Symptoms and preventive measures for infringement of a hernia of the spine
Many people suffering from herniated discs know firsthand about sharp, sudden pains that severely restrict movement. The pain syndrome usually develops abruptly, and can last for several hours, and sometimes several days.
The most common cause of the development of acute pain syndrome is the infringement of the spinal nerve in the area where the defect of the intervertebral disc is located.
If a person has a hernia already formed, nothing can insure him against the development of infringement. In this case, it is necessary to know what the main symptoms of the pathology are, how to help a person relieve pain in an acutely developed unfavorable situation, and what further treatment should be.
Hernia - what is it
Everyone knows that the spinal column is made up of vertebrae. Between them, in order to reduce the rate of their erasure and improve cushioning, evolution has placed intervertebral discs. These anatomical structures are a soft nucleus pulposus "wrapped" in a fibrous sheath. Thanks to these structures, it is possible to ensure that the spine serves a person for a long time, wearing out minimally during life.
A herniated disc develops when the anatomical structures lose their consistency. Many reasons can contribute to this, including the presence of excess weight, and exorbitant physical activity, or, conversely, their absence, and malnutrition.
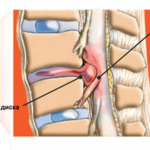
As soon as the intervertebral disc ceases to cope with its loads, its fibrous membrane ruptures. As a result, the nucleus pulposus is outside the previously strong frame, forming the same hernial protrusion.
Interestingly, a hernia can form in different directions. Depending on the direction in which the pathological protrusion occurred, the risk of developing an infringement increases or decreases.
So, for example, with an anterior protrusion, the patient may not know at all that he has a disease of the musculoskeletal system, since there are no symptoms. If the protrusion has occurred in the back side, that is, towards the spinal foramen, there is a high risk of infringement, since the hernia is in close proximity to the spinal nerves.
Infringement is also possible with posterolateral pathological protrusions, since in this case the hernia can pinch the branches of the vertebral nerves that exit through special openings.
Why abuse happens
When infringement of the intervertebral hernia occurs compression of the spinal nerve. Most often, the structures of the spine and the resulting pathological protrusion put pressure on it. Sometimes pathology develops if a hernia fills a hole through which one of the spinal nerves exits.
There are several contributing factors:
- the presence of osteochondrosis (a pathology in which there is a gradual dystrophy of the articular and cartilaginous surfaces with the loss of their functions);
- various posture disorders (improper posture leads to an incorrect distribution of the load on the spinal column, due to which the areas affected by the hernia are forced to overstrain, which only aggravates the pathology);
- spasm of muscle structures (the inability to properly and fully relax the muscles also increases the load on the spinal column, contributing to the development of pathology);
- high physical stress on the back (may be in athletes or people whose lives are associated with active physical labor);
- the presence of excess weight (obesity increases the intensity of the load on the spine in much the same way as physical activity, which is done uncontrollably);
- the presence of various injuries of the spinal column;
tumor neoplasms.
The impact of any of these causes can first lead to the formation of a hernia, and then to its infringement. True, doctors note that the effect of exposure to not one, but several provoking factors at once is much more often observed.
The main signs and symptoms of the disease
When the spine is affected, symptoms can vary from person to person. The localization of the process, the presence or absence of inflammation, the severity of pinching and its duration will influence the severity of the pathology.
First of all, all patients always distinguish pain as the main symptom. The localization of pain will vary significantly if the nerve is pinched in the lumbar or, for example, the cervical region. This must be taken into account when diagnosing a patient.
With infringement, it is possible to involve large nerves in the pathological process, such as the sciatic, cervical. In this case, not only pain develops, but also loss of sensitivity, and sometimes paresis or paralysis.
The pain will be characterized by the following features:
- diverse nature (the picture described by different patients is significantly different, the syndrome can be stabbing, cutting, dull);
- patients note the appearance of heaviness and specific tingling in the projection of the formation of pinching;
- the pain is debilitating, the patient quickly gets tired of it.
The symptoms of compression may differ depending on whether the sensory or motor nerve root has been pinched.
When a sensitive or autonomic nerve is infringed, pathological changes in the work of a number of organs (mainly in the pelvic area) can be observed. Also, the patient will complain of a feeling of numbness in the limbs, their progressive weakness.
