How is a bulging disc different from a herniated disc?
Protrusion of the intervertebral disc is an x-ray sign indicating the initial stage of osteochondrosis. The latter is diagnosed in people of different age groups, especially often the pathology occurs in adolescents and older men whose activities are associated with heavy physical work. Protrusion of the intervertebral disc is a complex of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine, which in themselves are not dangerous.
Pathological changes in the vertebrae and discs occur in almost everyone after 25 years, which is associated with the physiological aging of the body. With protrusion, the annulus and pulp suffer from a lack of moisture and nutrients, which for the most part come from the tissues surrounding the disc. Such a violation occurs without disk deformation, and with a hernia, destructive processes are already noted, which can result in the separation of part of the pulp and its migration along the spinal canal.
A herniated disc is diagnosed mainly in the elderly, but in children there is a congenital form of pathology. A spinal hernia ends fatally for a child, unless surgical treatment has been carried out in a timely manner.
To select an effective treatment, one should understand how protrusion differs from disc herniation, and what factors trigger the pathological process.
disc protrusion
Degenerative-dystrophic processes occur at the level of one or more vertebrae. With such a violation, the disk decreases in size. At the same time, the vertebrae approach each other, and begin to squeeze the fibrous body and the surrounding soft tissues even more. The patient may not be aware of protrusion for a long time, because the symptomatic complex appears only with concomitant deviations of the spinal column.
In rare cases, the following manifestations of disc protrusion are noted:
Neck department.
Feeling of tingling and numbness of the skin in the arms, shoulder girdle and shoulder blades. The patient is worried about chronic fatigue, frequent headaches. Of the neurological symptoms, irritability, apathy, constant drowsiness are noted. In a neglected case, there is a violation of cerebral circulation, and this will already become a factor in the occurrence of an early stroke.
Thoracic department.
Pain and discomfort in the chest area. Staying in one position for a long time increases discomfort. Pain syndrome occurs when walking, sitting, while running, and it can be confused with pain in the heart. It is not uncommon for angina pectoris to lead the patient to the doctor, and disc pathology is discovered by chance when examining x-rays.
Lumbar.
Unlike a hernia in the lumbar and lumbosacral regions, with protrusion, the patient has only mild pain with a long preservation of one body position and during sudden movements. In this regard, the patient is contraindicated for a long time to sit, drive a car, exercise on an exercise bike and a treadmill.
A good way to understand what exactly worries, protrusion or hernia, will be training. With hernias, exercise will be accompanied by pain, and worse, this symptom can occur at any time, regardless of body position and activity.
The main factors for the appearance of protrusion of the spine:
- malnutrition of the disc due to hypodynamia;
- regular high loads on the spinal column;
- negative impact of occupational hazards (sedentary work).
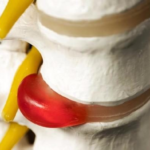
Spinal hernia
A herniated disc is a pathology in which a part of the disc bulges into the spinal space with a part of the pulp torn off or its integrity preserved. The defect can be of different sizes, on which the symptomatic complex and treatment tactics will depend. The difference in the approach to therapy is due to other disorders that the defect provokes. With any size of the protrusion, a hernia can only be cured surgically, but a small defect can be affected by minimally invasive techniques, including laser vaporization.
With disc herniations, conservative treatment can only temporarily suspend the pathological process, but with protrusion, only this approach is shown. The difference lies in the fact that in the first case the risk of complications is much higher, and it remains even after the operation.
Protrusion and hernia - what's the difference:
- During protrusion, the integrity of the disc is preserved.
- With a hernia, compression of the nerve roots occurs.
- With protrusion, the symptomatic complex may be absent.
- With a hernia, the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the annulus fibrosus.
- With protrusion, the treatment is conservative.
- With a hernia, non-surgical methods are indicated, but according to indications, an operation is performed.
Light protrusions and hernias of the spine are similar in that in these diseases the intervertebral disc is broken, reduced in size and deformed, but the severity of these abnormalities is different.
The causes of these pathologies are largely similar, because the prolapse of the disc begins with a violation of its nutrition, which precedes degenerative changes. Protrusions and hernias of the intervertebral discs have different symptoms, but the first violation in most cases ends with a bulging of the fibrous body.
The nature of spinal hernias is ambiguous. Despite the fact that osteochondrosis, that is, the weakening and gradual destruction of the disc, remains its main factor in its appearance, this pathology can also occur suddenly. This happens during an injury or after surgery.
This disease is also different, because protrusion does not develop at one moment, but the disk is destroyed for a long time.
Treatment of hernias and protrusions
How to treat protrusion of the intervertebral disc:
- Medical treatment. Painkillers, decongestants, anti-inflammatory, chondroprotective drugs are used.
- Physiotherapy procedures . Laser therapy, electrotherapy, magnetotherapy, mud baths, massage, manual therapy will be useful. These techniques have contraindications and the attending physician will be able to determine whether their use helps with spinal pathologies.
- Spinal traction . Executed by hardware. Eliminates disc compression and nerve root compression.
- Exercise therapy and kinesitherapy . Movement treatment is carried out at any stage of the disease, because strengthening the muscles and improving microcirculation contributes to the normal nutrition of the damaged disc. In specialized rehabilitation centers, specialists work with the patient, who select an individual set of exercises for protrusions and hernias of the spine.
The different clinical picture of the diseases already indicates that the approach to treatment will be different. Etiotropic therapy is similar. Symptomatic treatment is different, because with a herniated disc, all manifestations are more pronounced.
How to treat a herniated disc:
- Conducting anesthetic injections and blockades of the spine (injections are indicated in the acute period and for ambulance, in other cases, tablets are used).
- Performing a therapeutic set of exercises . With a hernia, physical education has many contraindications and classes are carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
- Taking chondroprotective drugs. It can be Chondrolone and Chondroxide. These drugs, like Almag for disc herniation, will contribute to the normal formation of cartilage tissue.
Prevention measures
Prevention of spinal pathologies includes the following activities:
- a balanced diet, including a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals;
- daily physical activity, exercise and exercises to stretch and strengthen the back muscles;
- exclusion of high loads, proper lifting of heavy objects, regular rest;
- an annual preventive examination by a neurologist, an MRI of the spine, which will allow time to suspect the onset of the pathological process.