Symptoms and treatment of a hernia of the cervical spine
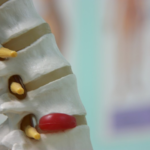
A hernia of the cervical spine is a pathological condition in which the ring of fibrous fibers surrounding the intervertebral disc ruptures and the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the vertebrae. In this case, the spinal nerves and ganglia are gradually compressed and damaged. Ultimately, hernias in the cervical spine may be the etiology of the development of radicular syndrome with characteristic symptoms.
The danger of the disease lies in those complications that can occur in the absence of proper therapy. If, with an intervertebral hernia of the neck, you remember the main symptoms and methods of treatment, then the probability of avoiding serious consequences is quite high.
Clinical manifestations of a hernia
Diseases associated with the musculoskeletal system almost always have an acute onset. And intervertebral hernia is no exception, because nerve fibers are involved in the process.
The main symptoms of a hernia in the cervical spine:
- Pronounced pain in the neck. Irradiation of pain along the damaged nerve: to the back of the head, shoulder and scapular region, upper limb. The pain is aggravated by turning the head, coughing.
- Feeling of numbness / numbness in the hand and fingers. Decreased hand sensitivity. With the progression of the disease, the development of paralysis or paresis is possible.
- Stiffness of movements in the neck, upper limbs. Weakening of muscle tone in these areas.
- Neurological disorders: disorders of the psychological and emotional state, coordination, sleep disorder, dizziness, tinnitus.
- Circulatory disorders, which can be manifested by jumps in systemic blood pressure, loss of consciousness.
Do the symptoms of a hernia of the cervical spine always manifest themselves in the same way? No, because the symptoms depend on which nerve is compressed, so the variety of manifestations of the disease is quite large. The fact is that a nerve fiber departs from each segment of the spinal cord, innervating a certain area. When it is compressed, it is precisely the area into which the nerve endings of this nerve depart that will suffer.
Pain will be a constant sign of intervertebral hernia, regardless of the area of damage, and it is possible to differentiate which segment is affected by additional symptoms:
With damage to the intervertebral disc between the 2nd and 3rd cervical vertebrae (spinal nerve (SMN) - C3):
- headache;
- increased sweating of the scalp;
- decrease in taste sensations;
- decreased mobility of the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- numbness of the skin of the neck on the affected side;
- decrease in the tone of the skin and muscles of the chin, and, as a result, its sagging;
With prolapse of the intervertebral disc between the 3rd and 4th cervical vertebrae (CMH-C4):
- pain in the collarbones and shoulders;
- increased pain when raising arms up;
- pain that mimics an attack of angina pectoris (long-lasting); pain on the right under the diaphragm in the region of the liver;
- decreased sense of smell.
With a herniated disc between the 4th and 5th cervical vertebrae (CMH-C5):
- irradiation of pain on the inside from the shoulder to the elbow;
- limited range of motion in the shoulder joint;
- inability to spread arms to the sides due to muscle weakness; paresis of facial muscles on the affected side;
- frequent diseases of the ears and nose.
With damage to the intervertebral disc between 5 and 6 vertebrae (CMH-C6):
- irradiation of pain from the neck to the scapula, along the entire inner part of the arm from the shoulder to the thumb;
- decreased tone of the biceps muscle of the shoulder;
- violation of flexion-extension in the wrist;
- hoarseness;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
With a herniated disc between the 6th and 7th cervical vertebrae (CMH-C7):
- irradiation of pain and numbness on the outside of the arm from the shoulder to the little finger;
- decreased tone of the triceps muscle of the shoulder;
- the appearance of a cough;
- hoarseness of voice;
- shortness of breath without physical exertion;
- violation of flexion-extension in the area of the elbow;
- inability to raise the arm on the affected side.
With prolapse of the intervertebral disc between the 7 cervical and 1 thoracic vertebrae (CMH- C8):
- intense irradiation of pain from the shoulder blade to the 2nd and 3rd fingers;
- numbness of the skin along the irradiation of pain;
- numbness of the hand, lethargy in the hand; violation of fine motor skills of the fingers;
- thyroid disease.
The symptoms of a herniated disc and their severity can vary from person to person. But most often, such a disease does not go unnoticed by the patient. Most of these signs are due to the developing radicular syndrome.
Treatment
When making a diagnosis, the patient is concerned about the question: how to treat an intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine? Most often, therapy is aimed at eliminating inflammation in the nerve area and strengthening the muscular frame of the neck and back. With this approach, most patients achieve a long-term remission, and the need for surgical intervention disappears.
