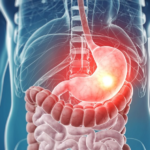
Removal of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
Abdominal hernias are a group of diseases that include protrusion of organs in the area of the umbilical ring, inguinal canal, thigh, linea spigelii, and linea alba. The latter type of disease is relatively rare, but like the others, it requires an operation. A hernia of the white line of the abdomen can be cured only by its removal, and in surgery, the method of open and laparoscopic hernioplasty is used for this.
The operation is performed to remove the hernial sac and restore the anatomy of the abdominal cavity.
An operation to remove a hernia of the white line of the abdomen is performed as planned on an outpatient basis or in a hospital, when there are complications and the patient's condition is unstable. During the operation, a mesh implant can be installed to the patient, which strengthens the area of the defect, preventing organs from coming out under the skin.
All hernia operations have their own risks, and postoperative recovery requires special attention from the surgeon and the patient himself to prevent complications.
When the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are weakened and intra-abdominal pressure rises, a hernia of the white line of the abdomen is formed and the operation in this case will be aimed at strengthening the tissues, which is also the prevention of the recurrence of the disease.
Causes of abdominal hernias
The immediate cause of this disease will be the divergence of the muscles along the midline, through which, with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the internal organs exit. Many internal and external factors can lead to this state.
What can cause a hernia of the white line:
- heavy physical labor - muscle strain will always play a role in the appearance of hernias, especially for people who lead a predominantly sedentary lifestyle and suffer from muscle weakness;
- congenital and acquired pathologies - rickets in children, a violation of the formation of connective tissue, prematurity can become factors in the appearance of pathology, in adults the causes will be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to bloating and constipation;
- previous injuries and operations - muscle damage can lead to a defect through which internal organs penetrate, and after abdominal surgery there is always a risk of ventral (postoperative) hernia in the area of the surgical suture;
- excess weight, pregnancy - these conditions increase the load on the anterior abdominal wall, with obesity, the muscles are replaced by adipose tissue that cannot withstand loads, and during pregnancy, muscle stretching and divergence occur, and if you do not follow preventive measures, you may encounter a hernia.
Features of the course of a hernia
The protrusion in the area of the white line occurs abruptly, but in most cases at the initial stages the disease is asymptomatic, which is already a factor in the appearance of complications. The absence of symptoms does not exclude a dangerous condition, because infringement can occur at any time . If the diagnosis is not established, in a serious condition, when complications arise, it will take more time to prepare for the operation, and then the risk of postoperative complications and surgeon errors during the operation is higher.
Even a small hernia that does not show up in any way needs to be removed. To improve the result of treatment, it is important to identify the disease in time.
With the appearance of a protrusion, the patient may not notice any changes or not attach importance to them. A hidden hernia still makes itself felt during straining and with muscle tension. Above the navel, along the central line, one can see a rounded formation, which independently appears and is set back with pressure and in the prone position. In addition to the external sign, the patient is disturbed by discomfort in the abdomen, but pain is extremely rare.
A progressive hernia of the abdomen already has a typical set of symptoms:
- painful formation in the midline;
- pain and bouts of nausea after filling the stomach;
- an increase in protrusion during straining, during muscle tension;
- constipation, bloating;
- heartburn, hiccups, belching with sour contents;
- nausea-vomiting reflex.
Stages and complications
The protrusion of the median line develops in 3 stages: lipoma, the initial form and the actual hernia. With a lipoma, fatty tissue comes out. At the initial stage, a hernial sac is formed. When the muscles diverge, the hernia itself develops, organs come out under the skin. The formed protrusion on palpation is dense, somewhat painful and is set back into the abdominal cavity.
Hernial orifices can be up to 15 cm in size, rarely several hernias and giant formations over 30 cm can be observed.
Regardless of size, a hernia without surgery can be complicated by the following conditions:
- infringement - squeezing of organs in the hernial sac, which is accompanied by compression of blood vessels and nerves, circulatory disturbance leads to ischemia, then necrotic processes and inflammation occur;
- internal bleeding is a rare complication, it is the result of rupture of organs and damage to blood vessels, this condition can occur during and after surgery;
- intestinal obstruction - fecal masses accumulate in the large intestine due to its compression, the body begins to be poisoned by decay products, and this condition requires urgent surgery, otherwise the organ may rupture.
Severe pain will indicate infringement. The hernia ceases to reduce, and at the same time increases in size.
Removal methods
A hernia of the white line is removed by hernioplasty. It is performed by stretching the patient's tissues or by reinforcing the defect with a mesh. Prior to surgery, the patient must wear a bandage, follow a diet, and exclude stress. This will be the key to a successful hernia repair. Depending on how much time has passed since the appearance of the protrusion, and whether there are complications, a planned or emergency operation is performed.
X od of a standard scheduled operation:
- A skin incision is made, excision of the aponeurosis to access the hernia.
- The bag is released, the organs are examined, returned to the abdominal cavity.
- The hernial sac is removed.
- The tissues are sutured by overlapping each other with tension plasty or strengthened with a mesh implant.
- Sutures are being applied.
Laparoscopic surgery is less traumatic.
Access is created through small punctures in the abdominal cavity. The surgeon observes what is happening on the screen, being able to see all the structures, eliminating their damage. The laparoscope is used to excise the hernial sac and fix the mesh, which eventually grows together with the tissues and does not affect the internal processes in any way.
The operation for a hernia of the white line of the abdomen is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia, depending on the technique and condition of the patient. For uninjured protrusion in adults, local anesthesia is preferred. It is extremely rare for a patient to be prescribed a spinal type of anesthesia.
Rehabilitation after hernia repair
Recovery after surgery includes wearing a postoperative corset, therapeutic diet, bed rest (the first day), exclusion of physical activity.
For normal health, the doctor prescribes NSAIDs, painkillers, drugs to improve digestion. After the operation, problems with the stomach, especially its inflammation, may occur, therefore enveloping preparations and agents for reducing the acidity of gastric juice are also indicated.
The patient is discharged home on the second day after the operation during laparoscopic surgery. After open hernioplasty, the patient stays in the hospital from two days to a week.
Possible complications of the operation:
- violation of the seam, its suppuration, inflammation of the wound;
- recurrence of hernia, repeated protrusion;
- postoperative hernia;
- infection;
- damage to nerves and blood vessels.
Prevention after hernia removal
Rehabilitation after surgery includes the following preventive measures:
- taking laxatives;
- visiting a doctor for dressing and examination;
- refusal of physical activity until the wound heals;
- normalization of weight, diet;
- wearing a bandage (put on for several hours a day);
- exclusion of constipation, bloating, cough (correction of nutrition and smoking cessation).
After laparoscopic surgery, recovery is faster. The operated on the second day ceases to need bed rest and goes home.
From the second day, you can move independently, eat and drink in the usual way, but taking into account the doctor's recommendations. On the third day, you can leave the house. After a week, with the permission of the doctor, exercises and light physical work are allowed.
The flexibility of the postoperative regimen does not exclude the need for regular visits to the doctor for preventive examinations. Even with good health, it is important to be examined, because a hernia recurrence can happen suddenly, but like a primary hernia, it can be asymptomatic for a long time.