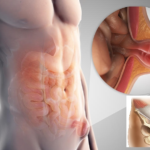
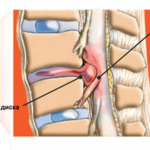
How are hernias of the abdomen and spine manifested?
A hernia is a surgical pathology characterized by pathological protrusion of several or one organ into another cavity. The process of exit itself occurs through normal or pathological openings. With a favorable course of the disease, the released organ often does not lend itself to organic damage, only its functional activity is disturbed.
The symptoms of a hernia are determined by the organ itself, which is out of its normal anatomical position, so there are no specific symptoms as such.
A hernia, as a structure, includes three components:
- Hernia gate . This is a defect in the muscle wall through which the organ goes beyond its limits. Congenital weak points of the body often act as gates, such as the exit of the spermatic and umbilical cord, the exits of nerve fibers or blood vessels. Acquired gates are formed as a result of trauma or surgery.
- The hernial sac is the soft tissues of the body that form a cavity that exits through the gate. In the structure of the bag, the neck, bottom and body are distinguished. Most often, the bag is covered with adipose tissue.
- The contents are several organs, an organ or part of it, which is in the hernial sac. Most often, intestinal loops, parts of the omentum, sections of the large intestine, and the mesentery are found as contents. Less often - tubes, ovaries, bladder, spleen.
Signs of a hernia
The clinical picture of hernial pathology is repelled from the place of protrusion, and from the organ that is located in the hernial sac. Therefore, the symptomatology should be disassembled by "levels".
Spinal hernia
Pathology in this area develops gradually.
As the protrusion in the spine grows, three syndromes develop:
- Pain syndrome. Often pain is the leading symptom of any hernia. Here, the pain sensations make themselves felt constantly. From the very beginning, the pain is insignificant, patients rarely pay attention to it. However, in the process of formation, the pain syndrome develops more and more intensively. Unpleasant sensations are aggravated when pressure is applied to the spinal column in the form of weight lifting, physical exercises.
- Root . Squeezing the spinal cord, the hernia often touches the outgoing nerve fibers. So, in the clinical picture, muscle weakness is observed, it is difficult for the patient to work, climb stairs and sometimes just lie down. Over time, the muscles weaken, decrease in size. Paresthesias are also fixed - a disorder of the neurological sphere, which is characterized by a sensation of tingling, numbness.
- Vertebral Syndrome . Constant pain causes the muscles to become in a state of constant spasm. Frequent and strong muscle contraction sometimes "pinches" some of the nerves, causing the pain syndrome to intensify more and more. It is already difficult for the patient to straighten his back and keep his posture even, so patients often take a stooped posture.
Features of the symptoms are determined by the level of location of the hernia.
Neck department:
- shootings in the neck muscles, extending to the shoulder joints;
- numbness of the hands, crawling on the skin, deterioration of tactile sensitivity;
- frequent mood swings, irritability, often tearfulness;
- headaches, dizziness; the patient may hear tinnitus and complain of blurred vision;
- memory loss, sleep disturbances, impaired accuracy of movements.
Thoracic:
- pain syndrome most often spreads to the back and lower back, may increase with exertion in the form of coughing, sneezing or after exercise; often the pain extends to the legs;
- due to disruption of the muscular apparatus, patients often experience difficulties associated with restriction of movement;
- patients feel weakness, complain of numbness;
- among the symptoms, you can also find a violation of urination.
Lumbar:
- pain radiating to the legs; pain extends only to one buttock or one leg, bilateral pain is quite rare;
- tingling, numbness on the skin of the thigh and lower back.
sacral department:
- an influx of cold or heat in the lumbar region and legs;
- weakness of the muscles of the lower extremities;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
abdominal hernia
The first signs of abdominal hernias are spreading pain along the anterior walls of the peritoneum. Also, pain in this area increases with active walking, physical activity and coughing.
There are such reasons for the formation of pathology in this place:
- Congenital muscle weakness.
- Excessive stress that exhausts the body.
- Work that is associated with a power load that increases intra-abdominal pressure.
- Obesity.
A protrusion in this area is manifested by such signs:
- constipation;
- periodic nausea with bouts of vomiting;
- belching.
What does a hernia look like? Most often, patients find a roundish compacted neoplasm in the abdomen or groin, which can disappear on its own in the supine position and also appears in the standing position.
It should be remembered that men and women have different symptoms.
The first case is characterized by:
- a rounded and large formation that can be palpated in the scrotum or inside it;
- the inguinal muscles are weakened, men feel strong pressure.
