Signs and treatment of hernia C6-C7 of the cervical spine
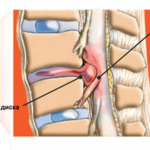
Hernia of the lower neck is a common disease in people with osteochondrosis. This pathology is the second most common among all hernias. Hernia c6 c7 of the cervical spine is a pathological condition characterized by partial or complete displacement of the intervertebral disc and its nucleus pulposus. Often this type of bulging is associated with a rupture of the fibrous ring.
A neglected course and untimely treatment can make a person disabled, or even disabled. This hernia precedes the complete rupture of the intervertebral disc - protrusion.
Mechanism of formation and causes
What is a hernia as such? This is the displacement of an organ or part of it into the wrong position for it. Normally, an organ is located in its biological environment, where it performs a number of functions at the proper level. But under the influence of factors, it can shift. One of the main factors is high blood pressure.
The intervertebral disc is a structure that absorbs the pressure exerted on it by the weight of the body, the spinal column, or any physical load. However, the disk is an organic formation that can collapse under the influence of various reasons.
Constant high pressure is just such a reason that destroys the intervertebral structure and causes it to shift in the direction of less resistance - into the spinal canal. In addition, many factors act on a person’s back during life, which can weaken the shock-absorbing function of the intervertebral discs.
These factors include:
- Overweight person.
- Back injuries : direct blows to the spine, unsuccessful falls.
- Back surgeries.
- Illiterate dosage of physical activity on the spinal column : amateur sports, living conditions, hard physical work.
- Background diseases of the skeletal system : osteochondrosis, osteoarthritis.
- Systemic endocrine diseases , accompanied by metabolic disorders, which leads to an imbalance of minerals in the musculoskeletal system.
- Sedentary lifestyle . The muscular corset of the back is one of the key phenomena that maintains the bones in a normal position. With a prolonged lack of load on the muscles, the latter lose their tone, and the support function deteriorates.
- Age-related (involutional) changes in the human body.
- Congenital diseases of the skeletal system.
- genetic predisposition.
Signs of pathology
The clinical picture of the disease, namely its intensity, depends on the size of the hernia, the degree of its protrusion and contact with the spinal cord, the compensatory capabilities of the patient's body.
Symptoms, the presence of which indicates the existence of a hernia:
- Pain syndrome in the neck . Pain with the course of the disease can spread not only along the neck, but also in the collarbone, chest region, upper limbs.
- Restriction of the mobility of the muscles of the neck . This sign is formed on the basis of the presence of pain and a partial violation of the innervation of the neck muscles.
- Paresthesias (quantitative sensory disturbances): numbness in the hands, tingling, crawling sensations on the skin.
- Weakness of the muscles of the upper limbs . The patient may complain that his muscles seem to have weakened.
- Persistent headaches of unspecified localization.
- Dizziness against the background of cerebrovascular accident.
- Hearing loss and visual impairment.
- Noise in ears.
Over time, the patient complains of rapid fatigue, deterioration in performance, sleep disturbance. The patient also becomes irritable, gloomy.
There are several types of disc herniation c6 c7, namely:
- posterior median hernia . This name suggests that the protrusion of the hernial sac runs along the median line of the intervertebral disc.
- Paramedian disc herniation. This variety is represented by a rupture of the fibrous ring, which is displaced into the lumen of the canal of the spinal column. This condition causes compression of the spinal cord on both sides. This hernia has several subspecies:
- paramedian sequestered , which indicates a complete prolapse of the nucleus pulposus into the space of the spinal canal;
- left-sided paramedian hernia - prolapse of the nucleus on the left side relative to the central axis of the peripheral part of the central nervous system.
- Schmorl's hernia . This variety is characterized by the fact that the hernial sac pushes the bodies of some vertebrae deep into due to the softening of the structure of the bone itself. It turns out that cone-shaped indentations of the cartilage are formed. The disease is dangerous because for a long period of time there are no symptoms. As a rule, such an ailment is discovered by chance when the patient undergoes an X-ray examination of the spinal column.
- Vertebral hernia in children . A pathological condition can be formed either in a congenital way, when the protrusion is formed during fetal development, or in a way acquired during life. The nature of the course of the disease in children differs from that in adults: in young people, hernias are more flexible and elastic, but the overall and large processes of the cervical vertebrae do not allow the intervertebral disc to return back and take its anatomical position.
Diagnostics
The definition of the disease, the diagnosis begins with the study of subjective complaints, an objective examination, the study of the anamnesis of life and disease. The diagnosis ends with specialized instrumental research methods.
First, the attending physician examines the external side of the disease:
- the specialist examines the entire spine, examines its bends in the prone and standing position;
- the study of violations of sensitivity by examining tactile, pain or temperature perception;
- study of tendon reflexes;
- palpation of a suspicious protrusion;
In the future, in order to clarify and study the complete picture, the patient needs to undergo a series of instrumental studies.
The doctor prescribes:
- x-ray of the cervical spine - this method does not provide information about a hernia, however, with the help of x-rays, the doctor will be able to distinguish the disease from tumors or any other injuries of the spine;
- computed tomography - often research is combined with a myelogram (introduction of dyes into the canal of the spinal cord, which provides information about the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid through the canal);
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- electromyography is a method that makes it possible to assess the condition of the muscles, their ability to contract, and with the help of EMG, you can investigate the cause of muscle weakening.
Treatment
First of all, therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms that appear. This is carried out with the help of the appointment of medications, which allow you to remove the phenomena of pain, swelling and muscle spasms. The second stage of treatment is the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Such drugs quickly relieve inflammation, thereby eliminating the pathological processes associated with compression of the outgoing nerve roots.
In the case when the patient has a pronounced pain syndrome, he is prescribed hormonal substances. The specialist also prescribes a number of muscle relaxants - drugs that relieve muscle spasms in the back, because constant muscle contractions provoke nerve compression.
The therapeutic plan also includes massage sessions and manual therapy. Massage is a natural substitute for muscle relaxants. In addition, back-relaxing sessions produce an important positive effect - they increase local blood flow, which contributes to the flow of blood and nutrients. This accelerates the restoration and regeneration of the bone tissue of the elements of the spine.
The number of therapeutic measures includes wearing a corset or bandage, doing simple therapeutic exercises.
Another way of treatment is surgery. The operation is indicated if the methods of conservative therapy have had a weak effect, or there was none at all. The most common surgical treatment is partial or complete removal of the disc that protrudes. Thus, a direct effect is made on the intervertebral disc, its pathological effect on the cervical sections of the spinal cord is eliminated. Access is usually from the front. This operation is called a discectomy.
Another common way to treat a hernia by surgery is minimally invasive surgery. From the name it follows that incisions and accesses are made with minimal trauma. The operation is performed using fine surgical instruments (endoscope and microscope).
Prevention
Any disease is better to prevent than to cure. The spinal cord is the most important structure with the help of which the regulation of many vital processes in the human body is carried out. Therefore, caring for the spinal column is an integral part of the lifestyle of every person.
In order to avoid the development of pathology, you should lead an active lifestyle, perform simple exercises, and follow a proper, balanced diet.
It is important to remember that exercises should not be difficult to perform. Compliance with the diet is to increase the daily diet of dairy products, fruits and vegetables. It is necessary to carefully monitor body weight, namely for its abrupt change. A person who wants to avoid a hernia is advised to stop smoking.