Causes, types and treatment of testicular hernia
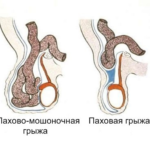
A testicular hernia in men is a type of hernial pathology in which the internal organs of the abdomen protrude into the testicular cavity. Often, bowel loops, a whole omentum or its separate part give in to prolapse. Outwardly, the scrotum significantly increases in size, the testicles can be squeezed, and the organ that has fallen out partially loses its performance up to a complete loss of function. The disease affects not only adults, but also children.
In medicine, congenital hernias are divided, that is, those that were formed as a result of pathological changes in the anatomy of the infant, and acquired - those hernias that were formed during life. In girls, based on the provisions of normal anatomy, testicular hernia does not exist.
Reasons for education
Congenital testicular hernia in a child
This kind of bulging is formed against the background of a violation of the normal descent of the testicles from the peritoneal cavity into the scrotum. During embryonic development, the testicles of the fetus are located in the abdomen, and only over time they gradually descend into the testicular sac, passing through clear periods. At the same time, after the birth of the baby, this channel, through which the testicles have made their way, should be overgrown.
But due to genetic factors, factors of improper embryonic development, overgrowth does not always occur. In this case, the organs follow the spermatic cord into the scrotum.
Acquired pathology
The cornerstone in the formation of an acquired hernia is excessive pressure due to the action of provoking factors. Normally, the pressure in the peritoneum and in any other cavity is balanced due to protective factors. With an abnormal increase in pressure in the abdomen, the organs located there tend to enter the area of low pressure.
Causes that can lead to excessive intra-abdominal tension:
- hereditary weakness of the muscular walls of the anterior wall of the abdomen;
- transferred sprain of the inguinal ligaments, weakening the strength;
- uncontrolled physical work with an unprepared body;
- lifestyle associated with strong strength exercises, constant work with disproportionate weights;
- background diseases that provoke coughing, sneezing, constipation, flatulence;
- surgery or injury in the groin;
- overweight or any fluctuations in weight;
- age-related changes in the body, leading to weakening of muscles and connective tissue;
- impaired blood and lymph circulation;
- inflammatory processes in the peritoneum, in the same place pathological suppurations, abscesses, empyema;
- male diseases: varicocele or hydrocele.
Testicular hernia in men and its symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease is as follows:
- Discomfort in the groin area. Often men complain about the presence of discomfort.
- Pain syndrome. He appears with any load on the stomach, when walking and any other movement. Pain intensifies when physical activity increases. Also, pain can appear when bending the torso.
- Patients complain of a burning sensation in the groin.
- Outwardly, swelling is observed.
- Against the background of impaired blood flow, the veins below the navel may increase in volume. Formed varicose veins of the testicles.
- On palpation of the groin area, patients find a dense tumor-like formation. Its size can vary from the size of a plum to a melon.
- The muscles of the anterior wall of the abdomen are weakened.
- With the development of complications, the patient develops nausea and vomiting. An intoxication syndrome is formed: fever, headache, weakness, lethargy, fatigue at work, sleep disturbance.
- When crying in an infant, the hernia increases.
- Sexual dysfunction in men: lack of erection, weakening of libido.
- Difficulty in urination. The process is accompanied by pain.
The specificity of the symptomatic complex does not depend on the contact of the protrusion with the right or left testicle.
Clinical picture of testicular hernia in newborn boys
In children and adults, the symptoms of pathology are different.
Infantile hernia is characterized by:
- during the initial examination of the child, the doctor fixes the presence of a large protrusion in the groin;
- when the child assumes a horizontal position, his hernia is reduced on its own, but reappears in a vertical position;
- when a boy sneezes or coughs heavily, his hernia visually increases;
There are different sizes of testicular hernia. Medicine knows cases when the volume of the scrotum reached the size of several soccer balls.
Diagnostics
Initially, the doctor examines the protrusion from the outside. He studies the size of the hernia, its condition, pain, texture, location. Palpation is carried out by the doctor in two positions: vertical and horizontal.
The next step in the study is the diagnosis of ultrasound. This method gives accurate information about the content of the hernial sac, about contact with neighboring structures and tissues, whether the contents of the sac are soldered to the sheath. This method is the foundation for making a diagnosis.
Auxiliary methods include: cystography - an x-ray image of the bladder, irrigoscopy - the study of the distal intestines by introducing contrast agents, herniography - an x-ray of the hernia itself.
Treatment of testicular hernia in men
Any doctor will say that it is necessary to treat a hernia only with the help of surgical methods. Conservative therapy is not indicated as the main one, but it is used only in cases where the patient, due to some conditions, is contraindicated in surgery. Drug treatment is carried out after the operation to relieve secondary symptoms, side effects and prevent consequences.
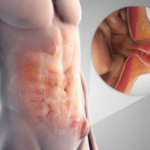
During the operation, the goal for surgeons is to release the clamped organ from the hernial sac and set it back. Then the doctors carry out the plasty of the hernia gate. The most common method of surgical reduction is the Liechtenstein technique, which is also called hernioplasty.
Operation steps:
- At the first stage, the hernial sac itself is dissected. This procession is carried out with the utmost care, as there is a risk of damage to the organs in the hernia. The incision is made small - up to 10-12 cm in length.
- When gaining access to the contents, the surgeon externally assesses the condition of the organs, the possibility of reduction. The organ is returned to its anatomical position.
- The hernial sac is removed, as well as its remnants. A medical synthetic mesh is sutured to the inguinal canal. Subsequently, the incision is sutured.
The mesh, made of synthetic material, helps prevent re-protrusion by containing and strengthening the inguinal canal. Over time, artificial tissue takes root, resolves. This technique significantly reduces the likelihood of a relapse.
Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes, when there is an indication (for example, if the patient is a child), hernioplasty is performed under general anesthesia (narcosis). In the future, the patient is recommended to wear a medical bandage.
In the postoperative period, the attending physician assesses the condition of the patient and his hernia. Based on the symptoms present, the specialist may prescribe some drugs that eliminate swelling, pain, or inflammation.
Recovery and prevention
The duration of the rehabilitation period depends on many factors, such as: the age of the patient, his current condition, the compensatory capabilities of the body, the difficulty of performing the operation. On average, the patient's stay in the hospital after surgery is several days, no more than three. If surgery was performed according to the Liechtenstein method, the patient's stay is limited to one day.
In the first week after treatment, it is necessary to exclude from the daily diet those foods that can potentially cause increased gas formation. In the first month, it is important to be at rest and not start performing power loads.
Preventive measures include:
- careful weight control: sudden jumps in body weight can provoke the development of a hernia;
- regulation of physical activity, their dosing;
- if pain is detected, it is not recommended to continue training and classes;
However, it is still important to remember that you should keep in shape at the proper level. Muscles must not be weakened.