Features of paramedian hernia of the spine
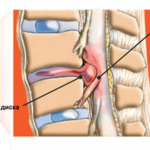
Paramedian disc herniation (paramedial) is a disease characterized by partial displacement of the intervertebral discs with their further gradual destruction. The disease is dangerous due to compression of the spinal cord in the protrusion section, which limits the patient's ability to work and quality of life.
Most often, the cause that determines the development of pathology is the presence of a background disease of the spinal column, such as osteochondrosis, scoliosis, or, less commonly, cartilage dysplasia. More than 70% of all hernias are found in this particular variety.
Types of paramedian hernias
The classification of a paramedian hernia is determined by the location of the pathology relative to the vertebra. So, often bulging occurs in the lateral sections. Injury to the anterior or posterior wall occurs much less frequently, as they have strong protective ligaments. Even less common is a protrusion in the midline (medial protrusion).
There are the following types of hernia:
- Dorsal (back). This includes right-sided and left-sided paramedian hernia. This group also includes median paramedian hernia. Pathological bulging in this case is directed towards the spinal cord and its canal. The severity of symptoms depends on the force of compression of the nervous tissue. So, with a slight contact of the peripheral part of the nervous system and a hernia, there may not be any symptoms at all. With close contact, the opposite happens - the height of the clinical picture is observed.
- Lateral (lateral). In this case, the bulging process is directed towards the intervertebral foramen, and such a pathology is called a paramedian foraminal hernia. Signs are determined by the degree of compression of the nerve roots emerging from the spinal cord.
- Sequestered . This is a full-fledged protrusion, part of which is located in the lumen of the spinal canal. The level of development of symptoms depends on the size and location of such a hernia. The most common sequestered type is a dorsal hernia.
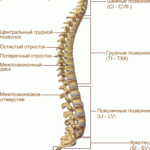
Another classification is based on the anatomical location of the hernia:
- Cervical hernia.
- Thoracic region (meets much less often than others).
- Lumbar (most common).
- sacral department.
Causes of the disease
Hernia is a disease of multifactorial origin.
There are many reasons for the development of the disease, including:
- Involutional (senile) processes in the musculoskeletal system , namely in the fibrocartilaginous tissue. The presence of such a background provokes the formation of a strong rupture of the fibrous ring, which is located in the structure of the intervertebral disc of the column. Thus, fibrous tissue eventually moves out of its anatomical position and occupies a certain niche in the spinal canal. This process is often found in the cervical vertebrae.
- Traumatic injuries of the spinal column. Bumps, falls, bruises, dislocations, fractures - all this is the cause of the development of a painful condition.
- Irregular physical work. Due to the excessive load on the spine, the discs located between the vertebrae experience high pressure, which they cannot compensate for with their mechanisms. Prolonged action of the load provokes damage to the fibrous discs and their exit beyond the normal boundaries of the location.
- Background diseases of the musculoskeletal system , accompanied by damage to bones and cartilage. This includes both diseases of the skeletal system (osteochondrosis, osteoporosis), and diseases characterized by a hormonal shift, in which excessive leaching of calcium occurs.
Paramedian disc herniation and its symptoms
The signs of the disease are determined by the level of the location of the hernia itself, its size and the degree of protrusion into the lumen of the spinal canal.
Manifestations of a hernia of the cervical spine largely depend on the specifics of the anatomical structure of the first two cervical vertebrae and their connection. So, the first and second vertebrae have connections without a disk, which in the future can lead to displacement of the brain stem, its bending or stretching.
Another point is the passage near the vertebrae of the artery and other vessels. Outgoing roots may also be subjected to compression.
Summarizing, we can determine the following symptoms of a hernia of this department:
- sudden loss of sensation in the upper limbs;
- severe pain at the site of protrusion of the hernial sac;
- frequent dizziness;
- headache;
- sleep disturbance;
- blood pressure imbalance: it can be high or low;
- hearing impairment;
- visual impairment;
- memory deterioration.
The location of the hernia on the left or right side also has its own specific manifestations. Left-sided hernia usually causes pain in the patient on the left side of the body, and vice versa. Left-sided hernia negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
A hernia in the lumbar region is most often located between the 4th and 5th fifth lumbar vertebrae.
The disease at this level has the following symptoms:
- non-rhythmic and uncontrolled twitching of the muscles of the legs, muscle twitching also depends on the side of the location of the bulge;
- hypoesthesia - a disorder characterized by a decrease in the sensitivity of the lower extremities and pelvis, often manifested by a deterioration in temperature, tactile and pain sensitivity;
- weakening of muscle strength;
- disorders of the function of organs located in the pelvic area (impaired urination, decreased libido or constipation);
Very often, this type of hernia is faced by a type of people whose occupation is associated with a sedentary lifestyle, such as: drivers, programmers, office workers. Squeezing some of the roots can lead to severe pain on the front of the thigh. Pain sensations can spread to the knee joint, causing the reflexes of the lower extremities to suffer. In more severe cases, reflexes may disappear altogether.
Hernia of the lumbosacral region occurs among all other such hernias most often. This frequency is explained by the fact that this place takes the load of the body to the greatest extent.
Signs of illness in the lumbar:
- severe pain in the lumbar region that occurs not only during movement or exertion, but also at rest;
- pain may begin in the thighs and slowly spread to the toes;
- weakening of the muscles of the lower extremities and pelvic muscles;
- disorders of the pelvic organs: patients note an uncontrolled act of defecation or urination;
- frequent numbness of the scrotum, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction.
The extreme degree of development of a hernia in this department is the "horse tail" syndrome.
The latter has the following symptoms:
- very severe back pain;
- numbness of the entire groin area;
- extreme weakening of the muscles, until the complete loss of their strength;
- lack of reflexes of the lower extremities;
Pathological protrusion in the thoracic region is quite rare. Most of the symptoms of this type of protrusion come down to pathological processes in the chest.
Associated manifestations include:
- pain in the heart;
- heartburn in the esophagus;
- pleurisy;
- angina;
- pericarditis;
- herpetic manifestations.
Diagnostic principles
The examination process consists of several stages:
- Examination of the patient and the study of the clinical picture of the disease (the study of reflexes, sensitivity and other disorders of the neurological sphere).
- Manual tricks.
- Instrumental research methods (radiography, magnetic resonance and computed tomography). Ultrasound examination of the affected area of the spinal cord is also shown.
Treatment
Therapy of this disease always begins with conservative treatment, and only the presence of serious complications, such as cauda equina syndrome, is an indication for surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment, as a rule, is reduced to taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory processes and drugs containing corticosteroids.
Doctors also prescribe muscle relaxants (means that relax muscles) and painkillers. Further treatment involves massage sessions, therapeutic exercises and various types of wave therapy. After treatment, a cured person is recommended to rest and reduce the load on the spinal column.