Radiography with a hernia of the spine
X-ray diagnostics is one of the ways to examine the structure of the spinal column along with computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Usually these methods are prescribed together - so the doctor gets an overall picture of what is happening.
The essence of radiography is the work of rays that are projected onto a selected area of the human body, including the spine. X-rays pass through layers of soft tissues almost unhindered, stopping at hard ones. That is why X-ray is not the main diagnostic method for examining a hernia, but only a secondary, additional one: a vertebral hernia, as a structure, is a soft tissue.
X-rays pass through the protrusion, at the end of their path reaching the hard tissues - the vertebrae. Can an x-ray as a method be useful for hernias?
X-ray method of diagnosis is considered as a stable base for further study of diseases of the spinal column, which also applies to spinal hernia.
If an x-ray does not give definitive information about a hernia, then why is it prescribed?
The totality of information in the images is always indirect evidence of the existence of pathological bulging, which may be indicated by such data:
- distance and height between the vertebrae, the presence of cavities;
- distinctness of the contours of the bones;
- pattern and degree of color of hard tissues of the spinal column;
- the presence of osteophytes - pathological outgrowths in the bones.
Also, fluoroscopy is a reliable source of information regarding:
- degenerative-dystrophic processes;
- cracks in the disks;
- curvature of the spine.
Outwardly, these disorders may resemble the symptoms of a hernia, which is important for differential diagnosis in the work of doctors.
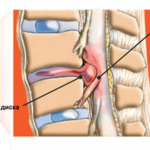
Osteochondrosis is a slow degenerative-dystrophic process in the spine. This is where the development of a hernia begins. It is in the pictures that you can see signs of a process that destroys the vertebrae.
Can you see Schmorl's hernia? This type of pathology is characterized by the indentation of the intervertebral disc into the depth of the vertebra, which is accompanied by its partial destruction, therefore, in the figure, it is possible to see a hernia.
Preparation for the procedure
The need for preparation is determined by the location of the protrusion. So, for examination of the cervical and thoracic region preparations are not needed. In case you need to explore the lower areas - the patient needs to prepare.
Such a need arises from one condition - the lumbar and sacral region is located at the level of the intestine, where fermentation processes take place that can distort the objective picture. To do this, it is obviously necessary to exclude certain products and make a cleansing enema. Within a week before the examination, the patient should exclude such foods from his diet: legumes, cabbage, white bread and other dishes that cause fermentation in the intestines.
Disadvantages and advantages of the X-ray method
As with any method, radiology is not an ideal diagnostic method.
X-ray weaknesses:
- the impossibility of studying the vertebral discs in dynamics, respectively, it is impossible to investigate the functionality of the spinal column;
- insignificant load on the body by radiation, which excludes the use of the method for young children and pregnant women;
- small resolution;
- imaging: the image provides poor quality information about the structures of the spine.
Advantages of the method:
- the ability to conduct differential diagnosis, which increases the likelihood of an accurate diagnosis;
- accessibility for any segment of the population;
- does not take much time;
- after carrying out no patient has no side effects.
Modern methods for diagnosing intervertebral hernias
Unlike Soviet times, today there are universal and informative research methods. X-ray is not a completely reliable means of detecting protrusions, and modern diagnostic methods come to replace it.
Namely:
- Magnetic resonance imaging. MRI is a method of studying the human body, which uses the strength of magnetic fields. Tomography allows you to get a layered image of high quality and resolution. The procedure is completely safe for the patient and does not take much time. MRI is always a reliable way to examine a herniated spinal column. The resulting images show not only a hernia, but also many other diseases: tumors, vascular pathologies, osteochondrosis.
- CT scan. Like x-rays, CT uses radiation. The method provides a layered image of the tissues of the back, allows you to study in detail the structure of the vertebrae and connective tissue.
The answer to the question of whether an x-ray will show a vertebral hernia will be as follows: the diagnostic method will not show the hernia itself, but will give the doctor an integral layer of information about other pathologies of the spinal column, which are similar in appearance to a hernia. X-ray examination fades into the background. The old method is being replaced by magnetic resonance and computed tomography - more accurate and reliable methods for diagnosing spinal hernias.