Symptoms and surgery for abdominal hernia in women
A hernia is a disease in which there is a pathological protrusion of internal organs into an adjacent cavity. Most often, men are predisposed to such an ailment, but abdominal hernia in women is no exception. The risk group includes women whose age has crossed the line of 45 years. Abdominal hernia is one of the most common surgical diseases.
In a narrower sense, a hernia of the abdominal cavity is a disease characterized by the movement of the abdominal organs (omentum, intestine or part of it) into any other cavity.
Often, the bulge migrates to the umbilical, femoral, inguinal, or diaphragmatic region. The location primarily depends on the type of surgical intervention and treatment in general.
Causes
The main factor influencing the formation of a hernia is unbalanced pressure in the abdominal cavity. The organ, like any other physical object, is able to succumb to the influence of pressure and move in the direction of less resistance - to the chest or pelvic region.
So, factors that increase pressure include:
- The first and main cause of hernia in women is pregnancy and childbirth . The fetus, by its very presence in the abdominal cavity, affects the disparity of pressure. Despite the fact that pregnancy is a normal physiological process, the gestation period still has its consequences for a woman. Especially the load increases during childbirth. Then the likelihood of hernia formation increases even more.
- Age . The increase in the number of years develops a peculiar background in the activity of the woman's body. Thus, the aging process in any person contributes to the weakening of a number of compensatory forces in him, such as the strength of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Hard physical labor . It is also a fundamental factor in the development of hernial pathology. Constant intensive loads on the body, muscles and the body as a whole contribute to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
- predisposition . The genetic background can provide an evil service in the form of congenital muscle weakness and other defects in the anterior abdominal wall.
- Overweight. Excessive body weight is associated with fatty growth of the omentum, which causes an increase in pressure in the peritoneum. Large fat layers seem to push the internal organs to the side.
- Previous abdominal trauma or surgery where surgeons did not properly suture.
- System diseases, or diseases of individual organs. This group of causes includes any factor that contributes to the formation of high pressure, namely: chronic severe coughing, constant constipation, sneezing. This also includes such pathological conditions as abscesses, accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Depending on the period of formation, the following types of hernias are distinguished:
- Congenital . Such a pathology is detected in almost all cases immediately after the birth of a child. This hernia was formed during fetal maturation.
- Acquired . They arise under the influence of a number of factors in the process of a woman's life.
- Postoperative . Such bulges usually appear almost immediately after surgery due to poor-quality suturing or the specifics of the hernia itself (larger dimensions).
- neuropathic . These hernias occur after the transfer of any diseases that weaken the strength of the muscles or form defects in the muscle walls.
The course of the disease plays an important role in choosing the type of treatment, therefore, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- reducible - hernias characterized by a low probability of developing complications and easily amenable to reduction;
- irreducible - completely opposite to the previous option: a high probability of complications, do not reduce and are difficult to conservative treatment;
- not infringed - an organ that has entered the space of the hernial sac does not violate its function and continues to work at the proper level;
- strangulated - a type of complication in which the organ located in the hernia sac loses its performance and loses some of its functions; has a number of negative consequences: necrosis (death of part of the organ), constipation.
In addition, abdominal hernias are distinguished by their location:
- umbilical - the protrusion is located at the navel, is characterized by clear contours, most often occurs during gestation;
- inguinal - in women it is extremely rare, but if it forms, girls find it in the groin area, and this hernia also causes difficulty in everyday walking;
- white line of the abdomen - usually found in women after 40-45 years, the burning symptom in the abdomen comes to the fore.
Symptoms of a hernia of the abdomen
It should be noted that the signs of a hernia of the abdomen do not develop immediately: the manifestations of the pathology mature gradually, over time. So, often making a diagnosis in the early stages of the course of the disease causes difficulties for the doctor, and even more so for the sick person.
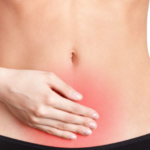
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of a small tumor-like formation in the abdomen. Its sizes range from a small berry to a soccer ball.
The size of the protrusion indicates the stage: the larger it is, the later the stage of the disease.
From the group of specific symptoms, there are:
- Pain syndrome formed in the abdomen . The pain is caused by compression of local nerve fibers or, worse, nerve plexuses. Pain can be aggravated by various physical activities, regardless of the location of the exercise itself. Also, pain can occur with strong bends forward or backward. Sometimes the pain syndrome spreads to adjacent structures: the groin, pelvis, chest cavity, often the sacrum and lower back.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Belching.
- Violation of the act of defecation.
- Formation of a firm and oblong protrusion on the abdomen. Dimensions are lubricated when the patient assumes a horizontal position of the body. The pain gets worse as it grows.
- During menstruation, women observe pain more than usual.
Hernia pathology also affects the development of common symptoms, such as:
- fatigue, unobvious fatigue;
- headache;
- sleep disturbance and irritability;
- often the body temperature rises.
It is important to understand that all symptoms are not taken “just like that”. The whole set of signs is determined by the location of the hernia and which organs or systems it compresses.
If the tumor-like formation presses on part of the stomach, belching and local pain appear. A hernia that presses on the intestines causes difficult defecation and difficulty in releasing gases.
It is important to know: small hernias can be reduced on their own with a long rest in a horizontal position. The disease acquires a latent character, falls into a "sleeping" state. However, with the actualization of physical activity or various psychogenic stresses, the pathological protrusion again makes itself felt, leaving through the hernial orifice.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are prescribed by the attending physician, who also makes the diagnosis itself. The latter is based on a number of objective and instrumental studies. It is instrumental research methods that give the most accurate picture of the disease. So, radiography, ultrasound diagnostics, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are used.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures mainly relate to surgical intervention. Complete treatment without surgery is simply impossible: conservative therapy does not eliminate the cause, but only masks and partially eliminates a number of symptoms that reactivate in one way or another after a while.
Surgery is the only way to completely get rid of the disease, and if not forever, then at least minimize the likelihood of a relapse to the slightest indicators.
There are several ways to treat by surgery:
- open operations. Such types of intervention are carried out by creating several incisions that provide access to the hernia itself. This category of operations has a number of disadvantages: numerous superficial injuries of the abdominal tissues, the need for a large number of sutures, the formation of postoperative scars, a long rehabilitation period, and the presence of pain after the intervention.
- Laparoscopic methods . These are modern and topical methods of treatment of hernial pathology. Advantages: fast recovery of damaged tissues, relatively short recovery period, almost complete absence of sutures and scars, the diameter of three scars does not exceed the size of three small dots (which is so important for girls), the absence of pain after the intervention. After a laparoscopic operation, a woman quickly gets on her feet.
Any operation related to hernias is a routine work for surgeons. As a rule, the implementation of surgical procedures does not cause difficulties for specialists.
Ways to close the hernial ring:
- tension hernioplasty - in this operation, the patient's own tissues are used, which are sewn together together;
- tension-free plastic - to cover and eliminate the defect, which is formed by the hernial ring, an implant mesh is used;
- combined plastic - both methods of treatment are used.
Only a child who has serious contraindications to surgery can be treated with conservative therapy. In all other respects, intervention is the main method in the treatment of abdominal hernias.