymnastics after hernia repair is also needed to eliminate muscle spasm, which causes constant pain.
How long does the rehabilitation after hernioplasty in women last:
- early period - the first 7 days;
- late period - 1-2 months;
- delayed period - throughout life.
The postoperative period is aimed at eliminating excess weight, eliminating bad habits, strengthening the muscle corset, and evenly distributing physical activity on all muscle groups.
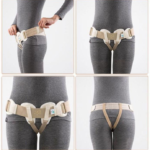
An inguinal bandage in the postoperative period is prescribed for women for the entire period of rehabilitation, because a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure can cause the development of re-protrusion in the groin or abdominal cavity.
Long-term use of the bandage will be an irrational solution, because it performs the function of a natural muscle corset, taking over the entire load. If the muscles are deprived of movement for a long time, this will cause them to atrophy, and then it will be difficult to do any work without a bandage.
Complications after surgery
Herniotomy in women can result in the following complications :
- damage to the bladder and bowel loops;
- thrombosis of the veins of the leg;
- recurrence of the disease immediately after surgery;
- postoperative abdominal hernia;
- dyspeptic phenomena;
- divergence of seams;
- the appearance of hematoma and seroma;
- damage to the hip joint;
- infection of the wound during or after surgery.
Prevention of complications
A frequent consequence of inguinal hernia surgery is the occurrence of a ventral protrusion on the abdominal wall. This complication is almost always combined with other consequences of hernia repair.
In order to prevent postoperative hernia, it is necessary to exclude the following conditions:
- suppuration of the wound due to infection during surgery or due to non-compliance with preventive measures by the patient after the intervention;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure with high load and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- scar disorder, muscle divergence.
Prevention after removal of an inguinal hernia in women includes:
- wearing a postoperative bandage;
- dieting;
- exclusion of physical activity the first month after surgery;
- timely treatment of pathology of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system;
- implementation of medical recommendations and compliance with the prescribed regimen.