Treatment of a hernia of the lumbosacral spine
Intervertebral hernia is a degenerative-dystrophic disease that contributes to the gradual destruction of the intervertebral discs, rupture of the fibrous rings and the release of nuclei outside the vertebral body. The spine is an integral structure, the lumbar region includes 5 vertebrae, and the sacral region is located under the fifth vertebra and passes into the coccyx region.
In the event that an intervertebral hernia of the lumbosacral spine is diagnosed, treatment can be carried out using both conservative and radical methods of treatment. The decision on how to treat emerging disorders is made by the doctor, taking into account the manifestations of the disease and the results of a comprehensive examination.
Symptoms
Depending on the symptoms that occur, the treatment is also selected. For example, to eliminate intense pain, both analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and blockades are used.
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbosacral region are manifested in the form of patient complaints about:
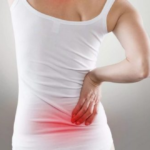
- Acute, sharp pains that occur in the lumbar region (lumbago, lumbago). The nature of pain: sharp, shooting, burning. Occur after intense physical overexertion or lifting heavy objects. As a result, the intervertebral disc falls out, and the nerve roots are irritated, which leads to a persistent reflex increase in muscle tone and the development of pain.
- Sensory disturbances in the groin and gluteal region, as well as in the ankles, thighs, legs. The patient complains of the formation of "goosebumps" and tingling sensations.
- A prolonged feeling of pain in the lumbar and sacral region, which can disturb the patient for a long period of time: from several months to several years.
- In the event that the internal organs located in the pelvic region are affected, symptoms may occur in the form of impaired potency and bowel movements, urinary incontinence.
- , excessive pressure of the hernia on the spinal roots occurs , followed by irritation of the large sciatic nerves. As a result, there are complaints about a pronounced feeling of soreness of a stabbing, aching, shooting character.
- The tone of the muscles of the lower extremities may decrease as a result of damage to the motor nerves.
- In the event that the vessels that supply blood to the lower extremities are compressed, the legs may become pale, spots form on them .
In severe spinal lesions, the symptoms of a hernia of the lumbosacral region may manifest as the development of paresis or paralysis.
Therapy
Conservative spinal therapy without surgery, as well as home treatment, are aimed at eliminating the symptoms of disorders, but do not affect the pathology itself. To provide a positive result, surgical treatment of the hernia is required. In most cases, surgical intervention is required without prior use of conservative and alternative methods.
Medical treatment
With a hernia of the lumbar spine, the following groups of medicines can be used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , which are widely presented in the form of tablets and capsules for oral administration, intramuscular injections, creams, ointments and gels for external application. Allows you to quickly cope with the feeling of soreness. To achieve a more pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, the doctor may recommend the use of several dosage forms at once: for example, tablets for internal use in combination with an ointment for external application.
- Corticosteroids - to provide a faster and more pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
As an auxiliary element, chondprotectors can be used - drugs that promote the regeneration of damaged cartilage tissue components.
Physiotherapy and exercise therapy: features of non-surgical treatment
Among the elements of physiotherapy, preference is given to:
- acupuncture - a specially trained specialist inserts thin needles into biologically active points on the body;
- diadynamic currents - the activation of the procedure helps to normalize blood circulation, provide an analgesic effect and reduce the excitability of nerve endings;
- electrophoresis - the introduction of drugs is carried out using the influence of an electric current, the most commonly used drugs are Karipain and Karipazin (enzyme preparations based on papaya extracts);
- it may also be recommended to use homeosiniatry - a specialist administers homeopathic medicines through punctures of the active zones of the body;
- cryotherapy - the effect of cold on the affected areas, a sharp temperature drop contributes to stenosis of the vessel, after the completion of the procedure, the vessels expand, the nutrition of the affected discs improves;
- during hirudotherapy , after the saliva of the leech enters the body, a powerful immune response and a pronounced increase in the blood supply to the affected area of the spine are observed.
Manual therapy is a questionable technique in terms of efficacy and safety for hernia of the lumbosacral region due to the high risk of displacement of the formation.
Performing all the necessary manipulations must be trusted only by qualified, proven specialists.
Under the supervision of specialists, the patient can also perform a set of specially selected exercises that are used for lumbar hernias of the spine. The selection of exercises that are suitable for the patient is recommended to be carried out on an individual basis, taking into account the accompanying disorders and the size of the hernia.
Surgery
Among the surgical techniques most often preferred are:
- Endoscopic intervention is a low-traumatic procedure that allows you to carry out all the necessary manipulations without incisions, using a single puncture.
- Microsurgical manipulations - in the process of performing the procedure, the doctor uses miniature instruments. At the same time, it is possible to remove the hernia with the help of a multiple enlarger, without affecting or injuring the surrounding tissues.
- Disc prosthetics - the doctor removes the damaged disc and replaces it with specially selected artificial implants.
- Laminectomy is a procedure performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, the doctor removes the bone tissue of the vertebra located above the nerve endings, resulting in the formation of a space surrounding the nerve. Blood circulation is normalized, pain sensations are eliminated.
Among surgeons, laminectomy is also mentioned, a procedure that involves the removal of part of the intervertebral arch. Such a classic, but complex and traumatic operation is rarely used due to the high risk of developing unpleasant consequences.
Features of laser treatment
Intervertebral and vertebral hernias of the sacral spine do not always require removal. Modern technologies contribute to the provision of a pronounced therapeutic effect, are characterized by low trauma and high safety.
Laser therapy is a relatively new treatment technique. During the procedure, the doctor makes a small puncture through which he inserts a needle and a laser light guide to the disc area. Dosed energy flows are fed through the light guide, which contribute to the transformation of the intradiscal fluid into a vapor state.
The procedure helps to reduce intradiscal pressure, reduce the irritating effect on the nerve endings. The technique demonstrates the greatest efficiency in the course of treatment of patients with hernias up to 6.6 mm in diameter.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Among the advantages of laser treatment are:
- minimal risk of developing instability in the spinal column;
- treatment of the spine with a laser does not contribute to the formation of scar tissue in the area of the skin and nervous structure;
- minimal risk of damage to other nerve structures, since the doctor uses local anesthetics and the patient can report discomfort at any time, because. is conscious;
- laser nucleoplasty can be used in multiple ways: if it is necessary to treat other vertebral segments.
Among the shortcomings of the technique, the absence of pronounced radicalism is distinguished, since a slight decrease in the volume of the disk is observed. This may result in the need to re-invoke the procedure.
Recovery period
After the procedure, it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of the doctor during the rehabilitation period:
- Over the next 30 days, it is recommended to refrain from active physical activity: swimming in the pool, exercising in the gym. Standard loads are allowed in the form of normal daily walking, short driving, doing household chores.
- During the rehabilitation period, the patient should use a semi-rigid corset for 1 month when there are loads on the spine.
- Refrain from using elements of physiotherapy in the form of balneotherapy, electrotherapy, massage. On the recommendation of a doctor, magnetotherapy can be used.
- Use drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on rheumoxicam or nimesulide.
In the event that the patient does not follow the recommendations of the doctor, this will lead to a decrease in the effectiveness of the procedure.
Additional Recommendations
In order to secure a positive result from laser or radical treatment, as well as to prevent the formation of hernias, it is important to follow some recommendations.
What is important after the operation:
- normalize body weight;
- carry out regular exercises to strengthen the muscular corset;
- swim regularly.
After the involvement of surgical intervention, any physical activity is permissible only by prior agreement with the attending physician.