Signs and treatment of herniated disc L4-L5
Disc herniation l4 l5 is a disease that is the protrusion of part of the intervertebral disc into the spinal column. 50% or more of all hernias fall on the lumbar spine, which is explained by the large load on this department. The medical nomenclature is as follows: the letter "l" means lumbar, lumbar. 4 and 5 are the serial numbers of the vertebrae.
Herniated disc l4 l5 means that the protrusion is located between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae.
By itself, a l5 hernia is not as terrible as its consequences are dangerous. The main threat is compression of part of the spinal cord and outgoing nerve roots, which causes a certain clinical picture. It is believed that this hernia is the most dangerous among all protrusions of the spine.
In a narrow sense, an intervertebral hernia is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system associated with partial migration of the central nucleus of the intervertebral disc, followed by rupture of the peripheral tissue of the ring.
Brief anatomy of the vertebrae and disc
The lumbar spine contains 5 vertebrae, interconnected by an intervertebral disc. The 4th and 5th vertebrae are the last in the section, followed by the sacral section. The structures located between the vertebrae are called discs. They perform the function of pressure absorption, preventing the vertebrae from touching each other closely, protecting them from destruction.
The disk itself consists of an outer peripheral part and an inner central part. The periphery consists of the annulus fibrosus, and the inner part consists of the nucleus pulposus, which is filled with a gel-like liquid.
The spinal column itself consists of 34 vertebrae, in which a long canal is located in their center, where the spinal cord lies. The peripheral part of the nervous system is extremely sensitive to all kinds of damage.
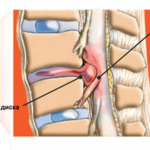
The actual herniation is formed when the peripheral part of the disc is destroyed, and its gel-like part passes through the crack. In the process of forming a protrusion, the disc simply wedged into the spinal cord, causing symptoms of the lesion.
At the physiological level, physical irritation of the nervous tissue occurs, nerve impulses are artificially created, which are supplied in excessive quantities to a certain area of the body.
Stages of formation
During its development, the protrusion goes through four stages:
- stage of protrusion . In the area of the fibrous ring, a small crack is formed through which part of the nucleus can pass. If at this time to stop the influence of provoking factors, the “wound” will heal. At this time, the bulging diameter is up to 3 mm.
- The second stage is the protrusion of the disc. The nucleus pulposus begins to partially shift into the region of the intervertebral canal. At this stage, the hernia is already beginning to compress the nerve roots and a little bit of the spinal cord. Muscles go into spasm. Dimensions reach 5 mm.
- Extrusion - strengthening the protrusion of the disc. The outer shell of the disc is torn. During this stage, the patient experiences severe pain in the lumbar region.
- Loss of the central part of the disk - the nucleus. A complete hernia is formed. There is a strong compression of the spinal cord and nerve fibers. There is a possibility of developing inflammatory processes that can spread to the entire part of the peripheral nervous system. Gradually, the disc undergoes calcification - it hardens, completely losing its function.
Reasons for development
There are a number of factors that affect the formation of a hernia:
- a sedentary lifestyle, when a person's back muscles weaken, atrophy and do not support the skeleton;
- inadequate load on the back. This mainly concerns people whose lives are connected with hard work and professional sports;
- spine diseases: scoliosis, kyphosis or lordosis. They are manifested by irregular bends to the side, back and forward, respectively;
- trauma of the spine or individual vertebra: fracture, bruise, dislocation;
- overweight, when the load on the intervertebral disc is significantly increased;
- people whose age is in the range from 30 to 50 years. With age, the body's compensatory capabilities weaken, ligaments and muscles become exhausted;
- genetic predisposition to weakness not only of the ligamentous apparatus, but also of the musculoskeletal system and muscles.
Varieties
A hernia of the lumbar spine is famous for its great variability.
So, the following types are distinguished:
- Median disc herniation l4 l5 . It is characterized by a median location of the protrusion relative to the central axis of the spinal cord.
