Signs, treatment and prevention of median hernias
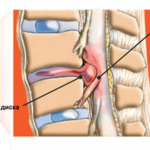
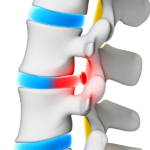
Posterior median hernia is one of the types of pathology, which can also be found under the name "median" or "median". With this disease, a protrusion of a separate section of the disc is observed, which over time can get into the region of the spinal canal.
The danger of median hernias is the likelihood of complications with compression of the spinal canals and their contents. The risk group includes people who prefer a sedentary lifestyle, as well as people prone to frequent spinal injuries.
Often there is the formation of hernias in several parts of the spine at once and the layering of symptoms on top of each other. A doctor cannot always immediately make a correct diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment, therefore it is recommended to contact only competent, qualified specialists.
Types of damage
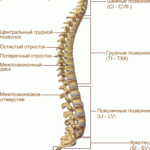
Doctors make a diagnosis of "posterior median hernia" if a displacement of discs localized in the middle of the spinal column is detected. The question often arises: what is L5 L4 disc herniation?
In most cases, the 4th and 5th vertebrae are damaged, and the letter L is an indication that they are localized in the lumbar region. This process may also be accompanied by rupture of the fibrous rings.
Depending on the direction, one of the types of hernia can be diagnosed:
- posterolateral;
- anterolateral;
- circular.
The greatest danger is represented by posterolateral injuries, among which there is also a medial hernia.
Causes
Among the main reasons that can provoke the development of the disease, the impact is distinguished:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Back overload.
- Childhood hip dysplasia.
- Traumatic lesions of the spine.
- Infringement of nerve endings.
- Bad habits: the tendency to smoke contributes to a decrease in blood oxygen saturation, as a result of which the delivery of essential nutrients to the intervertebral discs is disrupted.
- Road traffic accidents: after a “whiplash injury” (a sharp jerk of the head back and then forward), the initial symptoms of a hernia may appear 2-3 years after the accident.
- Sedentary lifestyle. In the event that in a person's life there are no normalized moderate physical activity, metabolic disorders, progression of osteochondrosis are observed.
- Intense physical activity.
The treatment regimen is selected, taking into account the degree of progression of the disease and the main manifestations of the hernia.
Manifestations
Median disc herniation has different sizes and at the initial stage the following symptoms occur:
- slight visible protrusion;
- complaints of a weak feeling of soreness;
- the pain may radiate from the lumbar region to the sacrum and thighs.
As the median disc herniation grows, patients complain and experience the following symptoms:
- skin becomes pale;
- sweating is disturbed;
- sensory disturbances in the lower extremities;
- posture disorders;
- when unbending the feet, there are complaints of a feeling of weakness;
- painful sensations of a aching nature, which can intensify over time.
With intervertebral hernias that occur at the level of 4 and 5 vertebrae, the patient has a feeling of stiffness and pain in the lumbar spine, as well as complaints of weakness in the big toe, sudden "goosebumps" on the skin.
Hernias of the lumbosacral region also manifest themselves in the form of:
- feelings of pain in the lumbar region;
- violations of sensitivity and weakness in the lower extremities;
- pain that gets worse when the patient sneezes or coughs;
- complaints of a feeling of soreness in the hip joints, buttocks, lower extremities, toes.
In the event that there is no timely therapy, the medial hernia will gradually grow, and the symptoms will intensify. Over time, there is a rupture of the posterior longitudinal ligament, compression of the spinal cord or cauda equina occurs. The progression of the disease leads to the fact that the patient's movements are difficult, gait changes are observed, complaints of pain occur when the patient is in a sitting position.
Treatment
The main goals of median hernia therapy are:
- Eliminate the feeling of pain with the use of special groups of drugs.
- Normalization of the patient's mobility. In order to eliminate the discomfort that occurs during movement, it is necessary to strengthen the patient's muscular corset. For this, the doctor prescribes a complex of therapeutic exercises.
Conservative treatment of median hernias involves the use of:
- Medications: drugs from the group of NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, drugs that normalize blood circulation. With intense pain, blockades with the use of painkillers are recommended.
- Massage.
- Elements of physiotherapy.
- Selection of special exercises of therapeutic gymnastics. Exercises can be performed only with the agreement and under the supervision of specialists.
To cope with the feeling of soreness allows traction of the spine, the use of acupuncture, manual treatment.
Surgical intervention
With the progression of the disease and the absence of the effect of the prescribed conservative treatment, surgical intervention is indicated. After the doctor removes the hernia, the damaged area of the spine will be replaced with an artificial implant to preserve the overall structure of the spinal column.
In some cases, after surgery, a recurrence of the disease is possible. In order to prevent the recurrence of a hernia, it is necessary to follow exactly all the instructions of the doctors during the rehabilitation period.
What complications can occur?
Among all possible types of protrusion, it is the posterior medial hernias that are the most dangerous, since they pass along the median (in the middle) of the intervertebral discs and are directed towards the center of the spinal cord. The distance between the hernia and the brain is small, which is fraught with the development of serious complications, including myelopathic syndrome. A combination of neurological disorders can affect the internal organs and lower limbs of the victim.
The consequences are manifested in the form of the following states:
- There is a development of acute pain in the lumbar region.
- Detection of cholecystitis and pancreatitis, renal failure.
- The likelihood of developing paraparesis of the lower extremities.
- With the development of cauda equina syndrome, the patient will have complaints of urinary disorders and shooting pain in the hip and calf muscles.
- In severe cases, there is a deformation of the dural sac - the membrane that protects the spinal cord.
When identifying the first signs of violations, it is recommended to refrain from self-treatment and turn to experienced, qualified specialists. Self-medication is unacceptable, since it may not have the proper therapeutic result and provoke the development of complications.