Is manual therapy effective for a hernia of the lumbar spine?
Manual therapy in traditional medicine is not considered as a therapeutic technique, but many of its techniques are used during the rehabilitation of patients with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. For many, this procedure seems painful and unsafe, and all because it is associated with bone-cutting. In fact, these are completely different concepts with different approaches to treatment.
The term manual therapy can be literally translated as "treatment with hands". In medical sources, one can see the definition of this procedure as a certain way of influencing the doctor's hands on the human body in order to alleviate the condition with various pathologies of the internal organs and the musculoskeletal system.
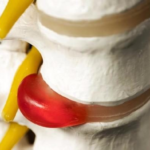
Now manual therapy is common in many rehabilitation centers and is offered both for the treatment and prevention of diseases of the spinal column. A chiropractor can be a salvation for a patient with a herniated disc, when the disease has not yet started, but affects the quality of life, accompanied by constant discomfort and pain.
The essence of manual therapy
Manual therapy for a hernia of the lumbar spine is necessary in cases where drugs are ineffective. Often, the protrusion of the intervertebral discs is combined with other pathologies of the spinal column, and then this technique will also be useful.
A gentle effect on certain parts of the back stimulates biologically active points, which in turn triggers recovery processes.
There are two ways of influencing the spine with disc pathology - relaxing and power. The first is more suitable for a feeling of stiffness, when the disease restricts movement, causing constant discomfort.
Forceful techniques are contraindicated in most patients with a herniated disc, but in rare cases they are prescribed to reduce the vertebrae in order to return them to their anatomical place.
A session of manual therapy includes several successive stages:
- Massage . Each technique that involves physical impact begins with warming up the muscles to prepare them for further stress. The chiropractor performs rubbing by massaging the back with creams or aromatic oils.
- Rhythmic or positional mobilization . The second stage involves the removal of individual parts of the body in a certain position. The therapist fixes the diseased part of the back, applying weighting or the weight of the patient himself. This is necessary to restore joint flexibility and eliminate stiffness.
- R relaxation . The stage is aimed at relaxing the lower back after tension.
- Stretching . _ The doctor performs separate techniques for stretching the muscles and reducing the ligaments. After several approaches, this leads to improved blood circulation and the elimination of spasms.
- P resura or "acupressure" . The final step is to relax the muscles.
The goal of treatment is to restore the natural position of the intervertebral discs and vertebrae. This simultaneously leads to a decrease in pain, which eliminates the need for medication and blockades.
As an independent method, manual therapy is more suitable for preventing displacement of the vertebrae, but when there is already a hernia, the treatment must be comprehensive. It is recommended to combine it with kinesitherapy, osteopathy, acupuncture and physiotherapy.
The course of treatment is selected for each patient individually. Before prescribing therapy, various studies and analyzes are necessarily carried out. It can be MRI, X-ray, ultrasound, CT.
The standard course of manual therapy for a herniated disc usually consists of 5-10 sessions with an interval of 3 days. One procedure lasts about half an hour. During the rehabilitation period after surgery, the course can last from 3 to 6 months. The effectiveness of the course will depend not only on the number of sessions and technique, but also on compliance with all recommendations prescribed by the therapist.
Indications and contraindications
Manual therapy is prescribed as an auxiliary method of hernia treatment when the patient's condition is satisfactory. It is indicated for pain of various origins, when the damaged disc begins to put pressure on the surrounding tissues.
This method of treatment has a number of contraindications:
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular system (thrombosis, myocardial insufficiency, myocardial infarction, hypertension);
- oncological diseases , including suspicion of a malignant process and metastases, therapy in this case will provoke the growth of pathological tissues, which already threatens a serious condition with a risk of death;
- inflammatory diseases because during manual therapy there is pressure on the affected area, which leads to the spread of inflammation to neighboring tissues;
- infections - as with inflammation, there is a risk of damage to healthy tissues against the background of accelerated blood flow.
Manual therapy is not carried out during pregnancy and is not prescribed for young children, with the exception of some techniques and techniques that are useful for everyone without exception.
Manual therapy is a potentially dangerous method of treatment, and a doctor's mistake can cost health and even life. In connection with all the risks, it is prescribed only after an accurate understanding of the nature of the pathological process and the general condition of the patient.
Techniques for influencing the spine
Manual treatment methods will not be able to get rid of this serious disease, but they will help return the vertebrae and bones to the desired position, thereby depriving the patient of chronic pain. For this purpose, several basic techniques are used, which are most effective in case of a prolapsed disc in the lumbar spine.
Methods of influencing the spine with a hernia in the lumbar region:
- Muscular - energetic . _ Receptions for the return of the vertebrae to the anatomical place. The technique of relaxation, mobilization, massage is used. This is a relatively soft technique, it excludes sharp and dynamic movements.
- Manipulation . _ Techniques for returning the position of the vertebrae relative to the axis. Contains fast, sharp, precise movements, tapping, pushing. This is an aggressive technique, it often ends with painful sensations for the patient.
- Relaxation ( postisometric ) . Receptions for elimination of a symptomatic complex. Movements are used that promote the resorption of hematomas, the elimination of edema and pain. Often combined with other techniques and serves as the final stage of the session.
- To early sacral osteopathy. Receptions for a complex effect on the entire spine. This is the safest way to restore the function of a diseased back with minimal risks.
- Muscular -fascial release. Receptions for the return of flexibility to the spinal column. The therapist makes gentle movements that do not cause discomfort. This technique is allowed for all patients at any age.
The effectiveness of therapy for hernia
The manual technique does not cure, it helps the body fight pathological changes on its own, activating reserve forces and the ability to self-heal. After the first session, the patient may feel lightness, because various techniques lead to an increase in the space between the vertebrae, and massage techniques improve metabolic processes.
The procedure helps to remove stagnant processes and normalize blood flow to the pelvic organs, which suffer significantly from pathology in the lumbar region.
After undergoing a course of manual therapy, the following improvements are noted:
- the pain syndrome is reduced or completely eliminated, which will depend on the mechanism of its development in a particular case;
- the natural muscular corset of the spine is strengthened, posture is corrected;
- the hernia decreases in size;
- the spinal column is aligned;
- tissue swelling is removed, muscle spasm goes away;
- the nutrition of the diseased vertebra and disc improves;
- the process of restoration of damaged structures is activated.
Complications
There is always a risk of complications, and this is especially true for impulse techniques with sudden movements. During the session, fractures of the ribs and processes of the vertebrae, ruptures of muscles and ligaments, and even the development of an ischemic stroke are not excluded. Incorrectly selected technique can cause blockage of the spine and displacement of the vertebrae.
An even more difficult consequence will be a strangulated disc herniation.
Manual therapy is not the most gentle method of treatment, but unlike drugs, its effect occurs directly on the cause of the disease, respectively, the effectiveness is many times higher.