The main methods of treatment of a hernia of the cervical spine:
- Medical treatment.
- Physiotherapy procedures.
- Physiotherapy.
- Traction therapy.
- Manual therapy, massage.
- laser treatment.
- Surgical intervention.
Let's take a closer look at each method and find out how to cure a hernia.
Drug treatment
Treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is the basis for the treatment of the consequences of hernial protrusion in the cervical spine. The preparations used are applied locally in the affected area. Their action is aimed at eliminating inflammation, and with it pain, swelling, numbness and other unpleasant symptoms.
The most commonly used drugs are:
- ibuprofen;
- Diclofenac;
- Voltaren;
- Ketoprofen; Ketorol etc.
In addition to NSAIDs, muscle relaxants can be prescribed. They will be required if the patient has a violation of the innervation of large muscles and their hypertonicity.
Major muscle relaxants:
- Mydocalm;
- Tolperisone;
- Sirdalud;
- Tizanil; Thezalud and others.
Chondroprotectors are used to strengthen cartilage tissue:
- Alflutop;
- Chondroitin sulfate;
- Chondrogard; Chondroxide etc.
It will be necessary to drink or pierce a course of B vitamins: • Neuromultivit for oral administration;
- Milgamma for intramuscular injections.
Corticosteroid injections may be given. But this method of treatment is used only in severe cases, when it is especially difficult to cure the patient, because steroid hormones have many undesirable side effects.
Physiotherapy
Treatment with this method is carried out after the acute pain syndrome has been eliminated and a course of anti-inflammatory drugs has been completed.
The main methods of physiotherapy for intervertebral hernia include:
- electrophoresis - the introduction of drugs using electric current;
- acupuncture (acupuncture);
- diadynamic currents - treatment with low frequency currents;
- ultrasound.
Physiotherapy
As an independent method of treatment, it is used extremely rarely and is usually combined with drug therapy and physiotherapy procedures. For patients with intervertebral hernias of the neck, a special set of exercises was created, which should be performed under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
In addition to treatment, such exercises are used as a prevention of relapse of the disease in patients with remission. It is necessary to consult with a doctor who will determine whether you can use this set of therapeutic exercises for the prevention or treatment of an intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine.
Traction therapy
Treatment of a hernia of the cervical spine using this method is only gaining popularity. The essence of the method is to stretch the spine, during which the hernial protrusion is gradually drawn inwards. Traction therapy is also often used to prevent intervertebral hernias, osteochondrosis, scoliosis, sciatica and other diseases of the osteoarticular system.
Manual therapy
It is used as an additional method of treatment. The procedure carried out by a chiropractor is aimed at relieving pain, repositioning displaced intervertebral discs, and reducing pressure on the roots of the spinal nerves.
laser treatment
The use of a laser for the treatment of intervertebral hernia has become relatively recent. The main advantages of this method include its high efficiency in eliminating the cause of the disease, as well as the ability to act quickly and focused on the problem.
During the operation, a needle with a laser emitter is inserted through a small puncture in the area of the hernia under local anesthesia. The entire operation takes place using an endoscope, so the effect of radiation will be point. Irradiation of the prolapsed intervertebral disc with a laser leads to a decrease in the protrusion and further to the elimination of the hernia.
The duration of the procedure is no more than an hour. In addition to eliminating a hernia, laser radiation strengthens cartilage tissue, which increases the likelihood of a stable remission of the disease.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is resorted to only if conservative methods of treatment are powerless. Also, the operation is indicated for those patients in whom compression of the nerves causes particularly severe disorders of the circulatory and nervous systems.
The "gold standard" in the surgical treatment of intervertebral hernias is microdiscectomy - intralaminar microsurgical removal of disc herniation.
The operation is performed using an operating microscope, which allows the surgeon to remove hernias of any size and location, and most importantly, minimizes the likelihood of touching vital structures.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia, so if general anesthesia is contraindicated for the patient, then this method, unfortunately, is excluded for him. The rehabilitation period takes from one to two weeks. A month after the operation, the patient is recommended to wear an orthopedic collar.
The newer anterolateral, anterior, or posterior endoscopic approach is not used by all surgeons, but is gradually gaining popularity. This is a minimally invasive operation with a very short rehabilitation period, which clearly indicates its promise. The only disadvantage of the method is some of its limitations - not all sizes and positions of the hernia may be available for this operation.
How to treat a cervical hernia in each individual patient is up to the doctor, because only he sees the full picture of the disease and can assess all the risks and consequences.