How does a hernia of the cervical spine manifest?
A hernia is a disease that is characterized by a pathological protrusion of structures from their natural anatomical position. This pathology is rare (8% of all hernias). Often this disease accompanies the able-bodied segment of the population (men and women from 30 to 40 years old). A separate category of hernias of the cervical vertebra is Schmorl's hernia , which is most often diagnosed in childhood and adolescence.
The formation of an intervertebral hernia in the cervical region is considered a dangerous phenomenon: in this region of the spine, there are many important regulation points for life, such as heartbeat or digestion centers. In addition, branches of the carotid artery and the jugular vein pass through the cervical region - the vessels that regulate the blood flow to the brain.
How pathology is formed
In order to understand the mechanism of cervical hernia formation, it is necessary to imagine the structure of the spine.
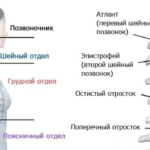
The cervical spine consists of 7 vertebrae, among which two stand out the most - the atlas - the first vertebra, and the axis - the second after it. The remaining five are standard and do not differ from each other.
In order for these vertebrae to be firmly connected to each other and perform a given function, articulation is necessary. The role of the latter is played by intervertebral discs, which are fibrocartilaginous plates (vertebrae of any level do not touch each other). On the periphery of these plates, fibrous rings are formed, in the middle of which is the nucleus pulposus, which is in a state of constant compression. Its function is to absorb the load that is placed on the cervical spine. Such an integral compact structure can be called a joint.
Actually the essence of the intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine lies in the fact that throughout the cervical region the structures of the intervertebral disc go beyond the normal boundaries of the joint, most often to the inside, that is, to the canal where the spinal cord passes.
However, there are other provisions for a hernia of the cervical region:
- Anterior hernias : These face towards the abdomen. Often this type of hernia does not have clinical manifestations at all, since their contour does not touch the nerve endings.
- Lateral localization: such hernias are located on the sides of the intervertebral disc, without entering the spinal canal.
- Hernia of the vertebrae at the level of C6-C7 . Pathology at this level stands out in a separate category: hernias of this location put pressure on the passing artery and nerve, causing a number of non-specific symptoms.
- Circular or circular: this variant is the nature of the protrusion of the nucleus on all sides of the cervical vertebrae.
The following groups of causes of hernia in this department will be distinguished:
- Involutional (age) changes. They are accompanied by a deterioration in the blood supply to the intervertebral discs, and, as a result, a violation of the trophism of the nucleus and surrounding tissues. Various neck injuries contribute to and increase the risk of hernia formation.
- Primary diseases , against which pathology occurs. Among such ailments, osteochondrosis and Bechterew's disease, which are accompanied by the destruction of intervertebral discs, take the first place. Also, other diseases can serve as a background for the development of pathology, whose essence rests on a disturbed hormonal balance.
- Constant stress or injury to the cervical region. This category includes people whose lives are connected with professional work, where they have to take unnatural positions of the neck for a long time. Representatives of active and extreme sports (boxers, fighters, racers, cyclists) can serve as an example.
- Lifestyle . This includes people who are overweight (the load on the vertebrae increases), smokers, and are sedentary.
- Genetic predisposition , in which people have congenital anomalies in the structure of the vertebrae or their abnormal relative position.
Symptoms of a hernia of the cervical spine
In the early stages of the course, the disease does not show signs of its existence. Initially, patients may sometimes complain of vague discomfort in the neck, and even pain, aggravated by various movements and loads. The height of the clinical picture appears when the hernia has reached a critical size, and its contours are actively in contact with the nerve endings and passing vessels. Symptoms can be both nonspecific and specific.
The first group includes:
- non-obvious and sudden sharp pain in the neck and arm;
- inability to make a complete circular movement of the head;
- paresthesia (violation of the sensitive sphere): numbness of the hands, a feeling of crawling;
- sharp and sudden changes in blood pressure;
- dizziness;
- feeling of muscle weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- irritability and sleep disturbance;
- diffuse (vague) pain in the region of the heart.
Specific symptoms are determined by the specific location of the hernia:
- Location at the level between the second and third vertebra:
- chronic pain syndrome;
- numbness of the tongue and its surrounding area. The tongue becomes difficult to manage, it is difficult to give in;
- subjective sensation of a lump in the throat;
- difficulty moving the head and neck
- deterioration of vision.
- Location between third and fourth:
- constant pain in the neck, in the collarbones;
- neck muscles are difficult to control;
- pain when lifting shoulders;
- painful shootings in the neck.
- Localization between the fourth and fifth:
- pain and weakness on the shoulder on one side;
- weakening of the flexor and extensor muscles of the shoulder and difficulty in moving it to the side.
- pain or numbness in the shoulder blade.
- the sensation of pain may be aggravated by raising the arm.