- Diffuse disc herniation l4 l5 . Its distinguishing features: uneven distribution of the central part of the disc along the lumen of the spinal canal.
- Foraminal disc herniation . This subtype is characterized by a specific location. A hernia grows at the point where the nerve roots originate from the spinal cord. In clinical practice, the symptoms of damage not so much to the spinal cord as to branching roots predominate. Variety: paraforaminal hernia - bilateral protrusion.
- Paramedian disc herniation. It is characterized by a uniform distribution of hernial tissue relative to the center of the peripheral nervous system. Paramedial pathology can be left- and right-sided. One subtype is the median paramedian hernia.
- A circular herniated disc is a herniated disc that surrounds the spinal cord at the level of the lower back.
- Dorsal hernia . It is characterized by the direction of protrusion towards the canal of the spinal column. Dorsal hernia mates with tight contact with the spinal cord. Dorsal disc herniation has a number of subspecies, among which are:
- dorsal diffuse disc herniation - uneven distribution of a gel-like fluid behind the spinal cord; posterior diffuse disc herniation most often occurs against the background of degenerative bone diseases;
- dorsal median hernia is located exactly behind the spinal cord along the central axis; posterior median hernia has a favorable course.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of hernial pathology appear already in the first stages of development. So, a person begins to feel pain in the lower back. The pain syndrome intensifies when the patient is engaged in physical labor, exercises.
There is a direct proportion: the larger the hernia in size, the more pronounced the pain.
In addition, there are the following signs:
- swelling in the lower back, shooting and aching pain;
- pain syndrome tends to spread to the pelvis and lower limbs, buttocks;
- all types of sensitivity are violated: temperature, tactile; the patient complains that he perceives sensations worse;
- paresthesia in the form of numbness, tingling, there is a feeling of crawling on the skin;
- vegetative disorders: a sharp cooling or warming of the skin, excessive sweating;
- disorders of the functionality of the pelvic organs: impaired urination, difficult defecation; in men, libido decreases, erectile function is weakened, in women - birth defects;
- weakness on leg extension.
Diagnostics
Instrumental diagnostic methods are of great importance in the basis of the diagnosis.
Such as:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- CT scan.
- X-ray diagnostics.
- Myelography.
Based on the data after the procedures, a final diagnosis is made and treatment begins.
Treatment
Therapy of the disease is based on conservative treatment and surgical intervention. The first type of treatment includes drug therapy and physiotherapy.
Medicines include:
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- muscle relaxants;
- vitamin complexes;
- chondroprotectors.
All these substances are aimed at relieving pain, relaxing muscles, eliminating and preventing inflammatory processes. Also, drug therapy is designed to regenerate connective tissue and increase the nutrition of bone and cartilage tissue.
After the doctors have relieved the pain, the stage of joining secondary treatments begins.
This includes:
- physiotherapy : treatment with long-wavelength types of radiation, the use of ultraviolet rays;
- occupation in the pool;
- massage sessions , medical staff teaches the patient self-massage;
- physiotherapy and gymnastics.
Gymnastics is designed to restore the patient's muscle balance, which is achieved through a series of exercises prescribed by the attending physician. It is not recommended to do the exercises on your own. Therapeutic exercise involves a load on the muscles of the press, push-ups.
Surgical treatment is to eradicate the cause of the pathology.
To date, the following types of surgical intervention are relevant:
- Microdiscectomy - removal of the protruding part of the disc. It is considered to be the most effective method of healing.
- Endoscopic intervention options . They are carried out by small punctures through which small tubes are inserted, with which the surgeon removes the hernia.
Surgery has several advantages over conservative therapy:
- the operation is painless, the therapeutic effect occurs almost immediately, and the patient gets on his feet after a few days;
- the patient quickly gets rid of suffering;
- the chance of recurrence drops to 5%.
The disadvantages of the operation include a slight risk of infectious complications during the execution of the surgical intervention itself.