If the motor nerve is involved in the process, then disturbances will be observed, first of all, from motor functions. There will be severe pain that will not quickly disappear, the patient may lose the ability to control the movements of the limbs.
Correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment
Before providing any specialized assistance to the injured person, the doctor must make sure that the diagnosis is correct. It may seem that the clinical picture is very obvious, and there simply cannot be double diagnoses, but this is not at all the case.
There are a number of diseases that can also lead to pinched spinal nerves, but the appearance of signs will not be associated with a hernia. This is possible, for example, with the development of a tumor.
If the patient has severe vertebral pain, and earlier he was observed by a doctor about a hernia, then he must be sent for an X-ray examination. Radiography allows you to determine the approximate position of the hernia, draw conclusions about its size and location.
Additionally, CT and MRI can be performed. In some cases, patients are shown additional myelography, with the help of which they evaluate how the cerebrospinal fluid moves in the spinal cord, and whether there are any pathological changes.
A full medical examination allows not only to establish the cause of pinching, but also to select the optimal set of measures for treatment, which will be most effective in this case.
First Aid Basics
Many patients are wondering what treatment is possible for a pinched spinal hernia? It is best, of course, to consult a doctor. But it is far from always possible to quickly get specialized help, especially if unpleasant symptoms are caught somewhere in the village, on the road or in other extreme conditions.
First of all, helping the patient is to provide him with maximum peace. In case of infringement of the intervertebral hernia, special belts or, in extreme cases, ordinary scarves can be used to immobilize the damaged area. After dressing the victim, they lay him back on a hard surface and try not to disturb him.
You can calm the pain symptom by taking any available pain reliever orally. It is recommended to take an anesthetic on your own only once, and in the future, coordinate the dose and the appropriate drug with your doctor.
It is important to remember that patients are categorically contraindicated in warming up the sore spot. The fact is that inflammation develops in the area of the hernial protrusion, which will only intensify if you try to act on it with heat.
Basic principles of treatment
Specialized assistance to a patient with infringement of an intervertebral hernia is provided by a doctor in a hospital setting.
The following measures are recommended in the acute period:
- providing bed rest during the development of acute pain syndrome;
- taking drugs from the group of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (medicines are selected by the doctor, as well as their dosage, which is strictly forbidden to exceed!);
- the use of anti-inflammatory local agents, such as ointments, creams, anti-inflammatory dressings, etc.;
- if the pain cannot be stopped for a long time, it is possible to use special drug blockades.
In the course of treatment, measures are taken to reduce the severity of compression, normalize the configuration of the damaged intervertebral disc, and eliminate muscle spasms. After an acute pain attack is stopped, the use of massage, exercise therapy, and physiotherapy is recommended. These techniques will help to normalize the state of the body and consolidate the results of the therapy carried out for infringement of the hernia.
ethnoscience
If the patient is concerned about the strangulated intervertebral hernia, you can turn to traditional medicine. Of course, you can use them only after consulting your doctor. Folk recipes give the best results in combination with classical methods of therapy, and not when used in isolation.
Useful recipes for spinal health:
- In a bath filled with warm water, you can pour an infusion of oak bark or calamus root. In the resulting mixture, you must lie down for 10-15 minutes (the water should not be hot!).
- Mix flour and honey in a 1:1 ratio until smooth. Make a comfortable compress, put on the area of pain localization and bandage with a woolen scarf.
- You can do rubbing with fir oil or valerian infusion. After rubbing, it is recommended to tie a scarf on the sore spot.
- You can rub a bay leaf tincture into the affected area. Preparing it is simple: 2 tablespoons of leaves are taken and poured with vodka or alcohol. Infuse the mixture for several days before rubbing it into a sore spot.
If you are allergic to any of the ingredients of folk recipes, then it is better to refuse to use them so as not to aggravate the situation.
A pinched intervertebral hernia is an unpleasant pathology from which no person suffering from problems with intervertebral discs is immune. To maintain the health of their spine and spinal cord, patients are advised to contact a doctor in a timely manner when symptoms of a pathology appear.
Timely treatment and prevention of a hernia will significantly reduce the risk of developing a pinched hernia, helping a person maintain good health of the musculoskeletal system.