Causes and treatment of spinal hernia
Spinal hernia in newborns is diagnosed in 60% of all congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. This is a complex disease that cannot be completely eliminated, and all therapeutic and surgical measures during pregnancy are aimed at preserving the child and creating conditions for a normal life with the possibility of self-care.
Congenital spinal hernia ends in disability for a third of patients, but modern methods of neonatal diagnosis allow timely identification of the pathological process to make a decision on treatment from the moment of birth.
It is still not known exactly why a hernia of the spinal cord develops, but there is evidence that the anomaly in the fetus is associated with a deficiency of minerals and vitamins. This pathology is often combined with other congenital malformations, including dropsy, clubfoot, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and pelvic organs.
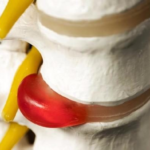
More often, the defect is localized in the lumbar spine, and it can be open or closed.
Why does spinal hernia occur?
The etiology of spinal hernia in infants is not well understood. The likelihood of developing an anomaly is influenced by several factors that can be combined. In the first 8 weeks of fetal development, the formation of the neural tube occurs. Unfavorable factors during this period can lead to incomplete fusion of the spinal canal, which will lead to the separation of several vertebrae. Through the gap formed, the hard membranes of the spinal cord, directly the cerebral fluid, and less often the nerve roots exit.
Spinal hernia in children is associated with the influence of the following factors:
- early pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements, especially vitamin B9;
- the future mother's use of alcohol, drugs;
- poisoning of a pregnant woman with heavy metals;
- transferred infectious and parasitic diseases.
Types of diseases
Spinal and craniocerebral hernias have various forms, depending on the location and severity. Some types of pathologies are manifested by a slight deformation of the spine with mild symptoms, then the treatment prognosis is favorable. Severe defects are always accompanied by a pronounced complex of neurological manifestations and an exit from the skin of the cerebrospinal fluid and the membranes of the spinal cord.
The most dangerous forms of the disease are characterized by the exit of the spinal cord and nerve roots.
Congenital hernia can be diagnosed in any part of the spine:
- In the neck . A rare type of pathology, there is a defect in the upper part of the spinal cord, which is responsible for the vocal cords, muscles of the face and neck. Pathology affects the possibility of normal motor activity, can affect the function of the cardiovascular system and respiratory organs.
- In the chest . It occurs more often, affects the function of the facial muscles, larynx, both the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are affected, the liver, stomach, intestines, and spleen are less likely to suffer.
- In the lumbar A frequent type of pathology that affects the motor function of the lower extremities, disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, leads to disorders of the genitourinary system already in adults.
According to the degree of protrusion of the elements of the spinal cord, 4 forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Mild form - meningocele. Only the spinal membrane penetrates into the spinal defect, the brain itself retains its normal structure and function, the symptoms are mild.
- Moderate severity - meningomyelocele . The substance of the spinal cord also extends beyond the baby's spine, the neural tube is not damaged, neurological manifestations are observed.
- Severe form - meningoradiculocele. Several elements come out in the area of the defect: the spinal cord, sheath, nerves and roots, the neural tube is preserved.
- Extremely severe - myelocystocele . The structure of the spinal cord is completely broken, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable.
In addition to the listed forms of pathology, an even more serious condition occurs when the spinal hernia is combined with a tumor. It can be a benign neoplasm, fibroma or lipoma. Therapeutic measures in this case are aimed at removing the protrusion simultaneously with the tumor. Without surgery, there is a risk of degeneration of benign cancer into malignant, which ends in death.
Clinical manifestations
Pathology can be hidden, then only a small notch in the spinal column and its deformation can be determined by external signs. More often, there are vivid symptoms of the disease, which combine the manifestations of several disorders at the same time, depending on the affected spine.
Symptoms of congenital spinal hernia in a child:
- violation or complete absence of pain and tactile sensitivity;
- circulatory disorders in the lower and upper limbs;
- paresis and paralysis;
- deviation of the function of the pelvic organs;
- dysfunction of the respiratory system and heart.
Such conditions lead to the addition of a secondary symptom complex.
The patient develops contractures, there is a violation of joint mobility, which becomes irreversible without appropriate treatment. The child may develop muscle atrophy, there are problems with thermoregulation. Less commonly, disorders such as trophic ulcers, bedsores, fecal incontinence and involuntary urination can be observed.
Examinations for a hernia in a child
When a baby has symptoms of a spinal hernia since birth, a series of studies are carried out to identify all associated disorders and select a treatment.
Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- consultation with a neurologist - examination by a doctor of a child, assessment of the baby's motor activity, muscle tone, determination of the location of the hernia and its severity;
- conducting magnetic resonance imaging or CT to study layered images and clarify all pathological processes in the spinal cord, MRI can be performed several times, this is a safe study for a newborn;
- examination of the baby by a neurosurgeon to assess the feasibility of surgical treatment and predict postoperative recovery;
- conducting contrast myelography - studying the structure of the damaged area of the spinal cord, the substance is injected intravenously and accumulates in separate areas of the pathological focus, highlighting diseased areas;
- transillumination - light scanning to assess the contents of the hernia.
Treatment Methods
Surgical treatment for spinal hernia can be performed in the perinatal period and after the birth of the baby. Surgery inside the womb is considered to be more effective, and the operation is performed between the 19th and 26th weeks of pregnancy. The goal of surgical treatment will be to close the gap in the spine in order to return the spinal cord to its place and prevent its protrusion with subsequent damage.
Childbirth is carried out only by caesarean section. After perinatal surgery, the prognosis is favorable, the consequences of surgical intervention are insignificant, and the correct regimen after birth allows them to be completely eliminated. Special care for the baby is to ensure the normal function of digestion, the functioning of the lungs and the heart. The child is constantly monitored by a specialist.
Perinatal operations are carried out only in a few Russian clinics, this technique is only being introduced, therefore, more often a child is operated on after birth.
Surgery after childbirth is indicated in the first days of life, after which surgical treatment will not be effective, the prognosis worsens. Untimely assistance leads to disability. In addition to the main operation, the child may be given bypass surgery to reduce intracranial pressure in hydrocephalus.
Rehabilitation
Postoperative management of the baby includes a number of measures to prevent relapse and maintain the normal function of internal organs. The recovery of the child takes place in a specialized center, where they provide the full range of necessary medical techniques (exercise therapy, massage, physiotherapy). After the operation, a sanatorium treatment is usually prescribed on the seashore, where the surgeon continues to observe the child. The goal of rehabilitation will also be to eliminate residual symptoms that are disturbing and affect the child's quality of life.
Postoperative recovery includes the following procedures:
- Exercise therapy - instructors are engaged in physiotherapy exercises with the child, exercise therapy is needed to restore normal mobility of the spine, as well as to strengthen the muscular corset, which will prolong the period of remission. The first exercises after surgery are usually performed underwater to avoid accidental injury and sudden movements. Exercise therapy is an obligatory stage of rehabilitation, and physical education should become a part of the life of a child, teenager and adult in the future.
- Therapeutic massage . With a congenital hernia, massage helps to improve blood circulation in the affected areas of the spine, legs and arms. It is performed only by a specialist, because many movements can damage the weakened skeleton of the baby.
Exercise therapy and massage are combined with wearing a postoperative bandage, diet, moderate activity for the full development of the child. This congenital disease can significantly affect a person's life, but an adequate approach to treatment eliminates many problems.