For women, this is the picture:
- discomfort and heaviness in the area of the rectum;
- disorders of the genitourinary system in the form of difficult urination.
A characteristic sign of a hernia in this place is the presence of pain syndrome, which is associated with a feeling of fullness. Also, patients often complain of acute pain in this area. The pains are pronounced, they are cramping.
Abdominal hernia has many varieties:
- Inguinal . This option, due to anatomical features, is most often found in the male sex. Usually, the protrusion makes itself felt during strong physical exertion, where the muscles of the groin and abdomen are mainly involved. The inguinal variety of pathology is manifested by pain in the abdomen, often vomiting and discomfort when walking.
- Femoral . This variety is fixed mainly in middle-aged women (from 40 to 60 years). The first signs are the formation of a solid formation in the thigh area. Usually, the femoral variant of the disease develops as a result of trauma or surgery. Manifested by discomfort, bloating, pain, less often - constipation.
- White line hernia . In the early stages of the course, a hernia may not appear. Often, the presence of the disease is accidentally recorded after the examination. Hernias of the white line are manifested by pain in the middle part of the abdomen.
- Umbilical . The localization of this variety is the umbilical ring. Symptoms: pain spreading to the entire abdomen and occasional nausea.
Hernia in children
How to recognize a hernia in a child? Signs and nuances of diagnosis depend on the age of the child. Pathology in a newborn, as a rule, is detected immediately after birth.
This is facilitated by the presence of such symptoms:
- the baby screams, his navel or stomach as a whole will protrude. The bulge gets bigger when the baby screams or cries a lot;
- the abdomen may expand when the child pushes.
Older children often report pain themselves. Most often they indicate the location of the pain syndrome. It is in that place that it is possible to detect a protrusion. In the prone position, the hernia can self-reset.
How to identify a hernia
In case of detection of several symptoms at once, it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor will be able to recognize a hernia after first conducting a general and objective examination, and then using instrumental research methods. It should be remembered that the pathology is recognizable even in the early stages of the course, therefore, the sooner you turn to a specialist, the greater the likelihood of a complete cure.
You can diagnose a hernia from the moment it appears on your own: you just have to carefully examine your body and try to detect a slight protrusion.
Diagnosis of a hernia consists of three stages:
- General inspection . At this stage, the doctor examines the patient, asks about the patient's complaints, examines his lifestyle, the specifics of working conditions, studies the genetic predisposition and the number of surgeries and injuries (if a person has already had a hernia, the likelihood of its recurrence increases).
- Objective examination . The doctor moves on to the hernia itself. He examines its location, mobility, density of the neoplasm and signs associated with the presence of a protrusion.
- Instrumental research methods . At this stage, hernias are diagnosed most accurately. The most common options for instrumental research are magnetic resonance and computed tomography, radiography. Also, additional methods include myography, angiography and ultrasound.
After going through all the procedures, you will know the doctor's decision and further tactics of therapeutic measures.
Signs of complicated hernias
The clinical picture of the complication includes the following group of symptoms:
- the appearance of sudden, severe and sharp pain at the site of the protrusion; sometimes the pain is so severe that it is impossible to take painkillers;
- the hernia quickly grows in size;
- it cannot be corrected;
- the patient may go into shock or collapse;
- the patient's condition is rapidly deteriorating;
- weak pulse;
- lowering blood pressure;
- frequent and shallow breathing.
In especially severe cases:
- rapid increase in body temperature;
- frequent pulse;
- severe bloating;
- vomiting with fecal contents and a corresponding smell;
- edema develops in the area of bulging.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a variant of diagnosis, which consists in the fact that doctors operate on common and different signs of various diseases. In the process of differentiation, specialists exclude inappropriate signs, and ultimately reduce the diagnosis to a single disease.
Any variant of pathology is taken into account. Inguinal hernia, for example, is differentiated from outwardly similar diseases, such as hydrocele, femoral hernia, or varicocele. Abdominal hernias must be differentiated from other tumor-like protrusions (various variations of cancerous tumors). Most often, benign tumors are taken into account . Doctors also distinguish between a hernia with metastases and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Differential diagnosis of complicated hernias is a complex and costly task.
In typical situations, the diagnosis is not difficult, but sometimes the recognition process is extremely difficult. First of all, experts study the degree of reduction of the hernia, its soreness and the manifestation of a cough impulse. And in the future, based on the information received, they build a first aid plan.