Symptoms and methods of treatment of a hernia in the thoracic spine
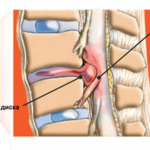
A hernia of the thoracic spine is a pathology that is defined as the protrusion of the intervertebral disc or part of it beyond the normal limits of the vertebral region. The problem of the disease lies in the fact that it is rather difficult to diagnose a hernia in the early stages of formation, since the disease disguises itself as many other diseases associated with the thoracic region.
This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the thoracic spinal cord has many nerve branches that go to the heart, lungs, and muscles.
So, the presence of an intervertebral hernia of the thoracic spine can mimic heart pain. Often patients with pain in the stomach can be taken for granted as gastritis or an ulcer, with pain in the heart - as angina pectoris or heart failure.
What is the hernia itself?
Normally, an intervertebral disc is located between the individual vertebrae, which performs the function of depreciation. The disc plays the role of a cushion, preventing the vertebrae from touching each other, thereby not causing damage to the bone tissue. However, due to various factors, one disc or a number of discs can be damaged, weakened and subsequently completely or partially lose their function.
Reasons for the formation of pathology
Medicine implements its set of knowledge in practice according to the principle of "cause and effect". So, every disease has its beginning.
There are the following reasons for the formation of a hernia:
- The first on the list and the most common cause is the presence of osteochondrosis. In most cases, a hernia of the thoracic spine is preceded by the development of dystrophic changes in the bone tissue of the spine. Already at the second stage of osteochondrosis, active deformation of the discs begins, then the formation of a small protrusion.
- Other infectious, hereditary, congenital, acquired diseases that destroy the bone tissue of the ridge.
- Traumatization of some elements of the back, spine, muscles or nerves.
- Transferred operations.
- Diseases characterized by hormonal changes. It is known that hormones control almost all processes in the body. So, in some diseases, the exchange of calcitriol, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, fluorine, substances that are actively involved in the formation of bone tissue, is disturbed.
- Uneven physical activity, artificially creating strong tension in the intervertebral region. Chronic participation in professional sports is one of the ways to earn a hernia.
- Excess weight. Overweight people are also prone to various hernias: a lot of weight creates strong pressure in some parts of the body, causing the vertebrae to move.
- Factors that indirectly provoke destructive processes in bone tissues:
- smoking, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- high growth;
- hypothermia;
- posture disorders: lordosis, kyphosis and scoliosis;
- a sedentary lifestyle, in which the muscle tissue of the back atrophies over time, weakens, and hardly performs the function of a muscular corset;
- pregnancy.
Signs of illness
A number of symptoms indicating the presence of a hernia in the thoracic region:
- Pain in the chest. The intensity of the pain syndrome depends on such parameters of the hernia: size, degree of displacement, degree of contact with the spinal cord. So, the larger the protrusion, the more pain the sick person will experience. In addition, pain may increase with physical exertion, while in a state of calm, discomfort in the back may disappear. Also, pain can appear when the body bends back or forward.
- Disorders of nerve activity : subjective sensations of crawling all over the body, unpleasant tingling, numbness of the muscles of the chest, muscles of the upper limbs, sometimes anesthesia can touch the upper abdomen.
- Over time, the muscles of the arms or chest weaken against the background of impaired innervation.
- With various complications, the clinical picture may show partial or complete paralysis below the level of the hernia . For example, if the bulge is located at the lower levels of the thoracic region, the lower limbs may completely lose their muscle strength. However, this phenomenon is extremely rare.
In addition to the general symptoms that are inherent in this pathology, there are separate ones for each level of the thoracic segment:
Level C7 - Th1 (between the last cervical and first chest):
- intense pain in the muscles of the neck;
- pain that resembles a heart attack or angina;
- the range of motor abilities of the hands is limited;
- paresthesia in the upper extremities.
Level Th2 - Th3:
- girdle spinal pain, sometimes radiating to the region of the heart;
- pain is aggravated when trying to touch the distant end of the chin to the chest - a specific symptom of Lasegue.
Th3-Th4:
- pain in the muscles of the back, aggravated by sneezing, coughing or strong laughter;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- ailments that mimic pleurisy, pneumonia or cardiac pathologies.
Th4 - Th7:
- intense pain in the chest;
- numbness;
- the respiratory act becomes difficult;
- symptoms masquerading as diseases of the digestive tract: burning in the esophagus, pain in the stomach.
Th7 - Th10:
- pain in the projection of the duodenum;
- urination disorders;
- pain in the kidney area.
Th11 - Th12:
- here the pains in the back take on a permanent character, they are aggravated by an attempt to diligently strain the muscles of the legs.
Diagnostics
An intervertebral hernia of the thoracic region is diagnosed by examining the life of the patient, questioning the details of the disease, examining its heredity. Then the doctor proceeds to an objective examination, where he studies the functionality of nervous activity, namely: tendon reflexes, sensation of pain, the ability of the skin to general sensitivity.
The next step for the patient is the passage of instrumental research methods that allow you to accurately look at the disease "from the inside".
These activities include:
- Radiography . This method does not allow you to study the hernia itself, but will give the doctor information about the degree of damage to the vertebrae and other adjacent structures.
- Magnetic resonance imaging . This is one of the most high-quality and informative methods in modern clinics. With the help of MRI, an accurate diagnosis of a hernia is carried out, its location, content and how formidable it is in prognostic terms are examined.
- Computed tomography . It is also a stable method, but inferior to MRI in its abilities.
- Myelography is a method that allows you to assess the patency of the spinal canal - the CSF pathways. It is also inferior to computer analogues of diagnostics, having a number of side effects.
Differential diagnosis is a method of qualitative difference between diseases. Due to the fact that the diseases of a certain group are similar to each other, doctors have to distinguish between them.
A hernia in the chest is differentiated with such diseases:
- angina pectoris - retrosternal pain, which manifests itself with mental stress, it is not associated with physical activity;
- gastritis, gastric or duodenal ulcer - pain in these ailments clearly communicate with meals;
- respiratory diseases - the latter have specific symptoms: productive cough with sputum, signs of intoxication.
Treatment
A hernia in the thoracic spine is treated in two traditional ways: surgery and conservative therapy.
Conservative therapy involves the following activities:
- Taking medication. These include: anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, corticosteroids, biostimulants and chondroprotectors. All these drugs relieve inflammation, suppress pain, relax muscles, activate regenerative abilities, restore cartilage tissue.
- Physiotherapy activities. This group includes manual therapy for hernia, exercise therapy, massage sessions.
Surgical treatment is considered the main one.
There are two main types of operation:
- Open interventions : discectomy and laminectomy. These are radical operations with a long recovery period.
- Minimally invasive endoscopic interventions. These include: endoscopy, microdiscectomy and laser hernia removal. Such operations are performed with minimal damage to the tissues surrounding the hernia. After the manipulation, the patient is able to lead an almost complete lifestyle after a few days.