- Location between the fifth and sixth vertebra:
- pain most often occurs on the surface of the hands or elbow;
- difficulty in bending the elbow or wrist joint;
- pain appears at rest of the muscles and spinal column;
- paresthesia: numbness of the hands, tingling, burning sensation of the skin.
- Localization of a hernia between the sixth and seventh:
- Difficulties in extension and flexion of the fingers and forearm muscles:
- sensations of burning, crawling and numbness.
- location of the hernia between the seventh cervical and first thoracic:
- weakness of the hands, "cotton hands";
- difficulty in writing with the dominant hand and difficulty in performing any minor manipulations;
- paresthesia.
When touched and squeezed by a hernia of blood vessels, the following symptoms appear:
- ear noise;
- violation of evenness of gait;
- disorders of coordination between the flexor and extensor muscles;
- constant pain in the head;
- "flies" appear before the eyes;
- decreased concentration, impaired performance.
For such a pathology, radicular syndrome is characteristic, which is manifested by such signs:
- pain starting in the neck and moving to the area of the scapula, back of the head and shoulders;
- the skin in this area loses sensitivity over time - it is increasingly difficult for the patient to feel temperature, touch or pain;
- weakening or complete loss of muscle strength.
How the disease is diagnosed
If you find such a clinical picture in yourself or in loved ones, you should contact a neurologist. The doctor will conduct a differential diagnosis with other diseases that have a similar picture.
These diseases include:
- Benign or malignant neoplasms of the spinal cord.
- The presence of metastases in the structures of the spine.
- Spinal cord injury due to diabetes mellitus.
Also, the specialist will conduct a general examination, and prescribe instrumental and diagnostic procedures.
Research for diagnosis:
- Magnetic resonance imaging . This method allows you to visualize the hernia, namely: its size, location and stage of formation of the protrusion.
- CT scan.
- Radiography of the spine . The method allows you to find signs of osteochondrosis or spondylarthrosis.
- Contrast myelography . With the help of it, doctors will be able to study the patency of the CSF pathways in the spinal cord.
- Electromyography . The essence of the method is to study the electrical activity of muscles.
Hernia treatment
Therapy of every ailment has its own goals.
When treating a hernia, doctors try to achieve the following guidelines:
- Immobilization and fixation of the cervical spine, preventing the protrusion from developing and affecting the structures of the nervous system.
- Elimination of inflammatory processes through the use of medications.
- Recovery and strengthening of weakened muscles . The development of muscles that maintain the condition and physiological curves of the spinal column.
The clinic considers two branches of treatment - conservative therapy and surgical intervention. The first option becomes a priority when there are no signs of circulatory and respiratory disorders, and when, in general, the patient's life is not in danger.
Activities with a conservative approach:
- Medical treatment . It includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen), muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors and blockade of the affected areas.
The action of muscle relaxants is to relax tense muscles. Relaxation of the clamped muscles leads to the removal of the muscle block, resulting in a decrease in pressure. Chondroprotectors in their action strengthen the intervertebral discs and improve its nutrition. Blockade also reduces inflammation.
- Physiotherapy . This branch of treatment is used in conjunction with medication. It includes:
- magnetotherapy;
- electric current stimulation of weakened muscles;
- electrophoresis.
- Therapeutic exercise . Exercises are prescribed in the first week of stay in the hospital. After seven days or more, the patient is recommended to perform exercises in the elbow and wrist joint.
In a condition where the patient suffers from circulatory disorders of the brain and spinal cord, and when conservative treatment has been ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated.
There are such types of operational manipulations:
- Hernia hydroplasty . The essence of the operation is to wash out the protrusion with saline under high pressure. There are no scars left after the operation. Such intervention almost does not cause traumatic complications.
- Laser hernia repair . The laser beam is directed to the surrounding protrusion and causes it to literally evaporate.
- Endoscopy . This operation is performed using an endoscope. Surgeons dissect and remove hernial tissue. It is performed under local anesthesia.
- Hernia laminectomy . This model of intervention involves the removal of the bone tissue of the vertebra. As a result, a large space is formed. Thus, local blood circulation is restored, the nerves do not come into contact with tissues and do not cause pain.
- Discectomy . This method is classical in hernia surgery. In most cases, discectomy is prescribed for large hernias. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. In its course, the hernia is removed and a prosthesis made of titanium material is inserted instead of the damaged intervertebral disc.
Complications and consequences of the disease
The neglected course of a hernia of the cervical region leads to many complications.
Among them are:
- Violation of the motor function of the upper limbs , which is manifested by weakness of the hands and difficulty in performing small movements. The most dangerous is the development of paralysis or muscle paresis.
- Deterioration or complete disappearance of skin sensitivity . As the disease progresses, sensitivity at the fingertips initially worsens and subsequently spreads to the area of the hands and forearm.
- Forced incorrect position of the neck . This phenomenon is due to muscle tension on the one hand and weakening on the other.