Symptoms and treatment of paramedian disc herniation L5-S1
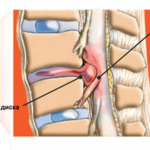
Paramedian disc herniation l5 s1 is a hernial disease characterized by the presence of a pathological protrusion in the form of a disc, localized between the fifth lumbar and the first sacral vertebra. The hernia itself appears to be a protrusion of an organ or part of it into an uncharacteristic location for it.
Paramedian hernia l5 s1 differs from other vertebral hernias in its shape: the disc in this place has a trapezoid shape, while others are rectangular. The disease poses a serious health hazard, as it has the effect of squeezing the spinal cord and local outgoing nerve roots.
Mechanisms and causes of the formation of the disease
The main reason for the formation of a hernia is the destruction of the disc elements under the influence of increased pressure. The disk itself performs a number of tasks, such as: increasing the stability of the spine to various vertical loads, absorbing pressure during power loads (running, walking, physical exercises), ensuring the mobility and flexibility of the spinal column itself.
Due to various factors, the disk loses its functions, leaving its position and shifting in a certain direction.
So, the following reasons for the development of hernial pathology are distinguished:
- Age-related involutional changes in the human body. With age, many elements in the human body lose their former flexibility and elasticity. The same applies to intervertebral discs.
- The action of a constant load on the back . This category includes people whose lifestyle is directly related to power loads (physical labor, professional sports).
- Congenital predisposition or weakness of the strengthening systems of the spine.
- Postponed injuries of the back. This also includes falls on the spine or blows to it.
- Background endocrinological diseases that are associated with a violation of metabolic processes in the body. This is especially true of those diseases that are associated with defects in the metabolism of calcium, phosphorus and other minerals.
- Excess body weight or constant frequent changes in weight. Sharp fluctuations adversely affect the ability of the intervertebral discs to maintain their functions.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system or pathologies of individual vessels that deliver blood to the paramedial sections of the spinal column. In this case, the flow of blood and nutrients with it is disturbed.
- Transferred operations in the area of the spinal cord, spinal column or back in general.
Classification
The disease is classified according to many features and accepted categories. As a rule, knowledge of the principles of grouping is extremely important for doctors, since based on an understanding of the overall picture of the disease, it is easier for a specialist to diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Varieties:
- left-sided paramedian disc herniation - the protrusion is directed to the left of the central axis of the spinal column;
- median paramedian disc herniation - bulging is located more centrally relative to the spine;
- right-sided hernia - the pathology is located to the right of the spine;
- foraminal hernia - such a subspecies is formed in the place where the nerve fibers branch off from the spinal cord and go beyond the boundaries of the spinal column;
- dorsal (back) is most often formed after traumatic lesions or against the background of the course of osteochondrosis, dorsal hernia entails changes in a person’s gait, in addition, the dorsal type of pathology affects the reduction in the volume of the thighs and lower leg.
Clinical picture of the disease
The manifestation of symptoms of pathology directly depends on the location of the protrusion. So, the symptomatology is completely determined by the fact that the hernia is located at the level between the lumbar and sacral vertebrae. In addition, the qualitative side of the severity of the symptom also depends on the size of the hernia itself.
Signs:
- Pain syndrome . This is the leading symptom of the disease: first of all, parts of the spinal cord and nerves are affected, which causes pain. As a rule, the pain is background and aching, with various exercises and loads - sharp and acute. Localization of pain sensations - the lower part of the lumbar region.
- Unpleasant sensations in the form of a burning sensation at the site of the lower leg and ankle.
- Nerve conduction disorders: numbness of the extremities, a feeling of crawling on the skin, dulling of tactile, pain and temperature sensitivity.
- At the site of the presence of a hernia, swelling can be observed outwardly, sometimes swelling, which causes discomfort to the patient.
- As time passes, the muscles of the lower extremities and pelvis weaken, the patients complain that their muscles are weakened and not as strong as before.
- In a sitting position, men feel numbness of the scrotum.
- Periodic uncontrolled act of defecation and urination.
- Decreased superficial tendon and skin reflexes.
In addition to specific symptoms, a hernia affects the patient's quality of life.
The following general signs are observed:
- Frequent headaches.
- Increased body temperature.
- Exhaustion, rapid fatigue with minor loads.
- Sleep quality disorder.
In men, the presence of a hernia is associated with disorders of the genitourinary system: erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, difficulty urinating. In women, inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs can be observed, and libido also decreases.
Diagnostic measures
Hernial pathology is a disease that makes itself felt early. For the patient, the main thing is to seek help from a specialist at the first sign of illness. Otherwise, the neglected course entails the appearance of various consequences and complications.
First of all, the doctor examines the patient's condition, then examines the signs of a hernia closer - with palpation.
The specialist needs the following information:
- when the pains appeared;
- how the pain made itself felt;
- general objective signs: the activity of tendon reflexes, edema, muscle strength, the nature of pain and a number of other manifestations.
After collecting these data, the doctor prescribes instrumental research methods, which are the defining points in making a diagnosis.
The modern world of medicine offers such effective methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging . The method uses nuclear magnetic resonance, which provides accurate visualized information about the structure of the tissues of the spinal cord and spinal column. However, if the patient has a pacemaker or any other electronic implant, the study is contraindicated.
- Computed tomography . With the help of this technique, tissues are examined in their layered structure. The method is based on the specifics of tissue density and uses X-ray radiation.
- Electromyography - allows you to evaluate the activity of muscle fibers.
- X-ray tomography is a method that makes it possible to study volumetric formations such as a hernia in the region of the spine. RTG is based on pictures of the spinal column.
Treatment
The leading method of treatment is surgery. It is resorted to in almost all cases, but with such indications, the operation is a decisive way to cure the disease.
Indications:
- the absence or extremely low effectiveness of treatment with conservative methods over a long period of time;
- the severity of the clinical picture, serious motor disorders, sensitivity disorders;
- a large volume of hernia, which compresses the spinal cord up to the development of paralysis of the lower extremities.
In such cases, the operation is performed first, without prior preparation with medications. With a stable course of the disease, conservative therapy is first applied. Treatment is carried out on the basis of medicines, such as: painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, vitamin complexes.
Rehabilitation
The recovery period in the hernia clinic plays an important role in preventing re-protrusion.
So, the main methods of rehabilitation are:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures using electrophoresis, manual therapy.
- Massage and self-massage are actively used.
- Physiotherapy.
When following all the doctor's instructions and adhering to a diet, the likelihood of re-formation of a hernia is reduced to minimal indications.